Encapsulants & Underfills
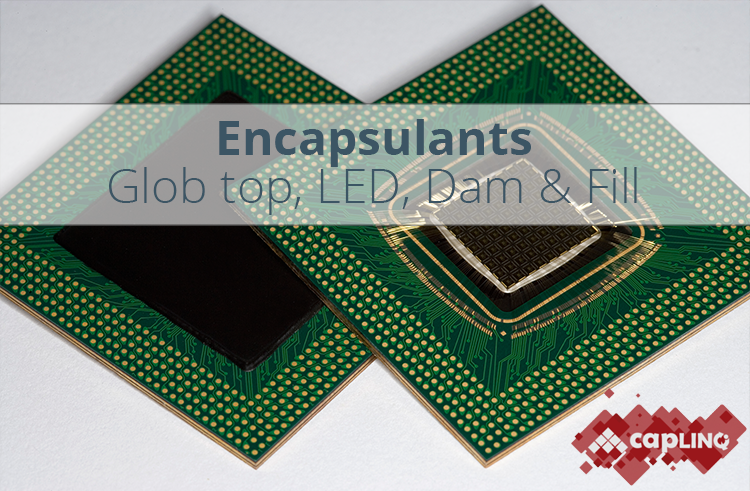
Chip on Board Liquid Encapsulants cure to form void-free globs when exposed to heat, with formulations for low CTE, minimizing stress on wire bonds during thermal cycling. These encapsulants are easy-to-dispense, minimize induced stresses, provide improved temperature cycling performance, and offer excellent chemical resistance.
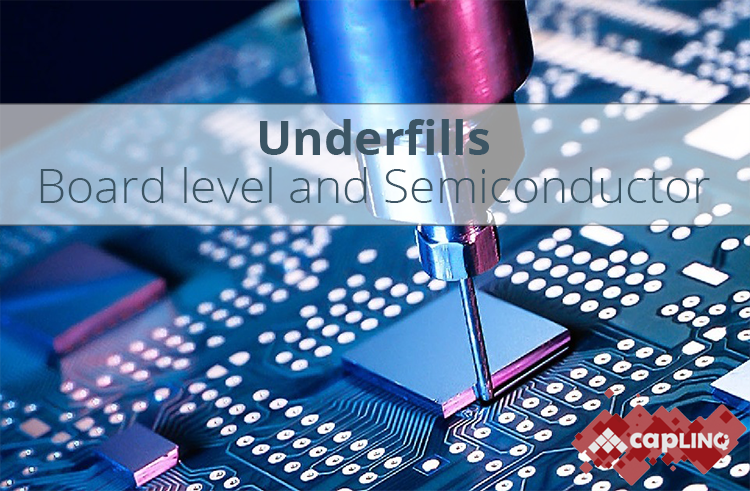
Underfills offer easy reworkability as well as excellent vibration and impact resistance. These underfills offer many processing advantages such as fast flow, fast cure, and long pot life. Our new Cornerbond technology fits easily into an SMT process flow and eliminates a separate underfill dispense and cure process, saving time and money.
Flip chip underfills are used in devices such as FC CSPs and FC BGAs for ASICs, chipsets, graphics chips, digital processors, and microprocessors. These fast flow materials permeate easily under large die. Offering excellent adhesion when used with a variety of no-clean fluxes, these underfills will not crack after thermal shock or thermal cycling.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions about Encapsulants and Underfills
What is the main difference between liquid encapsulants and molding compounds?
Liquid encapsulants and Epoxy molding compounds are generally two sides of the same coin. They are a thermosetting mixture of polymeric resin, a hardener and some fillers that come in both liquid and solid (pellets/powder) forms.
- Liquid encapsulants are dispensable materials that are preferred for flexible, lab-scale projects that need constant changes and alignments. They are using an easy and cheap dispensing system that is ideal for flexible projects with lower throughput. Research, development, and advanced packaging are definitely favoring this liquid encapsulation that facilitates innovation.
- Epoxy molding compounds are, as the name implies, moldable materials. They are commonly used with transfer (and rarely compression) molding. Transfer molding is a fixed, controlled, and expensive process. You need very specific mold designs and sophisticated equipment that can only be used for a single package. This makes this process completely rigid and requires a very large initial investment and a definite package design.
What would be the effect on the product's performance after the guaranteed shelf-life?
Effects of using 1-part epoxy after guaranteed shelf-life:
- Viscosity and Flowability Changes : Viscosity can change over time due to premature crosslinking even while stored. Crosslinking occurs when the polymer chains within the epoxy network form strong chemical bonds, resulting in a more rigid structure. As a result, its viscosity could increase beyond the optimal range. High viscosity can lead to difficulties during application, affecting the encapsulation process. Furthermore, a higher viscosity epoxy may not flow as easily into intricate spaces or around components, potentially compromising the encapsulation quality.
- Decrease in bonding performance: After the guaranteed shelf-life, the bonding performance of an epoxy may decline. Factors contributing to this include: (1) Incomplete Curing: Premature crosslinking can lead to incomplete curing. The epoxy may not achieve its full strength, impacting the bond’s durability. (2) Reduced Adhesion: Aging epoxy may lose its ability to adhere well to surfaces. This can result in poor bonding between the encapsulant and the components. (3) Chemical Changes: Over time, the epoxy’s chemical composition can alter due to exposure to environmental factors (e.g., temperature, humidity, UV light). These changes may affect its compatibility with different materials. (4) Weakened Mechanical Properties: Aging epoxy may become more brittle or less flexible, affecting its ability to withstand mechanical stress or thermal cycling.
Are there any SVHC free encapsulants?
There are SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) free encapsulants available. For instance, Loctite Eccobond 7010C DAM is an SVHC free dam encapsulant with high purity, designed for glob top applications and the encapsulation of bare wire bonded semiconductors. It operates at temperatures ranging from -40 to 150ºC and has good crack, chemical, and thermal resistance, along with low thermal expansion.
Another product, Loctite Eccobond 7010C FILL, is an SVHC free fill encapsulant suitable for high operating temperatures and is designed for use as a potting or encapsulation resin protection for stress-sensitive electronic components. It is formulated with a low thermal expansion and high Tg, making it ideally suited to survive severe thermal shock conditions with a high resistance to micro cracking. These products are examples of SVHC free encapsulants that are also REACH compliant, ensuring they meet strict European Union standards for chemical safety.
These products are examples of SVHC free encapsulants that are also REACH compliant, ensuring they meet strict European Union standards for chemical safety.
How can we maintain the optimal performance of the encapsulant?
To maintain optimal performance:
- Follow Shelf-Life Guidelines: Always adhere to the recommended shelf-life provided by the manufacturer. Using epoxy beyond this period increases the risk of performance issues.
- Proper Storage: Store epoxy encapsulants in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Avoid extreme temperatures or humidity.
- Test Fresh Batches: Before critical applications, test a fresh batch of epoxy to ensure it meets the desired properties (viscosity, curing time, adhesion strength).
- Consider Alternative Materials: If an epoxy has expired, consider using a new batch or exploring alternative encapsulant materials.
What’s the recommended dispensing process to avoid the voids?
Liquid encapsulants should be applied in a controlled and consistent manner. Abrupt pouring should be avoided. It is recommended to use dispensing equipment to control material flow and allow air to escape as the material fills the package. Mold design is also a factor along with the dispense pattern being used and the dispense volume consistency.
What are the main properties to be considered when choosing the right encapsulant or underfill?
When selecting the right encapsulant or underfill for a specific application, Viscosity, Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, Cure Temperature, and insulating properties are some of the properties that should be considered.
Learn More
Process and Handling
Process terms for encapsulants and underfills
Different process timing terms get used interchangeably, but they measure different parts of a thermoset’s life cycle. Mixing them up directly drives yield loss (voids, incomplete capillary fill, die shift, resin bleed, delamination, and package cracking). Shown below is the definition of each term, thier relevance and how can they be measured.
| Parameter | What it measures | Why it matters on the line | How to measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pot life | Time for viscosity to double at controlled room temperature after mixing (2-/3-part) or thawing (1-part). | Defines your safe mix-to-use / dispense window. | Track viscosity at set intervals with a rotational viscometer (e.g., Brookfield) held at 25 °C (or your defined room temperature) until it reaches 2× the starting value. Log instrument, spindle, and speed. |
| Working (open) life | How long the material stays usable in your process before flow/leveling becomes unacceptable. | Sets the assembly application window (jetting/needle, capillary underfill, fillet shape). | Define a clear pass/fail criterion on a standard test board: time until you can’t hit target bead width, flow length, or capillary fill at fixed settings. |
| Gel time | Time to the gel point when a solid network forms at your process temperature. | After gel, the material stops flowing and bubbles cannot escape. | Use a rheometer at process temperature; gel point occurs when G′ = G″ (elastic response equals viscous response). For a quick shop-floor check, use a gel timer on a hot plate set to the same temperature as your tool. |
| Cure time | Time to reach the desired degree of cure (crosslinking) under the specified cure profile. | Drives mechanical/electrical reliability and final Tg. | DSC (isothermal): hold at cure temperature and track reaction until ~90–95% conversion. Confirm chemistry with FTIR. Verify Tg and stability with DMA/TMA. |
Notes: Values are chemistry and profile-dependent. Always start with the product technical datasheet and verify equipment measurement, temperature, and part geometry.
Compliance & Regulations
What is REACH?
REACH is the acronym for Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals.
- European union regulation that started in 2007 and their goal is to improve the protection of human health and the environment from the risks that can be posed by chemicals.
- Encapsulants fall under the REACH regulations. That’s why manufacturers, importers and end users need to ensure that their products and the products that they are using are REACH compliant.
REACH places the burden of proof on companies.
- Companies must identify and manage the risks linked to the substances they manufacture and market in the European Union
- Companies must demonstrate to European Chemical Agency (ECHA) how the substance can be safely used, and they must communicate the risk management measures to the users
- If the risks cannot be managed, authorities can restrict the use of substances in different ways
- In the long run, the most hazardous substances should be substituted with less dangerous ones
REACH Services provided by CAPLINQ
- REACH Only Representative provides a legal entity in the European Union (EU) for the "chemical import responsibility" of substances into Europe.
- ORO, Brexit, Consulting, Registering and Testing
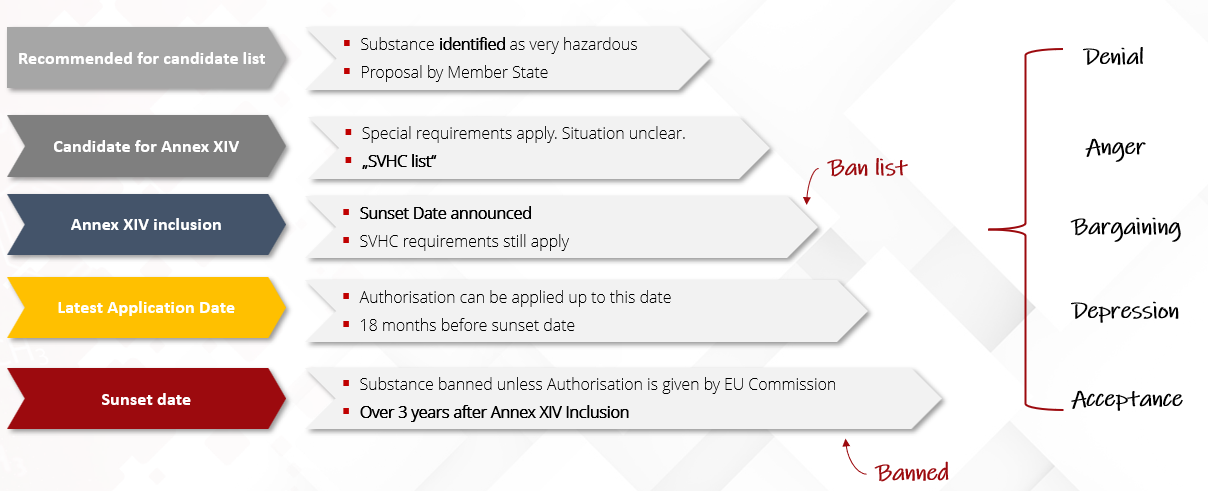
What does SVHC mean?
Substances fulfilling one or more of the criteria defined in Article 57 of the EU REACH regulation can be identified as “Substances of Very High Concern" (SVHC) and put on the “Candidate List for Authorization" which is also called "REACH SVHC list“
- Substances meeting the criteria for classification as Carcinogenic, Mutagenic or Reprotoxic (CMR) cat 1 or 2,
- Persistent, bio-accumulative and toxic (PBT) substances,
- Very persistent and very bio-accumulative (vPvB) substances,
- Substances for which there is evidence for similar concern, such as endocrine disruptors
Common Substances of Very High Concern.
- Many Semiconductor Grade encapsulants contain an Anhydride based resin system.
- Some of these Anhydrides are SVHC listed, so they may be banned for use in Europe in future
- All materials supplied by Henkel comply with REACH and SVHC regulations
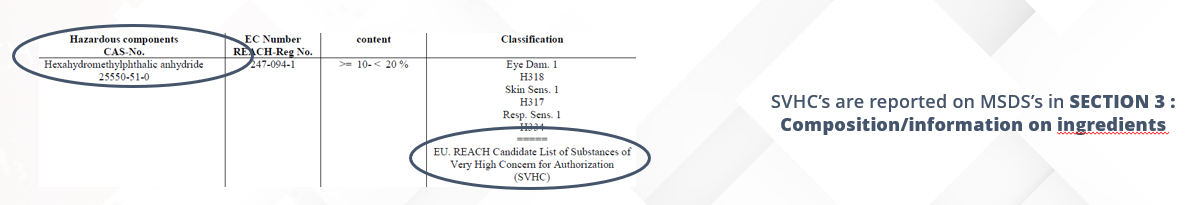
How does SVHC affect you?
LOCTITE ECCOBOND 7010C DAM & FIL are Hybrid encapsulants for stress sensitive electronic components which require SVHC free and CMR free materials. They are 80% silica filled products with 120um filler size that offer High Tg and low CTE.
Typically used in the Defence and aerospace markets, automotive applications, power electronics and any stress sensitive field. Successful applications include wirebond and component protection on multilayered PCB boards applications such as On-Off switch of generic energy flow in airplanes.
Dam & Fill encapsulation for stress sensitive electronic components
Low viscosity ensures good flow around wire bonds
First CMR & SVHC free, “REACH compliant” Dam & Fill encapsulant
Qualified in aerospace applications
Low moisture uptake (85°C/85%RH)
High Tg, low CTE for low stress
High reliability performance (-40/+150°C thermal shock)
Meets NASA outgassing test (ASTM E595-15)
Contains fluorescent dye to aid visual inspection

SVHC Free Encapsulants
Dam and Fill
| FP 4451TD | DAM 7010C | FP 4450HF | FP 4470 | FP 4651 | FP 4802 | FIL 7010C | |
| Type | Dam | Fill | |||||
| Silica filler (%) | 73 | 80 | 73 | 75 | 82 | 72 | 80 |
| Viscosity (cP) | 300,000 | 92,500 | 32,000 | 42,000 | 100,000 | 80,000 | 25,000 |
| CTE ?1 (ppm/°C) | 21 | 16 | 21 | 18 | 11 | 20 | 16 |
| Tg (°C) | 150 | 140 | 164 | 148 | 150 | 50 | 140 |
| Cure Time (min) | 30 + 90 | 60 + 60 | 30 + 90 | 30 + 90 | 150 + 150 | 30 + 90 | 60 + 60 |
| Cure Temperature | 125 + 165 | 100 + 150 | 125 + 165 | 125 + 165 | 110 + 150 | 125 + 165 | 100 + 150 |
Glob Top
| EO 1016 | EO 1072 | EO 7021 | FP 4460 | FP 50300HT | FP 50400-1 | FP4323 | EN 3838T | 8387BM | |
| Type | Refrigerated | Frozen | |||||||
| Viscosity (cP) | 62,000 | 80,000 | 17,000 | 300,000 | 130,000 | 40,000 | 100,000 | 6,700 | 14,000 |
| CTE ?1 (ppm/°C) | 46 | 43 | 67 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 28 | 57 | 88 |
| Tg (°C) | 126 | 135 | 125 | 173 | 140 | 140 | 174 | 2 | 122 |
| TC (W/mK) | ~0.4 | ~0.5 | ~0.5 | - | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.22 | - |
| Cure Time (min) | 20 | 5 | 60 | 180 | 120 | 120 | 240 | 8 | 60 |
| Cure Temp(°C) | 150 | 140 - 150 | 120 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 130 | 100 |
SVHC Free Underfills
LOCTITE® ECCOBOND UF 1173 material has been formulated without any reportable REACH SVHCs (current to June 2018) and the product is not CMR classified.