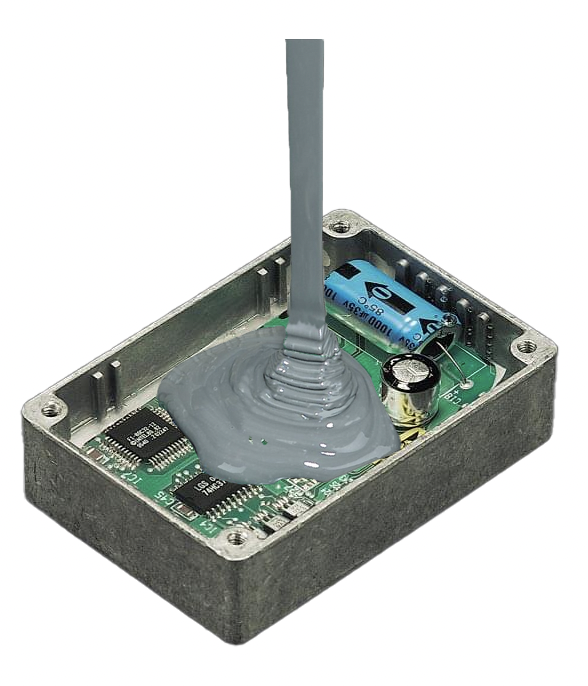
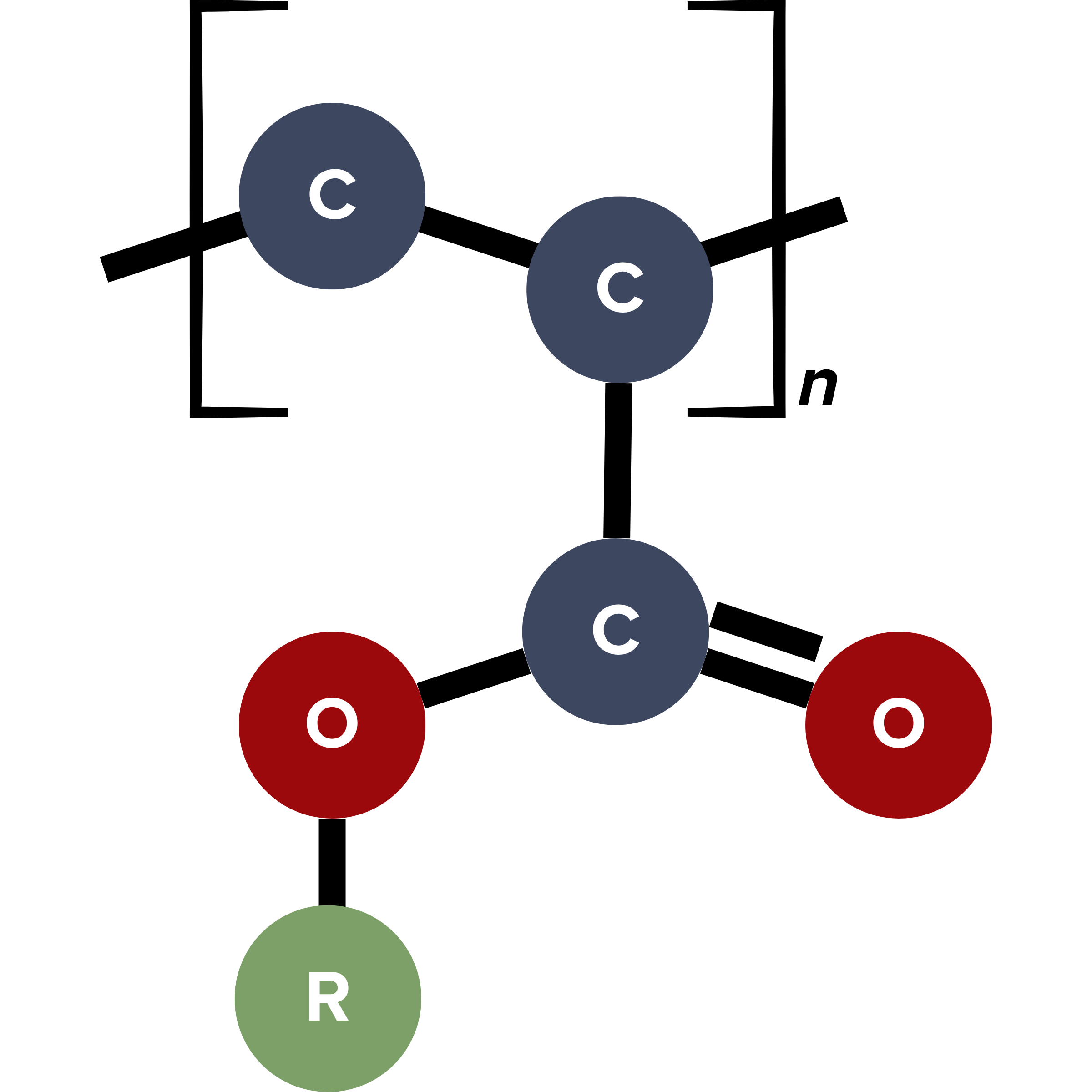
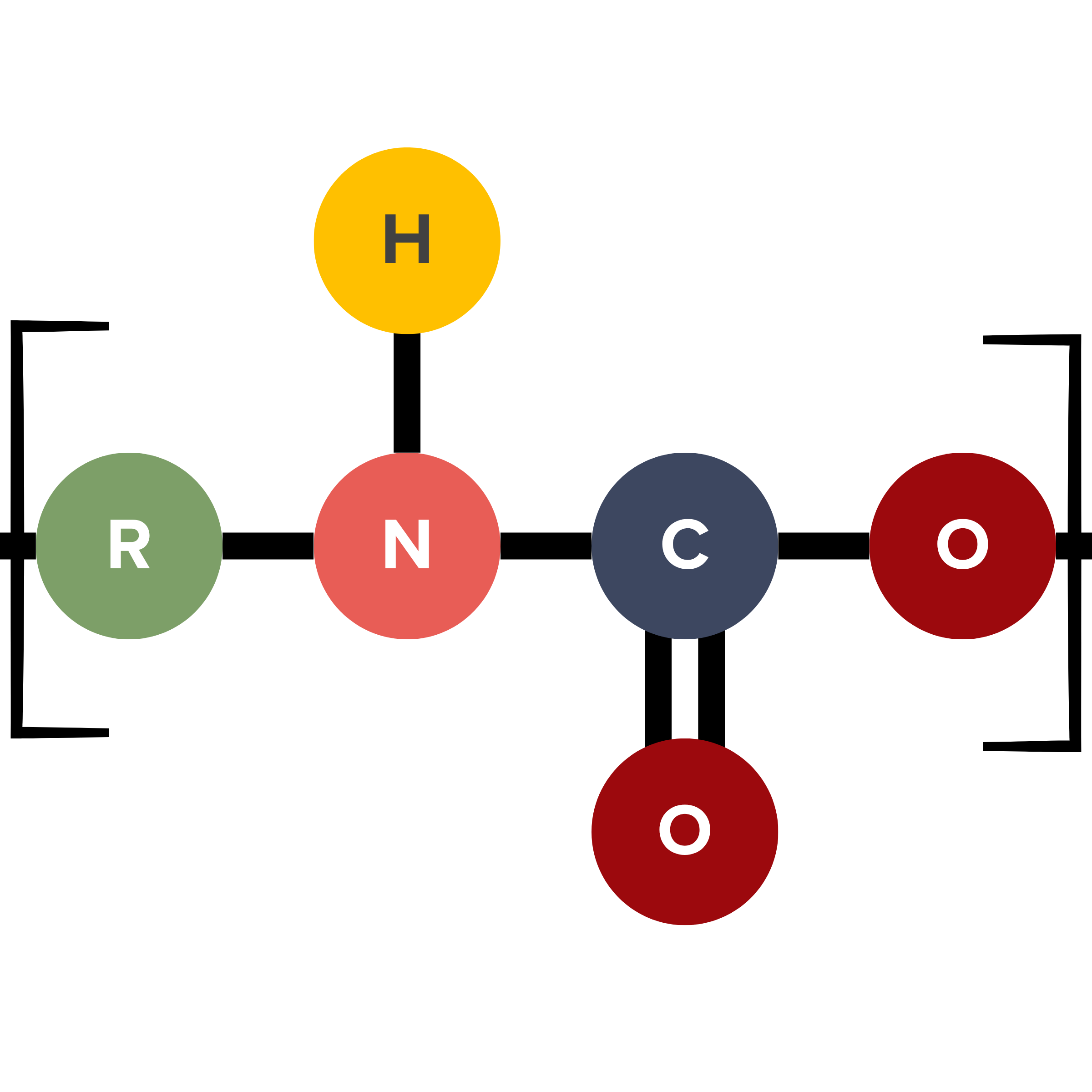
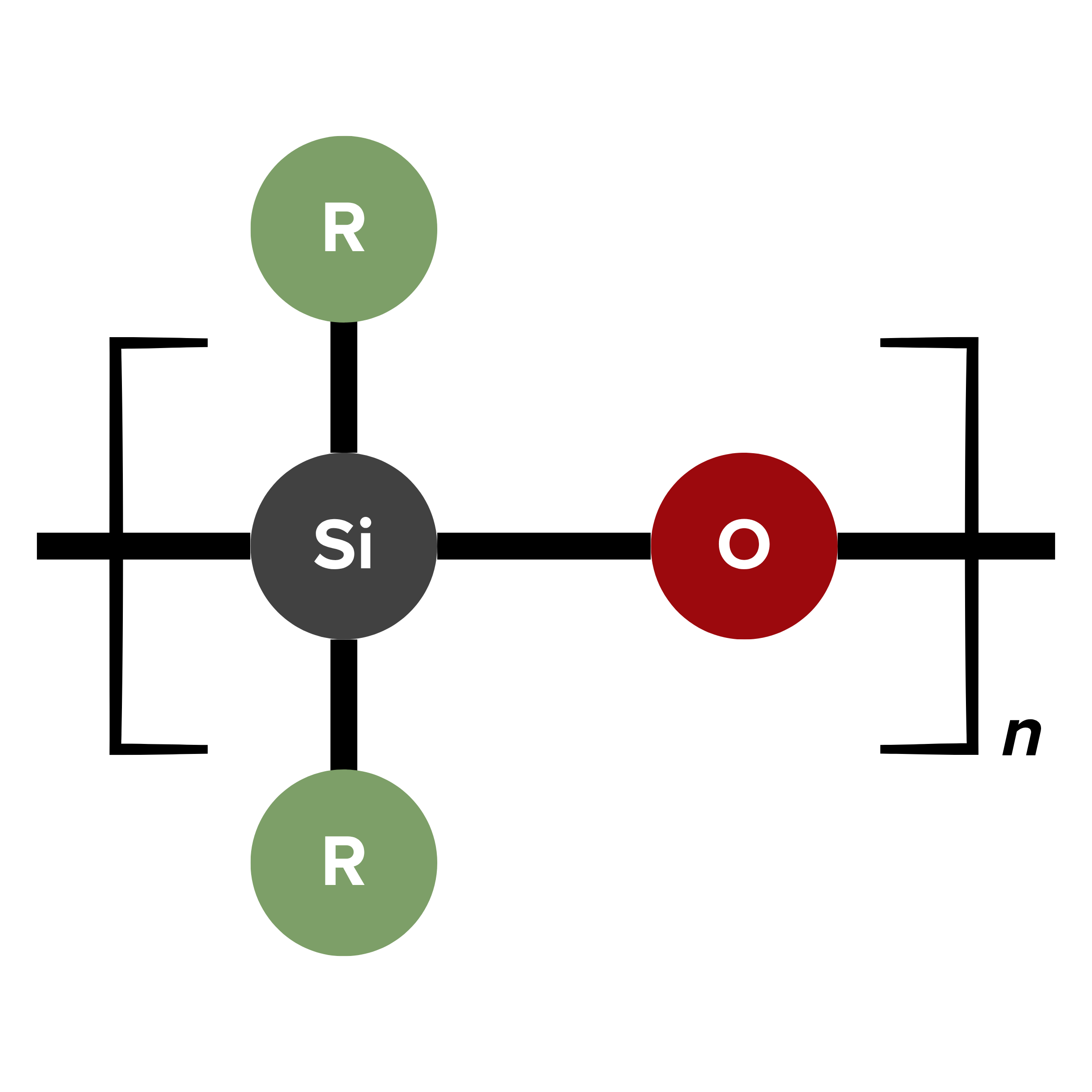
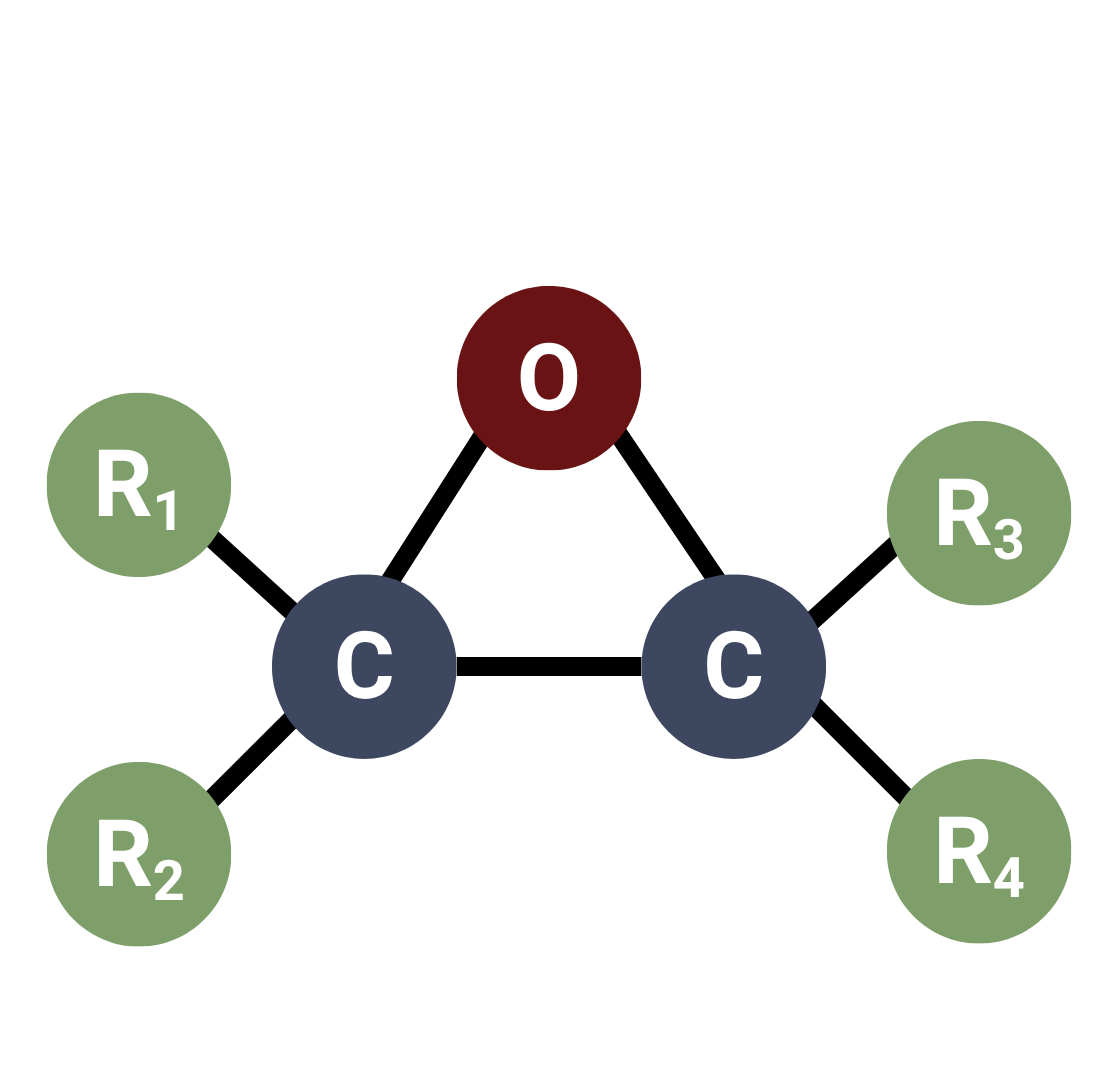
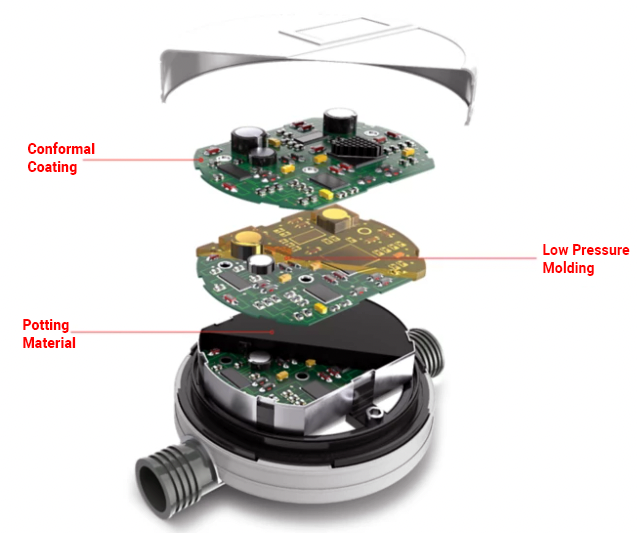
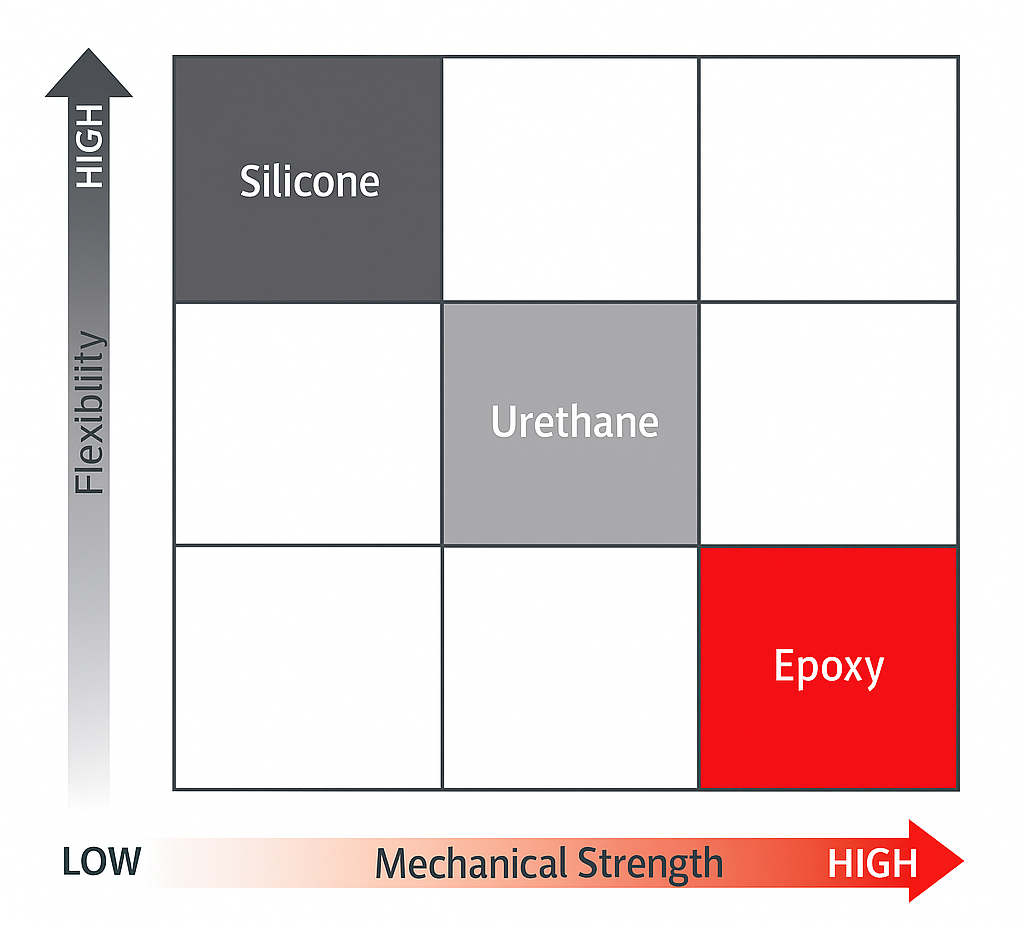
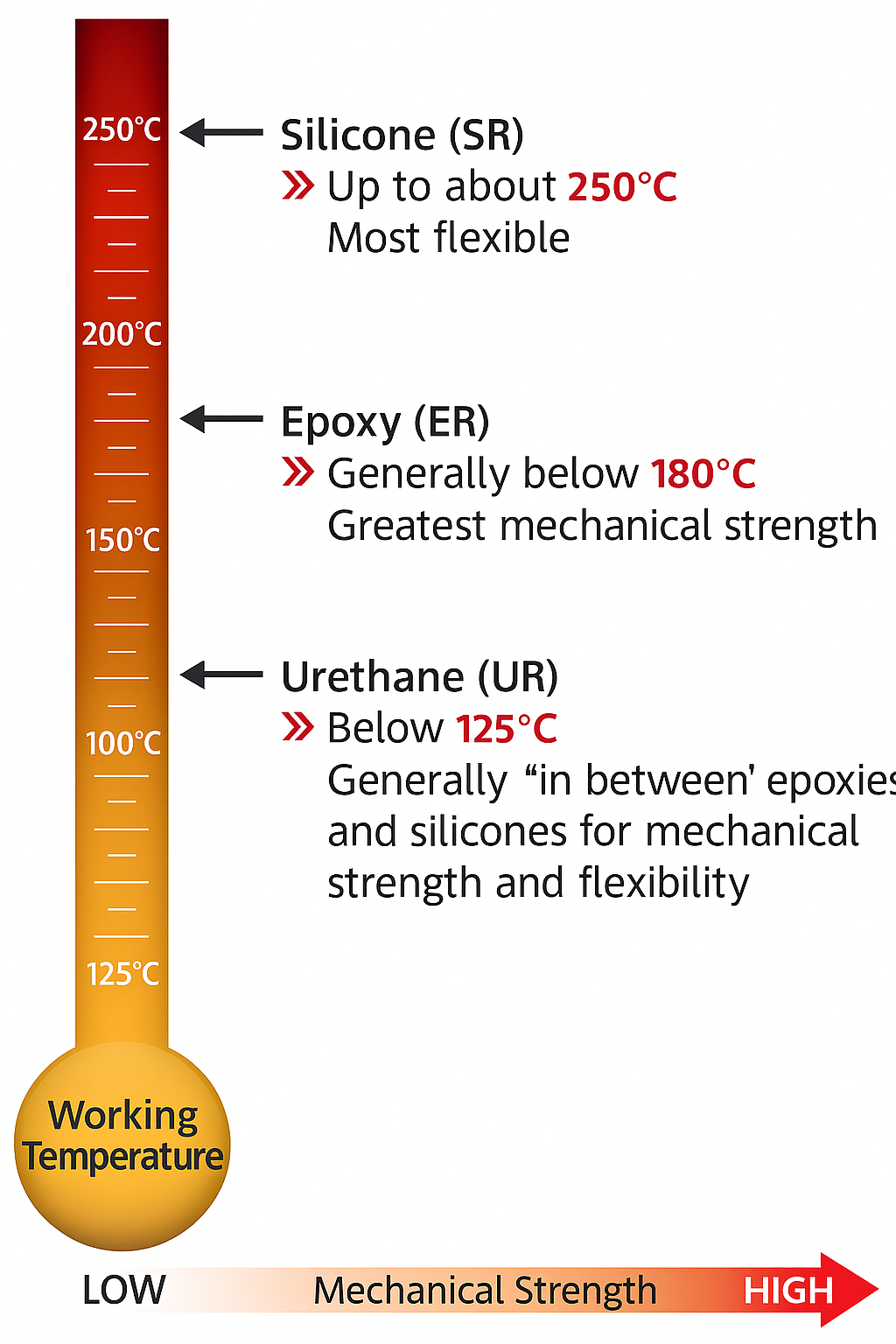
Formulating 1K and 2K Potting Materials
Two-Component (2K) Potting
2K potting compounds also comprise four elements, but the hardener (or its blend) is physically separated from the resin, preventing premature reaction before mixing. With 2K products, the elements must be weighed and blended, initiating the polymerization reaction upon mixing.
Single-Component (1K) Potting
1K potting compounds consist of a blend of four elements. The primary components, Resin and Hardener, are pre-mixed, eliminating the need for additional blending. This makes 1K potting materials ready for immediate use.