Adhesives & Sealants
Adhesives and Sealants are versatile materials designed for bonding various substrates and providing effective sealing solutions across a wide range of applications. These materials play a crucial role in industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and manufacturing.
Adhesives and Sealants, encompassing Epoxy, Acrylate, Silicone, SMP, Polyurethane, and gaskets, are integral to modern manufacturing and construction processes. Their diverse properties cater to a broad spectrum of applications, providing reliable bonding and sealing solutions that enhance product performance, longevity, and overall efficiency.
The right choice of adhesive or sealant can significantly impact the overall quality and durability of a product.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between adhesion and cohesion?
Cohesion is the attraction between comparable molecules within the same material or substance, whereas adhesion is the attraction between dissimilar molecules or materials. To hold substrates together, a variety of adhesive types that balance adhesion and cohesion are used in our industry.
Can a product be both an adhesive and a sealant?
Yes, many products are designed to offer both adhesive and sealing properties. These hybrid formulations are versatile and can be used in applications requiring a strong bond and a watertight or airtight seal. However, it's essential to carefully read the product specifications to ensure it meets the specific needs of your project.
When should I use a polyurethane sealant instead of a silicone sealant?
Paintability: If you need to paint over the sealed joint, polyurethane is the better option. Silicone sealants are not paintable.
Material Compatibility: Polyurethane sealants are generally compatible with most materials. However, acid-curing silicone sealants may not adhere well to strongly alkaline surfaces.
What is an ideal storage temperature?
The ideal storage temperature for all most of general type sealants, adhesives is 5°C to 25°C, but we should to prefer the storage condition in TDS.
What is an ideal application temperature?
The ideal application temperature for all most of general type of sealants are 10°C to 35°C, but we should to prefer the application temperature in TDS.
Learn More
Chemical-based adhesive and sealants:
Epoxy adhesives and sealants
Epoxy adhesives and sealant comprise an epoxy polymer and curing agent (polyamines, polyamides, or other hardeners). Depending on the type of hardener and curing method, they are available in both a one-component and a two-component package. Epoxy offers an excellent bonding strength to various substrates, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. Depending on the formulation, epoxy adhesives can range from brittle to highly flexible. Flexible epoxies are better suited for applications where the bond may experience stress or vibration. Epoxies generally resist chemicals, moisture, and temperature extremes well. However, they can become sensitive to UV radiation, especially when exposed to direct sunlight.
Acrylics adhesives and sealants
Acrylics are derived from acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, or other related compounds. Modified acrylic adhesives are thermosetting with one-part or two-part systems called reactive acrylics to distinguish them from other acrylic resins normally used in thermoplastic, pressure-sensitive applications. Structural acrylic adhesives have faster cure speed, and a moderate cost than epoxy, which provides high shear strength to many substrates (glass, metals, paper, textiles, metallic foils, and plastics), and has good levels of chemical, water, and corrosion resistance.
Silyl-modified polymers (SMPs)
Silyl-modified polymers (SMPs) are a class of materials that have been chemically modified with silyl groups (Si-O-R). These modifications enhance the adhesion and versatile properties, providing good bonding strength, durability, and elasticity to accommodate applications in various industries. The range of products offered as SMP adhesives in our selection guide is solvent- and isocyanate-free, without the need to add cleaners or primers during the preparation. Since they can withstand a wide range of temperature and humidity ratios, SMPs can be a great application for industries with high dynamic usage, such as EV battery manufacturing.
Polyurethane (PU) adhesives
Polyurethane (PU) adhesives derive their characteristics from the chemical group urethane present in the formulated or cured product. PUs exhibit a broad range of curing rates, processing flexibility, and mechanical properties, owing to the versatile nature of PU chemistry. Typically, PU adhesives are liquid two-part requiring the curing step, and PUR adhesives are one-part that apply like a hot melt and cure with ambient moisture. Notably, they offer exceptional adhesion to substrates containing hydroxyl groups, such as wood, wood-derived materials, brickwork, concrete, certain plastics, and paints. However, substrates like glass, aluminum, and alkaline surfaces may require primers for optimal bonding, promoting adhesion while shielding the adhesive from negative substrate interactions.
Silicone adhesive and sealant
Silicone adhesive and sealant is a polymer material based on the structure of polysiloxane. Its main chain is composed of silicon-oxygen bonds (Si-O-Si), which have high bond energy, making silicone adhesive have excellent heat resistance and electrical insulation. Besides that, they are highly flexible, have chemical stability, and have relatively low bond strength. Silicone adhesive is suitable for Circuit board protection and sealing and heat-resistant protection of electronic components, One-part RTV silicones are the most common type of silicone adhesive but Two-part RTV silicones and Heat-curing silicones often offer higher strength and faster curing times.
Anaerobic adhesives
Anaerobic adhesives are classified as anaerobic, though they have an acrylic chemistry base. These adhesives are employed for thread sealing, thread locking, retaining, and gasketing metal components. The curing process happens in a condition with no oxygen when the adhesive is in contact with metal (when the adhesive is confined between two metal surfaces). Anaerobic adhesives cure quickly, often within minutes or hours, depending on the specific formulation. It has high bond strengths, especially to metal surfaces, resistance to vibration and shock, chemical resistance, etc.
Cyanoacrylate adhesives
Cyanoacrylate adhesives are acrylic but classified as cyanoacrylate (or instant adhesives). Normally, they are called super glues or crazy glues. Cyanoacrylate adhesives are generally methyl or ethyl cyanoacrylate-based, single-component liquids with fast cure, excellent tensile shear strength, and good shelf life. It has very similar curing characteristics to the anaerobic adhesives, but cyanoacrylate resins are more rigid and less resistant to moisture.
What is different between Adhesive and Sealant?
Similar:
Adhesion: Both adhesives and sealants require proper adhesion to the substrates they are applied to to function effectively.
Durability: Both adhesives and sealants must maintain their bond strength and integrity over time, even when exposed to various environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, weather conditions, and chemical exposure.
Curing: Both adhesives and sealants are typically liquid when applied, allowing them to wet the surfaces and establish an initial bond. They then undergo a curing process, which involves hardening or solidifying to achieve their desired physical properties.
Different:
| Feature | Adhesives | Sealants |
| Main Function | Primarily used to bond materials together | Primarily used to create a barrier between materials and prevent leakage or intrusion |
| Properties | They typically have high strength, flexibility, and durability. Depending on the application, they may also be conductive or insulating. | Often have a more elastic or flexible nature, and may be waterproof, weatherproof, or chemical-resistant. |
| Applications | Structural bonding, decorative applications, repairs | Sealing gaps, cracks, joints, and seams; waterproofing surfaces; preventing corrosion |
| Typical materials | Epoxies, acrylics, cyanoacrylates, urethanes | Silicones, caulk, polyurethane sealants, gasket materials |
| Curing methods | May require heat, UV light, or moisture to cure | Often cure by exposure to air moisture or heat |
Application of Adhesive and Sealant in Automotive and Electronic consumers
Automotive
Adhesives and sealants play a crucial role in the automotive industry, common assembly and sealing applications include:
Body-in-White (body panels, doors,..)
Interior Trim (dashboards, seats,..).
Windshield Bonding,
Gasket Sealing(engine blocks and cylinder heads)
Sensor Mounting
Lighting Systems,
Electrical Systems (Securing wires, connectors)
Roof Racks and Spoilers,
Wheel Covers and Hubcaps,..
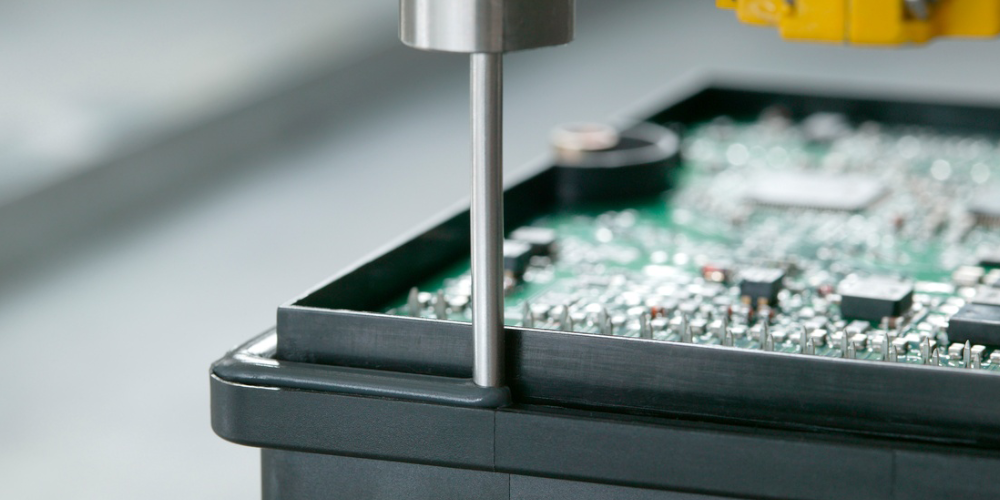
Electronic consumer
Adhesives and sealants play a crucial role in the assembly and protection of electronic consumer products, ensuring their reliability, performance, and durability. Here are some of the key applications:
Smartphones (Bonding screen, battery, and internal circuitry, Sealing the device),
Laptops, and Tablets (Bonding keyboard, display, and internal circuitry, Sealing the device) Wearable Devices (Bonding watches, fitness trackers,...)
Audio Equipment (Bonding speakers, amplifiers,...)
Gaming Consoles and other accessories.
Key Considerations for Selecting Adhesives and Sealants:
Environmental Conditions: The adhesive or sealant must be compatible with the operating environment, including temperature, humidity, vibration, and chemical exposure.
Mechanical Properties: The adhesive or sealant should have the required strength, flexibility, and durability to withstand the stresses encountered in the application.
Electrical Properties: For electronic applications, the adhesive or sealant must have appropriate electrical properties, such as conductivity or insulation.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the adhesive or sealant meets relevant industry standards and regulations, such as RoHS, REACH, and UL.





