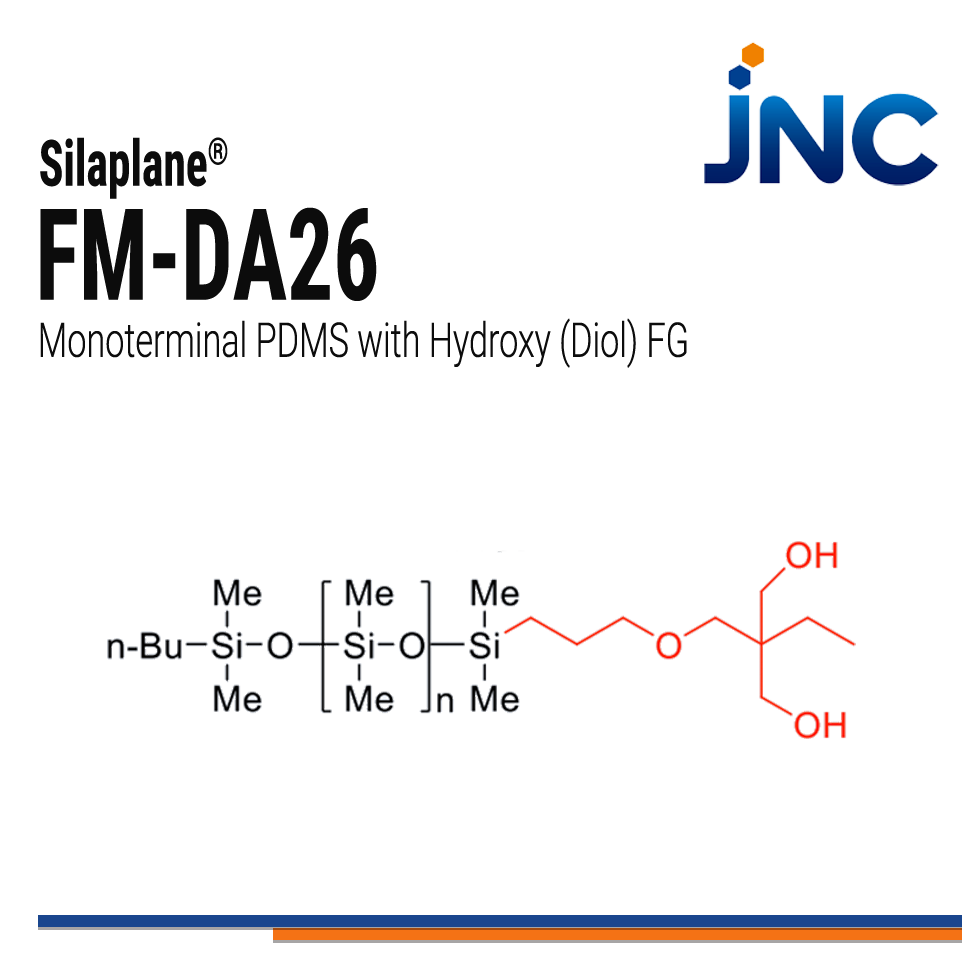
FM-DA26 | Reactive PDMS - Monoterminal Hydroxy (Diol)
- Mono terminal
- 15,000 g/mol | 500 mPas
- Hydroxy (Diol) functional group
Product Description
Silaplane® FM-DA26 is a reactive polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) based polymer with a molecular weight of 15,000 g/mol and a Viscosity of 500 mPas. This reactive silicone material offers the addition of silicone-type properties to non-Silicone materials in a variety of industries including electronics, semiconductors, automotive, biotech, healthcare, and clean energy applications. It offers narrow polydispersity and a low level of chemical impurities
Silaplane® FM-DA26 mono-terminal product has a Hydroxy (Diol) functional group that is reactive toward a variety of compounds and surfaces enabling chemical and physical changes to chemicals, particle surfaces and larger surface structures. Hydroxy groups are mainly reacting with Urethane and Ester compounds. The reactive functional group improves the adsorption to the filler surface and makes the inorganic filler easier to blend into the silicone binder resin. At the same time it displays high affinity for the silicone binder resin which improves the wettability between the filler and the binder. This product stabilizes the filler dispersion due to the repulsive force between fillers, achieved by silicone repulsion and the osmotic pressure effect.
Product Benefits:
- Filler dispersion stabilization with low viscosity
- Water/Oil repellency
- Gas permeability (Oxygen, CO2, CH4, etc.)
- Mold releasability
- Anti-Abrasion resistance, Anti-fouling
Technical Specifications
| General Properties | |
| Molecular weight | 15000 g/mol |
| Specific Gravity Specific Gravity Specific gravity (SG) is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance; equivalently, it is the ratio of the mass of a substance to the mass of a reference substance for the same given volume. For liquids, the reference substance is almost always water (1), while for gases, it is air (1.18) at room temperature. Specific gravity is unitless. | 0.97 |
| Physical Properties | |
| Viscosity Viscosity Viscosity is a measurement of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Viscosity is commonly measured in centiPoise (cP). One cP is defined as the viscosity of water and all other viscosities are derived from this base. MPa is another common unit with a 1:1 conversion to cP. A product like honey would have a much higher viscosity -around 10,000 cPs- compared to water. As a result, honey would flow much slower out of a tipped glass than water would. The viscosity of a material can be decreased with an increase in temperature in order to better suit an application | 500 mPa.s |