Reactive Silicones
Reactive Silicones grant permanent silicone properties to organic materials and other polymers. They harness the excellent heat resistance, flexibility, and mold release properties of Silicones and impart them to Organic materials while also maintaining abrasion resistance, water repellency, and good oxygen permeability.
They enhance the oxygen permeability of contact lenses, water repellency is added to functional paints, and artificial leathers are made to slide more by diminishing abrasion resistance. Reactive silicones have a very narrow molecular weight distribution, and very low volatiles such as cyclic siloxanes, enabling uniform reactivity
Reactive Silicones (Polydimethylsiloxanes), depending on their functional group, can react with a variety of organic compounds. Amino reactive groups react with Amide, Imide and Epoxies. Hydroxy reactive groups react with Urethanes and Esters. Finally Methacryloxy reactive groups are compatible with Acrylic resins.

FM-0411P | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Hydroxy
- Mono terminal
- 1,000 g/mol | 15 mPas
- Hydroxy functional group
- 12 weeks
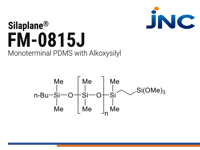
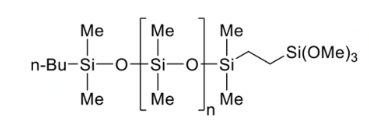
FM-0815J | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Alkoxysilyl
- Mono terminal
- 3,000 g/mol | 26 mPas
- Alkoxysilyl functional group
- 12 weeks
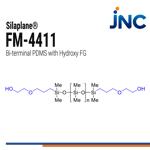
FM-4411 | Reactive PDMS - Bi terminal Hydroxy
- Bi terminal
- 1,000 g/mol | 35 mPas
- Hydroxy functional groups
- 12 weeks
FM-0421 | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Hydroxy
- Mono terminal
- 5,000 g/mol | 70 mPas
- Hydroxy functional group
- 12 weeks
FM-0425 | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Hydroxy
- Mono terminal
- 10,000 g/mol | 160 mPas
- Hydroxy functional group
- 12 weeks
FM-DA11 | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Hydroxy (Diol)
- Mono terminal
- 1,000 g/mol | 60 mPas
- Hydroxy (Diol) functional group
- 12 weeks
FM-DA21 | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Hydroxy (Diol)
- Mono terminal
- 5,000 g/mol | 120 mPas
- Hydroxy (Diol) functional group
- 2 weeks
FM-DA26 | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Hydroxy (Diol)
- Mono terminal
- 15,000 g/mol | 500 mPas
- Hydroxy (Diol) functional group
- 2 weeks
FM-0711 | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Methacryloxy
- Mono terminal
- 1,000 g/mol | 10 mPas
- Methacryloxy functional group
- 12 weeks
FM-0725 | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Methacryloxy
- Mono terminal
- 10,000 g/mol | 200 mPas
- Methacryloxy functional group
- 12 weeks
FM-3325 | Reactive PDMS - Bi terminal Amino
- Bi terminal
- 10,000 g/mol | 300 mPas
- Amino functional groups
- 12 weeks
FM-4421 | Reactive PDMS - Bi terminal Hydroxy
- Bi terminal
- 5,000 g/mol | 110 mPas
- Hydroxy functional groups
- 12 weeks
FM-7711 | Reactive PDMS - Bi terminal Methacryloxy
- Bi terminal
- 1,000 g/mol | 18 mPas
- Methacryloxy functional groups
- 12 weeks
Product Selector Guide
Mono Terminal
| Product | Structural formula | Molecular weight | Specific gravity | Viscosity |
| FM-0411P | Hydroxy | 1,000 | 0.96 | 10 - 25 |
| FM-0421 | 5,000 | 0.97 | 60 - 80 | |
| FM-0425 | 10,000 | 0.97 | 140 - 180 | |
| FM-DA11 | Diol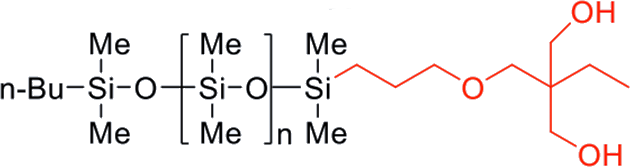 | 1,000 | 0.97 | 50 - 70 |
| FM-DA21 | 5,000 | 0.97 | 80 - 160 | |
| FM-DA26 | 15,000 | 0.97 | 300 - 700 | |
| FM-0711 | Methacryloxy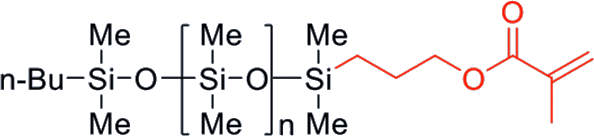 | 1,000 | 0.96 | 7 - 13 |
| FM-0721 | 5,000 | 0.97 | 54 - 79 | |
| FM-0725 | 10,000 | 0.97 | 150 - 260 | |
| TM-0701T | Methacryloxy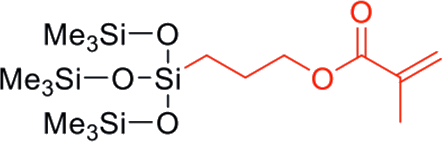 | 423 | 0.91 | 2.9 - 6.1 |
| FM-0815J | Alkoxysilyl
| 3000 | 0.96 | 20-30 |
Bi Terminal
| Product | Structural formula | Molecular weight | Specific gravity | Viscosity |
| FM-3311 | Amino | 1,000 | 0.95 | 11 - 15 |
| FM-3321 | 5,000 | 0.97 | 90 - 150 | |
| FM-3325 | 10,000 | 0.97 | 200 - 400 | |
| FM-4411 | Hydroxy | 1,000 | 0.97 | 30 - 40 |
| FM-4421 | 5,000 | 0.98 | 100 - 125 | |
| FM-4425 | 15,000 | 0.97 | 250 - 400 | |
| FM-7711 | Methacryloxy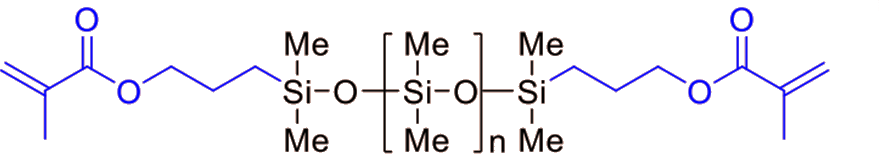 | 1,000 | 0.98 | 14 - 20 |
| FM-7721 | 5,000 | 0.98 | 30 - 100 |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the content of Volatile components?
We have data on volatile components and low molecular siloxane in JNC products. The content is not zero, but it is generally very low. You can expect the values to be similar between FM-04 and FM-DA series. For example, if Silaplane is used for filler disperson, the required Silaplane for filler dispersion is ±3-5%, making the overall volatiles insignificant.
Why do we need Reactive functional groups?
Silicones with reactive functional groups can react with surfaces and resins and remain in the system. Non reactive silicones (ie Silicone oil) are not grafted or blocked in place with their functional groups, leading to extensive bleed out. This is a result of plain mixing and zero copolymerization happening between the resin and the Silicone. Mixing doesn't bind anything into place so bleeding can occur very easily. Therefore, the use of silicone with reactive functional groups can reduce bleeding.
What solvent is compatible between the reaction of Polyethylene group methacrylate with Silaplane to ensure polymerization?
The reaction mentioned can be a potential in the paint industry to developed an anti abravie property paint coat. To ensure polymerization and no phase separation to occur the solvent that is recommended is butyl acetate or any that has its solvent polarity (SP) equivalent. Furthermore, for the synthesis method, we recommend that the initiator should be introduced after thoroughly mixing the monomers (Silaplane and PEG methacrylate) with the solvent.
What is the Shelf life and Opened bottle pot life of JNC materials?
Before opening, the product is basically guaranteed for 6 months after shipping which have exceptions depending on the grade. Once the product has been opened, JNC does not guarantee its quality.
Learn More
Mono and Bi Terminals
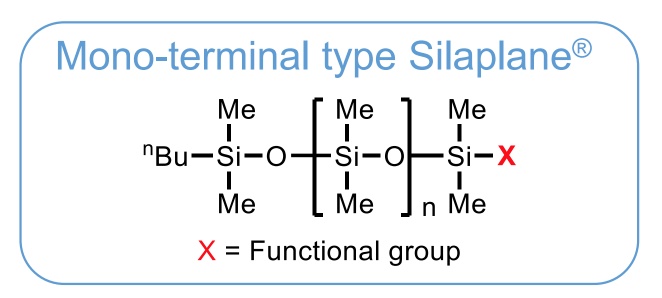
Reactive Polydimethylsiloxanes have two main grades. Mono and Bi terminals, meaning they have a reactive site in one or both ends of the chain. Monoterminal silicones are used for grafting polymers while bi terminal types are used for block polymers.
Mono terminal Polydimethylsiloxanes are grafted onto the resin, modifying the surface properties while biterminal Polydimethylsiloxanes are integrated into the block polymer, modifying the physical properties. Their narrow molecular weight distribution ensures uniform reactivity and low volatiles and impurities.

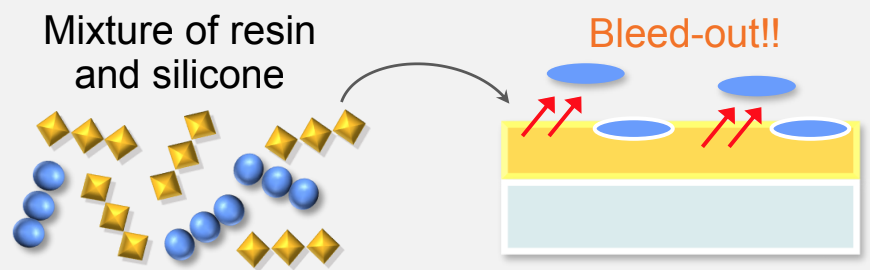
Not reactive silicones (ie Silicone oil) are not grafted or blocked in place with their functional groups, leading to extensive bleed out. This is a result of plain mixing and zero copolymerization happening between the resin and the Silicone. Mixing doesn't bind anything into place so bleeding can occur very easily.
Filler Dispersion
One of the main applications of the mono terminal Silaplane, which has a linear chain resin, is the ability to make the inorganic filler easier to blend into the silicone binder resin. In other words, it facilitates filler dispersion.
It improves the flowability of the highly filled filler dispersions and facilitates their handling. It is a perfect fit for applications that would benefit from the introduction of higher filler content, such as Thermal Interface Materials.
The product's narrow molecular weight distribution ensures uniform reactivity, low impurities and also low volatiles. With this variability, we can fine tune the silicone and compatibility buttons and have a product that perfectly fits the best of both worlds.
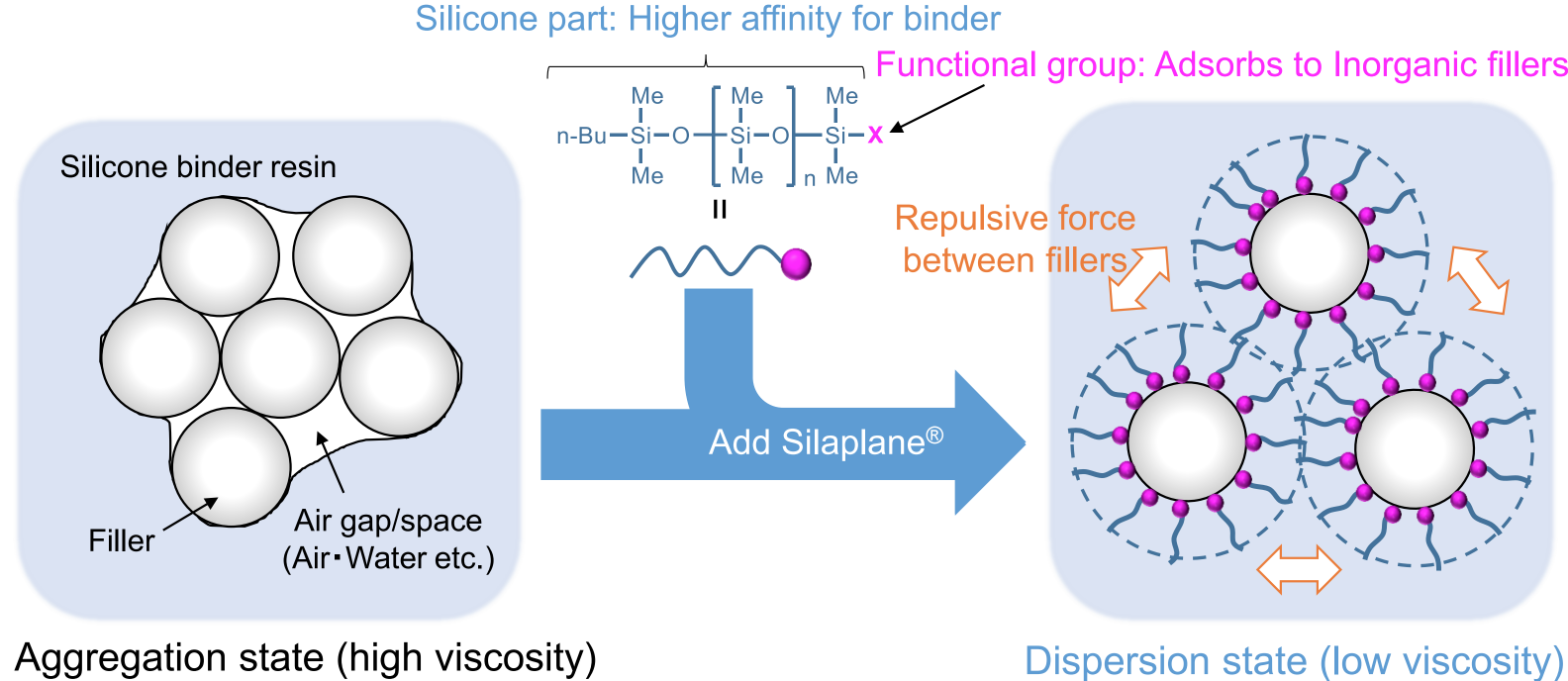
The silicone functional group of our Reactive PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) has a very high affinity to bind on the silicone binding resin. This improves the wettability between the resin and the filler. Additionally, the repulsive force that is created between the fillers, stabilizes the dispersion. This is a result of the silicone repulsion and the osmotic pressure effect.
The material turns from a highly viscous fluid that is in an aggregated state to a low viscosity one in a dispersion state that flows easier while also retaining higher filler content than it otherwise could. This results in higher flowability compared to other common silane dispersants.
In practical terms this means two things:
- Reactive silicones can lower the viscosity while keeping the same thermal conductivity and filler ratio
- Reactive silicones can increase thermal conductivity by allowing an increase in filler content.
Filler dispersion applications can benefit from the grafting properties of Mono terminal PDMS and the repulsive force that is created between the fillers. That's why we suggest them for this type of application. Hydroxy and Diol Hydroxy functional groups lend themselves better as a filler dispersant and have been used successfully on TIM applications.
Silaplane molecular weight distribution is very narrow (~1.03-1.4 Mw/Mn compared to the 1.8 or higher of general reactive silicones) and you have a choice between compatibility and acquired silicone properties to fine-tune your end product.
Here's how Silaplane can be used in Alumina-filled dispersion and how it affects the Viscosity
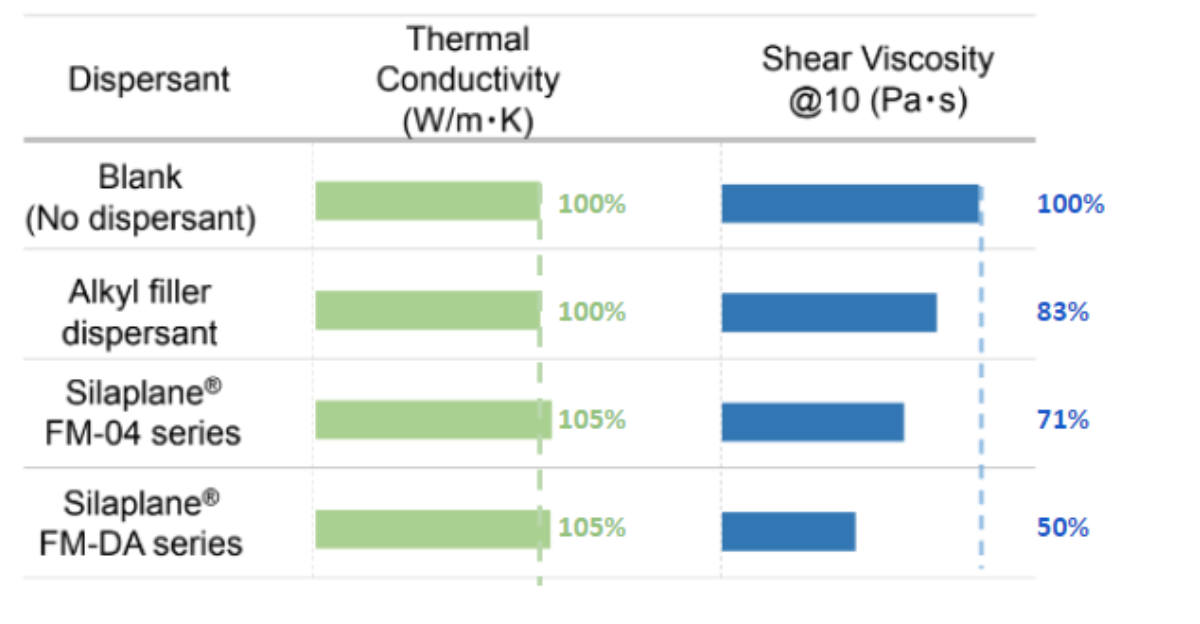
Practically, this means two things
- It lowers the viscosity of dispersion, maintaining the thermal conductivity with the same filler fill ratio
- It increases the heat dissipation perfromance (thermal conductivity)by further increase of the filler filling ratio
Products for Filler dispersion
| Product | Structural formula | Molecular weight | Specific gravity | Viscosity |
| FM-0411P | Hydroxy | 1,000 | 0.96 | 10 - 25 |
| FM-0421 | 5,000 | 0.97 | 60 - 80 | |
| FM-0425 | 10,000 | 0.97 | 140 - 180 | |
| FM-DA11 | Diol | 1,000 | 0.97 | 50 - 70 |
| FM-DA21 | 5,000 | 0.97 | 80 - 160 | |
| FM-DA26 | 15,000 | 0.97 | 300 - 700 |