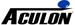Adhesion Primers & Promoters
Adhesion Promoters and Adhesion Primers improve adhesion between substrates and coatings or adhesives by creating an interface for additional covalent bonds. This increases adhesion and the bond between the substrate and the coating or adhesive: improving the performance of the coating or adhesive.
One of the most common applications for adhesion promoters is to enhance the adhesion strength and performance of die attach between the die, the die attach, and the substate or copper lead-frame. Adhesion Promoters can be used for copper foil applications for the adhesion of low dielectric resins to copper for printed circuit boards and chip scale packaging. By pretreating the intended copper surface with an adhesion promoter significantly higher peel strengths can be obtained. Aculon has demonstrated superior performance to silane adhesion promoters in terms of peel strength on smooth copper (600 hours in autoclave).
Different adhesion promoters have different base chemistries but all of them work on a molecular level. For example Aculons Primers contain self- assembled monolayers of phosphonates (SAMPs) which improve the adhesion of metals to polymeric coatings. They do this by using reactive groups to create strong bonds with coatings that contain functional groups such as epoxies, polyurethanes, acrylates, and oxide particles.
Examples of the Adhesion Promoters with different base chemistries can be seen in Aculon’s range of adhesion promoters and primers. Thiol based primers promote adhesion between substrates and epoxy (meth)acyrlics. Acrylate primers promote adhesion between substrates and (meth)acrylates, amines, and thiol based coatings. Hydroxyls primers promote adhesion between substrates and polyurethanes, iso-cyanates, melamine formaldehydes, phenolic epoxy based coatings.
Hydroxyl Functional Adhesion Promoter
- Enhances the adhesive capabilities of a metal surface
- 2-4 nm thickness
- Can be used as an additive
- 6 weeks
Methacrylate Functional Adhesion Promoter
- Enhances the adhesive capabilities of a surface
- 2-4 nm thickness
- Can be used as an additive
- 6 weeks
Balance Weight Adhesion Promoter
- Increases adhesion to the wheel surface
- Provide increased safety and reliability
- Already succesfully used on Alcoa DuraBright wheels
- In stock
OP-216 | Nano-Scale Adhesion-Promoting Surface Treatment
- Improved adhesion strength of paints/coatings on metal surfaces
- No outgassing
- No stress build-up on the substrates
- 6 weeks
OP-225 | Nano-Scale Adhesion-Promoting Surface Treatment
- Improved adhesion strength of paints/coatings on metal surfaces
- No outgassing
- No stress build-up on the substrates
- 8 weeks
OP-234 | Nano-Scale Adhesion-Promoting Surface Treatment
- Improved adhesion strength of paints/coatings on metal surfaces
- No outgassing
- No stress build-up on the substrates
- 8 weeks
OP-247 | Nano-Scale Adhesion-Promoting Surface Treatment
- Improved adhesion strength of paints/coatings on metal surfaces
- No outgassing
- No stress build-up on the substrates
- 8 weeks
OP-272 | Nano-Scale Adhesion-Promoting Surface Treatment
- Improved adhesion strength of paints/coatings on metal surfaces
- No outgassing
- No stress build-up on the substrates
- 8 weeks
Product Selector Guide
| Product Name | Primer/Promoter Base | Application Examples | Application Method | Visible to Naked Eye | Thickness | Dry Time | Cure required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl Functional Adhesion Promoter | Hydroxyl | Polyurethanes and iso-cyanates, melamine formaldehydes, phenolic epoxy based coatings | Spray/Dip/Wipe | No | 2+ nm | 30 sec | For less than 5 minute cure, only Ti, Al and epoxy need a cure |
| Methacrylate Functional Adhesion Promoter | Acrylate | (Meth)acrylates, amines, thiol based coatings | Spray/Dip/Wipe | No | 2+ nm | 30 sec | For less than 5 minute cure, only Ti, Al and epoxy need a cure |
| OP-216 | Isopropanol | Carboxylic acid functional groups such as epoxies and melamine-formaldehyde | Spray/Dip | No | 2-4 nm | 30 sec | Short dip times or spray-application treated substrates are best cured at 120℃ peak metal temperature for approximately 30 seconds. Only Si, TiO2 need cure for up to 5 minutes. |
| OP-225 | Methanol | Olefinic (vinyl) functional groups such as silanes and radiation-cured coatings | Spray/Dip | No | 2-4 nm | 30 sec | Short dip times or spray-application treated substrates are best cured at 120℃ peak metal temperature for approximately 30 seconds. Only Si, TiO2 need cure for up to 5 minutes. |
| OP-234 | Isopropanol | Thiol functional groups such as epoxies and (meth)acrylics | Spray/Dip/Wipe | No | - | 30 sec | Short dip times or spray-application treated substrates are best cured at 120℃ peak metal temperature for approximately 30 seconds. Only Si, TiO2 need cure for up to 5 minutes. |
| OP-247 | Isopropanol | Acrylic functional groups such as (meth)acrylate, amine, and thiol-based coatings | Spray/Dip | No | 2-4 nm | 30 sec | Short dip times or spray-application treated substrates are best cured at 120℃ peak metal temperature for approximately 30 seconds. Only Si, TiO2 need cure for up to 5 minutes. |
| OP-272 | Isopropanol | Hydroxyl functional groups such as urethane, melamine-formaldehyde, and phenolic-epoxy based coatings | Spray/Dip | No | 2-4 | 30 sec | Short dip times or spray-application treated substrates are best cured at 120℃ peak metal temperature for approximately 30 seconds. Only Si, TiO2 need cure for up to 5 minutes. |
Learn More
Adhesion Promoters and Adhesion Primers improve adhesion between substrates and coatings or adhesives by creating an interface for additional covalent bonds. This increases adhesion and the bond between the substrate and the coating or adhesive: improving the performance of the coating or adhesive.
One of the most common applications for adhesion promoters is to enhance the adhesion strength and performance of die attach between the die, the die attach, and the substate or copper lead-frame.
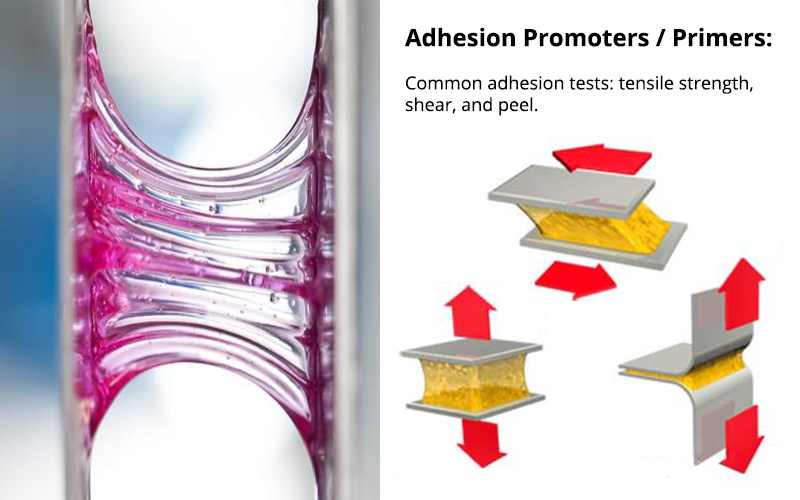
There are many potential tests which can be performed to define the adhesive strength of a coating or adhesive. For example in the shear test force is applied at a 90 degree angle to the substrate or die until failure occurs.
There are three main types of result. Cohesion failure is where the die attach or adhesive being used fails: depending on requirements a stronger die attach or adhesive may need to be found. Substrate or Die failure is where the substrate or die breaks: this can be considered a success on the part of the adhesive. Adhesion failure is where the bond between the die attach or adhesive and the substrate or die fails: this indicates that an adhesion promoter or primer should be used.
Adhesion Promoter Chemistries
Essentially adhesion promoters are a kind of primer: a surface treatment that primes surfaces of metals and other oxo or hydroxyl functional substrates before an adhesive is place on them.
Different adhesion promoters have different base chemistries but all of them work on a molecular level. For example Aculons Primers contain self- assembled monolayers of phosphonates (SAMPs) which improve the adhesion of metals to polymeric coatings. They do this by using reactive groups to create strong bonds with coatings that contain functional groups such as epoxies, polyurethanes, acrylates, and oxide particles.
Examples of the Adhesion Promoters with different base chemistries can be seen in Aculon’s range of adhesion promoters and primers. Thiol based primers promote adhesion between substrates and epoxy (meth)acyrlics. Acrylate primers promote adhesion between substrates and (meth)acrylates, amines, and thiol based coatings. Hydroxyls primers promote adhesion between substrates and polyurethanes, iso-cyanates, melamine formaldehydes, phenolic epoxy based coatings.
Thiols, Acrylates, Hydroxyls adhesion promoters work best with different types of adhesives.
| Thiols | Acrylates | Hydroxyls | |
| Adhesion Examples | Epoxy (Meth)acrylics | (Meth)acrylates, amines, thiol based | Polyurethanes and iso-cyanates, melamine formaldehydes, phenolic epoxy based |
| Application | Spray / Dip / Wipe | Spray / Dip / Wipe | Spray / Dip / Wipe |
| Visible to Naked Eye | No | No | No |
| Thickness (nm) | 2+ | 2+ | 2+ |
| Dry Time (sec) | < 20 | < 30 | < 30 |
| Cure Required | For <5 min cure, only Ti, Al and epoxy need a cure | For <5 min cure, only Ti, Al and epoxy need a cure | For <5 min cure, only Ti, Al and epoxy need a cure |
Adhesive Promoter Applications:
Adhesion Promoters can be used for copper foil applications for the adhesion of low dielectric resins to copper for printed circuit boards and chip scale packaging. By pretreating the intended copper surface with an adhesion promoter significantly higher peel strengths can be obtained. Aculon has demonstrated superior performance to silane adhesion promoters in terms of peel strength on smooth copper (600 hours in autoclave).
Adhesion promoters are most commonly used to pre-treat metal lead-frames. Aculon’s adhesion promoters have shown superior bonding of die attach adhesives, and epoxy molding compounds to numerous types of lead frame materials (Au, Pd, Cu, Ag, Ni).
Pre-Cleaning Surfaces prior to Application
As adhesion promoters work on a molecular level the substrate that they are applied to need to be perfectly clean. Otherwise adhesion strength is only as strong as the adhesion strength of the layer of contamination to the surface it is contaminating. Not only do the surfaces of the part being treated need to be degreased and cleaned of visually perceivable contaminants, but a further step must be taken so that the surfaces can pass a “Water-Break-Free” Test.
If any contamination in the form of oils, oxidation, etc. is present water will separate around those particles: the surface of the water will break. So passing the “Water-Break-Free” test means that a thin film of water can be supported on the surface to be primed without having any breaks in the water’s surface.
Passing the “Water-Break-Free” test is a sign that the molecular structure of the surface of the substrate has now been directly exposed. Now the surface of the substrate can be directly bonded to without contamination or oxides forming obstacles to covalent bonds.
However, cleaning the substrate to be perfectly clean and “Water-Break-Free” can require some very caustic and dangerous chemicals or processes. These include: Aculon® 907 (Heated Caustic cleaning dip), Argon Plasma, Corona Discharge, and a Piranha bath (H2SO4/H2O2)
Sometimes your production process needs to be simpler and not all surfaces are critical and need to be perfectly clean. In these cases you can use less aggressive chemicals and processes, including: Aculon® 905 (Room Temp Caustic cleaner), Ceria polish (abrasive scrub), Comet abrasive (or other polishing compound).

Applying adhesion promoter and primers
Once the intended part or surface is sufficiently clean, adhesion promoters or primers can be applied by dip bath: this method ensures a uniform coverage of the entire part. They can also be applied by wipe: simply using a clean cloth to wipe the treatment across the intended surface. Finally, they can be applied by spray using double passes. For each application method, post-application curing is recommended to achieve the best performance.