Epoxy Binding Resins
Epoxy Binding Resins, often called Epoxy Binding Compounds or organic binding compounds are functional thermoset polymers typically made of epoxy, polyester or phenolics. They are used in mixtures with metal alloys including Molypermalloy powder, Sendust, Iron or other metal alloys to create ferrite cores and accessories including E-cores and pot cores.
There are several types of organic epoxy binding resins. The differences depend mostly on the final application and the application method. CAPLINQ offers Class B and Class F variants with Class H epoxy binding resins in development. Depending on whether the cores are cold pressed or mixed into a slurry before pressing, CAPLINQ can help you select the right binding epoxy compound for your application.
DK15-02 | Brown Insulating Epoxy resin binder
- For powdered iron core or pot-core type reactors or induction devices
- Blow coating and Fluidized bed application
- Brown, insulating, binding resin
- No longer available
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions about Epoxy Binding Resins
How are Epoxy Binding Resins Used?
There are two main ways that epoxy binding resins are used. The first is to fix the organic resin in a solvent to create a liquid slurry. In this slurry is mixed the metal alloy. The solvent is then evaporated leaving only the organic binder behind. The second method is to mix about 5% by weight of the organic epoxy into the metal alloy, blend it and the cold press the mixture together and heat it in the oven to get the final cure.
What is the difference between a Class B and Class F Epoxy Binding resin?
Class B resins are suitable for applications that demand 10,000 hours at 105°C. Class F resins can be used in applications that demand 10,000 hours at 130°C. The difference in the materials themselves is that the higher Class materials also have a higher glass transition temperature, Tg.
Learn More

Epoxy Binding Resin for pot cores used in inductor motors
Whether it’s wind turbines, tidal energy, solar energy, geothermal, electric motors or generators: a lot of renewable energy technology depends on a single crucial component: the magnetic core.
Renewable energy: the last best hope for a sustainable human future free from climate change.
Magnetic cores convert mechanical energy and store and release it into another system. That’s why they’re used in applications for converting mechanical energy into power including inside high-speed trains. There are two main types of magnetic core: ferrite pot cores and powder cores.
Every epoxy coating powder company has their own version of DK18-05 in their product portfolio.
Ferrite Pot cores are used in differential inductors, power inductors, converter and inverter transformers, and power transformers. They are made of 90% ferrite powder along with about 10% epoxy coating powder which is used as an organic binder to increase green strength and adhesion.
Powder cores are also used in inductors and are made of Molypermalloy (MPP), Iron, Sendust, and other alloy powders. Both Ferrite Pot cores and Powder cores can be produced either in a pressing process or a slurry process.

Epoxy Binding Resin for Cores: The pressing production process
In the pressing production process, 100 to 800 MT presses are used to press the iron powder along with the epoxy binding resin into the form of an E-core. For the process compatible particle size between the epoxy binding resin and the metal powder is important. Too wide of a differential will result in weak green strength.
Important considerations when selecting an epoxy binding resin for production via pressing are high green strength, high thermal class, and minimal impact on induction value.
High green strength after pressing and before cure is important because parts have to be physically moved to the oven. Another important consideration is higher Tg for a higher Thermal Class rating. This process creates a core with excellent green strength and high-temperature resistance without affecting inductance value as a function of field strength.
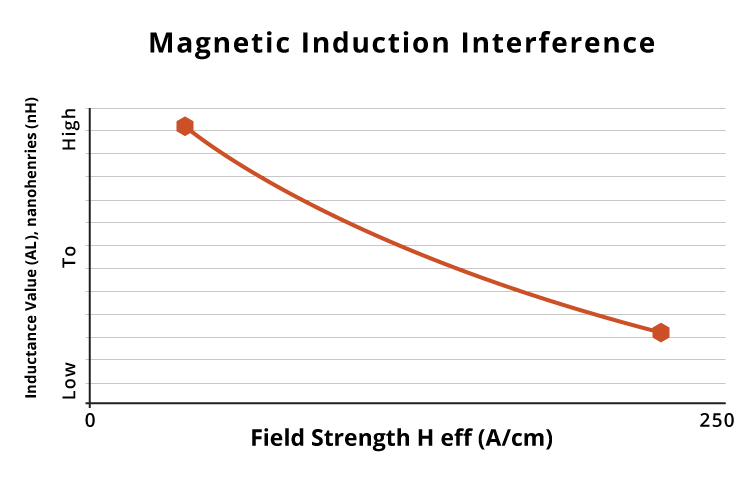
Epoxy Binding Resin for Cores: The slurry production process
Other than pressing pot cores and powders can be made by mixing the micro metal powders and bind resin into a slurry which is then cured in a mold. This process makes green strength and so particle size less relevant.
So, depending on the production process being used, a different epoxy binding resin maybe more appropriate. However, whichever the method, in both cases the epoxy binding resin must minimize core stress by having low shrinkage and low moisture absorption. Low moisture absorption is important because water’s natural expansion and contraction acts as an additional mechanical force on E-core
All epoxy powders are automatically considered Thermal Class B (130°C) because of their high silica content, but the higher thermal classes: Class F 155°C and Class H 180°C are more desirable because there is an industry trend towards higher power and therefore higher temperatures.
The Main Contenders: DK15-02, DK14-2100
Selecting the right Epoxy Binding Resin for you
At CAPLINQ we work with some of the largest international clients in Europe, Israel, China, and beyond supplying them the epoxy binding resin that they need for their cores. We work with them on selecting the right product, adjusting the formulations for their production process. We also with them to develop completely new and unique customized epoxy binding resin formulations for their unique and specific pot core design requirements.
Epoxy Binding Resins for Pot Core Applications
CAPLINQ offers a range of epoxy binding resin applications including brown and black variants and Class B and Class F candidates.

Technical Papers & Brochures
CAPLINQ offers a wealth of Technical Papers, Marketing Brochures, Technical Data Sheets and SDS covering our Epoxy Binding Resins.

Read our Blog on Epoxy Binding Resins
We try to post as much information as we can on our blogs, to help you find more relevant information about how to select, use and apply epoxy coating powders.

Industry Standard DK15-02 for Class B Pot Cores
DK15-02 Brown has been used for more than 20 years as an epoxy binding resin compound for Class F E-Cores and Pot Cores