Optically Clear Materials
Liquid resins are used in two main ways in encapsulations processes. The first methods is glob top and dam & fill alternatively known as frame & fill. The second method is Casting and Potting that can be used to encapsulate sensitive electronics as well as opto-electronic devices. In the case of LEDs they can be both cast or potted.
When an LED is cast, liquid resin is poured into the LED chamber and cured into the shape of the cavity. This produces a stand-alone device which can then become a component in another printed circuit board assembly. In the potting process, LEDs are already wired and connected to a circuit board or substrate. The circuit board or substrate usually already has a frame or cavity which is then filled with a liquid resin and then cured. This results in a group of LEDs set in a ready-to-go circuit board or substrate.
OLS-1000HF | Liquid Encapsulant - Two part Epoxy
- Liquid epoxy encapsulant
- LED applications
- Low Halogen
- 6 weeks
OLS-1305 | Liquid Encapsulant - Two part Epoxy
- Extremely low viscosity
- Rapid cure at moderate temperatures
- Excellent mechanical properties
- 6 weeks
OLS-1557 | Liquid Encapsulant - Two part Epoxy
- Low viscosity
- Good workability
- High temperature resistance
- 6 weeks
OLS-3712 | Liquid encapsulant - Two part silicone
- low-temperature resistance
- Excellent thermal and light resistance
- Excellent adhesion to various materials
- 12 weeks
OLS-5812 | Liquid encapsulant - Two part silicone
- High reliability
- Excellent thermal and light resistance
- Excellent adhesion to different materials
- 12 weeks
OPTOLINQ LE-5031 | Two part epoxy resin
- Low viscosity
- High transparency
- Excellent solvent, aging, and thermal resistance
- 8 weeks
OPTOLINQ LE-5031HY | Two part epoxy resin
- Low viscosity
- High transparency
- Excellent solvent, aging, anti yellowing, and thermal resistance
- 12 weeks
OPTOLINQ LE-2161 | Two part epoxy resin
- Low viscosity
- Fast curing
- High transparency and good electrical properties
- 12 weeks
OPTOLINQ LE-8011HT | Two part epoxy resin
- Excellent thermal stability
- Excellent UV stability
- High light transmittance
- 12 weeks
OPTOLINQ LE-2161HT | Two part BPA-free epoxy resin
- Low viscosity
- Non-yellowing
- High transparency and good mechanical properties
- 2 weeks
OLS-1000LV | Liquid encapsulant - Two part Epoxy
- Extremely Low viscosity
- Rapid Cure
- Visible Light Blocking
- 8 weeks
OLS-1000HV | Liquid encapsulant - Two part Epoxy
- Excellent Mechanical Properties
- Halogen Free
- Rapid Cure
- 8 weeks
OPTOLINQ PM-1212 | Two-part silicone potting
- High optical transparency
- Excellent UV and thermal resistance
- Excellent adhesion to different materials
- 12 weeks
OPTOLINQ OLS-5812M | Liquid encapsulant - Two part silicone
- High reliability
- Excellent thermal and light resistance
- Excellent adhesion to different materials
- 12 weeks
OPTOLINQ PM-1213 | Two-part silicone potting
- High optical transparency
- Excellent thermal resistance
- Excellent adhesion to different materials
- 6 weeks
OPTOLINQ LE-EP123 | One-Part Epoxy encapsulant
- Excellent thermal stability
- Excellent UV stability
- High light transmittance
- 12 weeks
OPTOLINQ LE-EP246D | Optically Transparent Epoxy Resin
- Low working time and viscosity
- Perfect surface gloss
- Good chemical resistance
- 12 weeks
OPTOLINQ LE-EP567D | Epoxy Resin for Composite Bonding
- High bonding strength
- Excellent insulation
- Good chemical resistance
- 12 weeks
LE-8011U | UV-Resistant Clear Epoxy Resin
- High thermal stability with a Tg> 160°C
- Strong resistance to UV degradation
- High light transmittance
- 12 weeks
LE-2441 | One-Part Optically Clear Epoxy Resin
- High thermal stability (Tg = 157 °C)
- UV curable encapsulation
- High optical transmittance
- 12 weeks
LOCTITE STYCAST OA4000
- LED Encapsulation
- Moisture resistant
- Excellent thermal shock properties
- 12 weeks
Product Selector Guide
OPTOLINQ™ Optically Clear Epoxy Liquid Encapsulant and Casting Compounds
| Product | Chemistry | Key Benefit | Mix Ratio (w/w) | Mixed Viscosity at 25°C (cP) | Hardness | Glass Transition Temperature (°C) | CTE 1 / CTE 2 | Refractive Index | Optical Transmittance | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Baking Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LE-2161 | Epoxy | Non-Yellowing | 300:100 | 548 | 70 Shore D | - | 80 | - | >90 | 20 | 24h @ 25°C, 4h @ 50–60°C |
| LE-2161HT | Epoxy + PU Hybrid | BPA Free | 300:100 | 370 | 77 Shore D | - | 80 | - | >90 | >16 | 24h @ 25°C, 4h @ 50–60°C, 2h @ 80°C |
| LE-5031 | Epoxy | Halogen Free | 300:100 | 450 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 24h @ 25°C, 2-4h @ under 60°C, 1h @ 100°C |
| LE-5031HY | Epoxy | Yellowing Resistant | 300:100 | 449 | 72 Shore D | - | - | 84.5 at 550 nm | 12-18 | - | 24h @ 25°C, 2-4h @ under 60°C, 1h @ 100°C |
| LE-8011 | Epoxy | UV and Thermal Resistant | 100:95 | 400-800 | - | 167-173 | 65-75/170-190 | - | >80% at 900nm -1000nm | - | 1 h at 130 °C and 4 h at 150 °C |
| LE-8011U | Epoxy | UV and Thermal Resistant | 100:95 | 400-800 | - | 167-173 | 65-75/170-190 | - | >80% at 400nm -1000nm | - | 1 h at 130 °C and 4 h at 150 °C |
| LE-EP123 | Epoxy | Single Component, UV and Thermal Resistant | - | 15000 | 85 Shore D | 115 | 62/190 | 1.527 | >90 | - | 1 h at 150℃ |
| LE-EP246D | Epoxy | Low working time and viscosity | 100:33 | 262.5 | 82 Shore D | 90 | 38/30 | - | >96 at 550–900 nm | - | See Curing Conditions |
| OLS-1000 | Epoxy | Low Cost | 100:100 | - | 88 Shore D | 130 | 60/183 | 1.52 at 460nm | >90% at 460nm | >23 | See Curing Conditions |
| OLS-1000HF | Epoxy | Low Halogen, High Transmittance | 100:100 | 1000 | 88 Shore D | 159 | 66/1179 | 1.51 at 460nm | >90% at 400nm -1000nm | >23 | See Curing Conditions |
| OLS-1211 | Epoxy | Anti-blue decay | 100:100 | 1100 | 85 Shore D | 127 | - | 1.52 at 460nm | >99% at 400nm -1000nm | - | See Curing Conditions |
| OLS-1000HV | Epoxy | Available with VIS Light Blockers | 100:100 | 840±170 | 85±5 Shore D | 137±5 | <80/- | - | >90% at 400nm -1000nm | 20 | 1 - 1.5hrs at 130-145°C |
| OLS-1000LV | Epoxy | Available with VIS Light Blockers | 100:100 | 100±50 | - | 143±5 | <80/- | - | >90% at 400nm -1000nm | 20 | 1 - 1.5hrs at 130-145°C |
| OLS-1305 | Epoxy | Low Viscosity | 100:20 | 250±100 | - | 122–132 | 85/- | - | - | 20 | 4-6 hrs at 150°C |
| OLS-1557 | Epoxy | - | 100:100 | - | - | 81-91 | 40/- | - | - | - | 5 mins at 150 °C and 6–8 hrs at 130–135 °C |
| Top of Page | |||||||||||
OPTOLINQ™ Optically Clear Silicone Liquid Encapsulant and Casting Compounds
| Product | Chemistry | Key Benefit | Mix Ratio (w/w) | Mixed Viscosity at 25°C (cP) | Hardness | Glass Transition Temperature | CTE α1 / CTE α2 | Refractive Index | Optical Transmittance | Temperature Resistance (°C) | Baking Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS-3263 | Dimethyl Silicone | Very High Transmittance | 100:100 | 3500 | 3 Shore D | - | -/270 | 1.41 | >99 | Up to 170 | 1 h at 80°C and 3 hrs at 150°C |
| OLS-5291 | Phenyl Silicone | Sulfur Resistant | 100:500 | 4200 | 35 Shore D | 13 | 105/153 | 1.54 | >95 | Up to150 | 1 h at 80°C and 4 hrs at 150°C |
| OLS-5812 | Silicone | High Power Applications | 1:10 | 3300-4500 | 40-46 Shore D | 30 | 1.48-1.50 | >95 | - | 100–200 s at 110–130 °C and 2 hrs at 150 °C | |
| OLS-5812M | Silicone | High Optical Transparency | 100:400 | 2500 | 42 Shore D | - | - | 1.53 | >95 | - | 5 mins at 125 °C and 3 hrs at 150 °C |
| OLS-3712 | Silicone | High Reliability | 1:10 | 3200 | 65 Shore D | 42 | >95 | - | 1 h at 80 °C and 4 h at 150 °C | ||
| PM-1213 | Silicone | High Elasticity | 100:100 | 4400 | 50 Shore A | - | - | 1.41 | >95 | - | 1 h at 80 °C and 3 h at 150 °C |
| PM-1212 | Silicone | High Power Applications | 1:10 | 110 | 49 shore A | - | - | 1.41 | >95 | - | 1 h at 60-80 °C and 3 h at 150 °C |
| Top of Page | |||||||||||
Learn More
What is Potting and Casting?
Casting and Potting can be used to encapsulate sensitive electronics as well as opto-electronic devices. In the case of LEDs they can be both cast or potted.
In the casting process, liquid resin is poured into the LED chamber and cured into the shape of the cavity. This produces a stand-alone device which can then become a component in another printed circuit board assembly.
In the potting process, LEDs are already wired and connected to a circuit board or substrate. The circuit board or substrate usually already has a frame or cavity which is then filled with a liquid resin and then cured. This results in a group of LEDs set in a ready-to-go circuit board or substrate.
CAPLINQ offers a range of Encapsulants, Potting Materials and Casting Materials
CAPLINQ OPTOLINQ™ OLS-Series are a family of optically clear (often called “water-white”) liquid encapsulants that are used to encapsulate optical or optoelectronic devices that require both a high level of light transmittance as well as a good level of mechanical protection. Products in this OLS-Series family can be epoxies, silicones or hybrid technologies. They are used extensively for the encapsulation of LED devices but could be well suited for other applications that require a clear, optical grade encapsulation system.
Liquid Resins For Potting
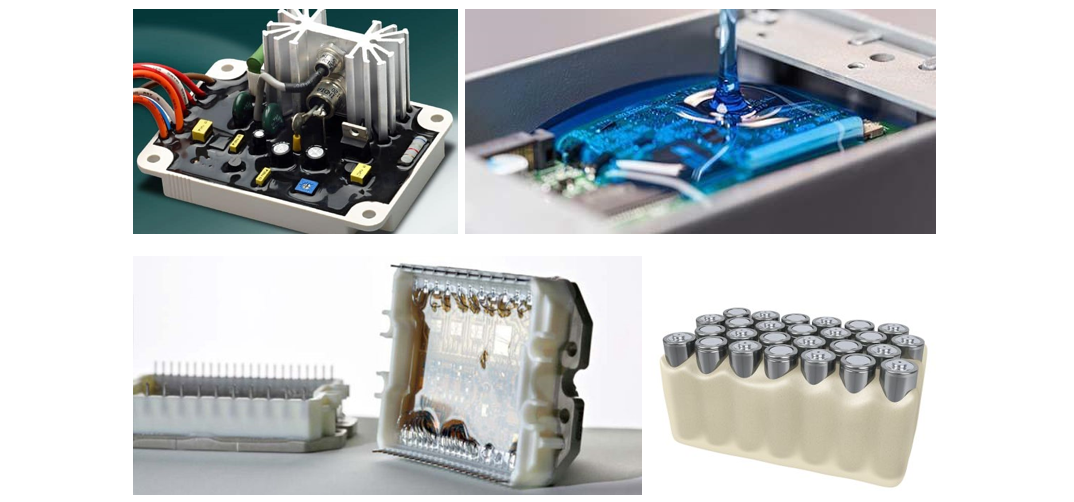
There are three main types of liquid resin for potting and casting applications: Epoxy, Polyurethane, and Silicone.
Resin encapsulants are used to protect and insulate electronic components from harsh environments, including moisture, thermal shock, physical vibration and shock, chemicals and dust, etc, which help electronics achieve stable performance in long term. Potting resin encapsulants are widely applied due to their usage flexibility and easy automation.
In order to meet different application needs, the properties of resin encapsulants could be adjusted. There are mainly three types of resin chemistry systems being widely applied as liquid encapsulants. The comparison between the key performance considerations is shown in the table below. Some other considerations are not mentioned here, such as flame retardancy, volatility, dielectric resistance, etc.
| PROPERTIES / RESIN TYPES | EPOXY | POLY-URETHANE | SILICONE |
| Glass Transition Temperature | High | Medium/Low | Very Low |
| Hardness (Shore) | High Shore D | Shore A to Shore D | Low Shore A |
| Heat Resistance | Tj Up To 160 ~ 180 °C | Tj Up To 135 °C | Tj Up To 230 ~ 260 °C |
| Flexibility | Brittle | Flexible, Crack Resist | Very Flexible |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Medium | Very Low |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Adhesion | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Material Cost | Medium | Low | High |
| Reworkability | Very Hard | Hard | Easy |
| Stress & Heat During Curing | High | Medium | Very Low |
| Suitable For |
|
|
|
*Reworkability: Epoxy and urethane are hard materials, providing good mechanical strength and protection for electronics. Besides, their strong adhesion to components makes them very hard to remove and rework.
*Stress & Heat During Curing: Epoxy and urethane materials produce heat while curing and create stress from shrinkage. Both the heat and stress generated could cause damage to sensitive components and wire connections.
Liquid Potting Resins Key Considerations
After deciding the basic chemistry of potting materials for your applications, there are some other features to be considered while selecting.
Hardness It is a key consideration for selecting materials. Depending on your applications and purpose of encapsulating, you need different levels of hardness. Hard materials provide better mechanical protection against the environment. Soft materials absorb vibrations well and make the component easy to repair and rework.
Thermal Conductivity The components being encapsulated may generate different levels of heat in the area, especially high power electronics. Potting materials could help to dissipate heat to ensure long-term reliability of electronics. The thermal conductive value could be adjusted by adding various fillers.
Color & Viscosity Depending on the visibility requirement of your application, you may need transparent, dark opaque, or even specific colors; Generally speaking, potting materials are designed to have low viscosity (<10 Pa.s) to ensure flowability and self-leveling for easy usage. Medium and high viscosity (>100 Pa.s) products are suitable for sealing and adhesion.
Curing Process Besides the above-mentioned properties, you may consider the curing conditions like temperature and time which suit your production and also the components. Pot life and application process also.

Potting Material Application Questions
- What kind of device/component will be potted? What is the volume of the cavity or pot being filled?
- What will the operating environment be like? Temperature range?
- Will there be exposure to moisture? Solvents or other chemicals? Vibration?
- What is the acceptable curing time or gel time? What is the curing mechanism? UV? Room temperature? Oven?
- What is the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the potting compound?
- Will the material need to be flame-retardant?
- What is the desired hardness of the cured compound?
Epoxy resins
Epoxy resin is super adhesive: making seamless uniform bonds to a wide variety of substrates and cures to become hard with high elastic modulus, great mechanical strength, and toughness. It also has absolutely unparalleled high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation. Epoxy resin cures relatively slowly especially in smaller volumes, and so may require fast-cure hardeners that generate an exothermic reaction that may damage sensitive electrical components via mechanical stress on both the components and circuit.
Polyurethane resins
Polyurethane resins are the kings of process adaptability. Almost every single characteristic of the final cured resin can be dialed in and regulated by adding a little more or a little of a certain additive. Hardness, cure speed, color, gel time, viscosity, all of these can be easily adjusted to suit production requirements. Polyurethanes cure faster and at lower temperatures than epoxy. Polyurethanes have a low elastic modulus in their cured state they are better for extra delicate components such as sensors and reed switches. However, they are notorious for high moisture absorption unless a Polybutadiene base is used.

































