Adhesives
Adhesives are essential bonding solutions used across industries to hold materials together and resist separation. Caplinq's adhesives are engineered to deliver superior performance and ease of application across various industries. Our comprehensive bonding solutions, including epoxy, acrylic, cyanoacrylate, polyurethane, silicon, and hybrid adhesives, cater to diverse needs from electronic, automotive, and other industrial engineering.
We offer options tailored to your specific application, including different curing methods such as UV-curing, temperature-curing, one-part or two-part adhesive, various viscosity range, etc. Our products boast exceptional adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals and environmental factors, ensuring reliable performance even in the most demanding conditions.
SIMSON ISR 70-03 | Silyl Modified Polymers (SMP)
- Elastic bonding adhesive
- Durable and reliable bonds
- Free from Isocyanates, Solvents and Silicone
- 8 weeks
BS-2000 Series | Silyl Modified Polymers (SMP)
- High Temperature Gap Filler
- Silicone-Free & Silyl Modified Polymer (SMP) Chemistry
- Stable thermal performance during Aging test
- 8 weeks
LINQBOND AD-008MT | Two-component Acrylic-based Adhesive
- No surface treatment required
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Zero solvent formulation
- 12 weeks
LINQBOND SO-115CM | Moisture Curing Modified Silicone Adhesive
- One-component
- Fast cure at low temperature
- High stability
- 8 weeks
LINQBOND SO-168CM | Tin-free Moisture Curing Modified Silicone Adhesive
- Tin-free
- Fast cure at low temperature
- High stability
- 8 weeks
LINQBOND SO-332CM | Moisture Curing Modified Silicone Adhesive
- Tin catalyst-free adhesive
- Fast cure at low temperature
- High stability
- 8 weeks
LINQBOND SO-191GL | Moisture Curing Modified Silicone Adhesive
- One-component
- Fast cure at low temperature
- High stability
- 8 weeks
LINQBOND SO-196CM | One-component Moisture Curing Silicone Adhesive
- One-component
- Fast cure at low temperature
- High stability
- 8 weeks
LINQBOND ED-416CM | Two-component Epoxy Adhesive
- No surface treatment required
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Zero solvent formulation
- 8 weeks
LINQBOND T242 | Medium Strength Threadlocker
- Good adhesion to ferrous and non-ferrous metals
- Good chemical resistance
- Removable
- 6 weeks
LINQBOND T243 | Fast-curing Medium Strength Threadlocker
- Improved oil resistance
- Non-migrating, thick forumation
- Good chemical resistance
- 6 weeks
LINQBOND EO-322PL
- High adhesion
- Medium-high temperature cure
- Ideal for sensitive components
- 12 weeks
ED-490CM | Two-part Epoxy Adhesive for Casting & Bonding
- Excellent toughness
- Reliable in humid conditions
- Low thermal stress
- 12 weeks
ED-645CM | Two-Part Epoxy Adhesive for General Applications
- Excellent electrical insulation
- Reliable in humid conditions
- High Viscosity
- 12 weeks
ED-425PL | One-Part Epoxy Adhesive for Rubber & Plastics
- Strong adhesion to electronic components
- Excellent toughness
- Low outgassing
- 12 weeks
EO-830MT | One-part Epoxy Adhesive for Metal Bonding
- High crack & fatigue resistance
- Excellent adhesion on metals
- RoHS compliant
- 12 weeks
ED-845CM | Fast-curing Epoxy Adhesive for Electronics Bonding
- Fast-curing
- Excellent adhesion
- High insulation, chemical resistance and anti-vibration
- 12 weeks
T262 | High Strength Threadlocker
- Thixotropic formulation
- Excellent adhesion
- Good chemical resistance
- 12 weeks
T272 | Temperature-Resistant Threadlocker
- Great adhesion to several surfaces
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Higher operating temperature
- 12 weeks
UV-349 | Light UV Cure Adhesive
- Medium viscosity (4,000 - 8,000 cPs)
- Compatible with different substrates
- Flexible
- 12 weeks
C401 | Low-Medium Viscosity Cyanoacrylate Adhesive
- Low to medium viscosity
- Rapid cure
- Biocompatible
- 12 weeks
ISR 70-03-FR | Silyl Modified Polymers (SMP)
- EN 45545 fire safety standards
- Meets the highest hazard level 3
- Permanent elastic within temperature range -40°C to 100°C
- 20 weeks
GPU 9303 | Polyurethane Adhesive (PU)
- Solvent free, without mercury salt
- High strength and good thixotropy
- Good temperature and humidity resistance
- 8 weeks
GCR 6101 | Silyl Modified Polymers (SMP)
- Very good UV-resistance and ageing properties
- Good adhesion on several substrates without the use of a primer
- High Modulus
- 8 weeks
Product Selector Guide
| Product | Application | Curing mechanism | Skin time | Open Time | Tensile strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Product features |
| BS-2000 V112 | Bonding/gap filling | Moisture Curing | - | - | 1.15 | 9.2 | High thermal conductivity |
| BS-6000 V101 | Bonding | Moisture Curing | - | 7.74 | - | 241 | High Modulus elastic adhesive |
| BS-7000 V3 | Bonding/gap filling | Moisture Curing | 10 | <15 | 2.0 | 250 | General purpose sealant with low residual tack |
| BS-7000F V3 | Bonding/gap filling | Moisture Curing | 10 | <15 | 3.0 | 200 | Meets the highest hazard level 3 |
| BS-7000 V7 | Bonding/gap filling | Moisture Curing | 30 | - | 1.5 | - | low viscous sprayable sealant, with a special spray structure for sealing overlapping seams |
| BS-7000 V8 | Bonding/gap filling | Moisture Curing | 15 | <15 | 2.9 | 250 | Developed for the rapid and efficient bonding of windscreens |
| Product | Application | Curing mechanism | Mixing ratio | Shear strength (MPa) | Tensile strength (psi) | Elongation (%) | Product features |
| BS-9000 V303 | Bonding | Moisture Curing | 1:1 | 14 | 16 | 14 | Good adhesive performance with FRP, Composite material, metal and plastic |
| Product | Application | Curing mechanism | Mixing ratio | Mixed viscosity (MPa) | Tensile strength (psi) | Elongation (%) | Product features |
| BS-1000 V8 | Bonding | Moisture Curing | 1:1 | 375000 | 1.8 | 315% | Fast room-temperature curing silicone for durable electronics |
| Product | Application | Curing mechanism | Mixing ratio | Volume Resistivity (Ω⋅cm) | Shear Strength (kgf/cm2) | Application Temperature | Product features |
| AD-008MT | Bonding | Moisture Curing | 10:1 | 4.5×1013 | 50 | –40 to 100 | No surface treatment required & excellent chemical resistance |
| Product | Application | Substrate | Appearance | Viscosity (mPa•s) | Thixotropic Index | Tg (℃) | α1 (ppm/℃) | α2 (ppm/℃) | Pot Life (hours) |
| EO-322PL | Electronic Components | Plastics | Black | 19,000 - 25,000 | 2-3 | 130 | 66 | 178 | 72 |
| ED-416CM | Electronic Components | Metals & Plastics | Milky - Light Yellow | - | - | 40 - 49 | 223 | - | - |
| Product | Application | Substrate | Viscosity (mPa•s) | Tg (℃) | α1 (ppm/℃) | α2 (ppm/℃) | Application Temperature (℃) |
| SO-115CM | Electronic Components | Plastics | 30,000 | < -40 | - | - | -40 - 100 |
| SO-168CM | Electronic Components | Combination | 150,000 - 300,000 | < -40 | - | - | -50 - 100 |
| Product | Application | Curing mechanism | Breakaway Torque Range on Steel (N•m) | Prevail Torque Range on Steel (N•m) | Fixture Time on Steel (mins) | Full Cure Time (hours) | Application Temperature (℃) |
| T242 | Threadlocker | Anaerobic | 3.4–11.3 | 2.9–8.1 | 15-20 | 24 | –50 to 150 |
| T243 | Threadlocker | Anaerobic | 13.5–16.8 | 7.8–10 | 5-8 | 24 | –50 to 150 |
| T262 | Threadlocker | Anaerobic | 18.08 | 28.25 - 33.90 | 15 | 24 | -50 to150 |
| T272 | Threadlocker | Anaerobic | 24.86 | 24.86 | 5 | 24 | - |
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions about Adhesives
Structural adhesives are specialized adhesives designed to bond materials together under mechanical stress. They are used in applications where the bond is expected to withstand forces such as tension, shear, or peel and provide long-lasting and durable bonds that can withstand significant loads.
The bondline thickness could work with a minimum of 2 mm thickness. This thickness impacts the elastic bonding properties of the SMP technology, so we recommend 20 mm for ideal elastic bonding properties.
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It essentially describes how thick or sticky a fluid is. A fluid with high viscosity flows slowly, while a fluid with low viscosity flows easily. The rheological index, on the other hand, is a dimensionless number that indicates how the viscosity of a fluid changes with the shear rate. This means it describes how the fluid's thickness changes when it is subjected to different levels of force.
Compared to 1 part PU, 2 part PU can cure more quickly and is not dependent on moisture or heat to cure, ambient temperature will do the justification.
Generally, the two-component polyurethane can be cured at room temperature at a certain curing time and one-component polyurethane cures typically by moisture reaction.
Learn More
Adhesive core benefits
Adhesives offer various benefits in various industries, including electronics, automotive, construction, and manufacturing.
.png)
High mechanical strength: Structural adhesives can achieve very high bond strengths, often exceeding those of mechanical fasteners
Material Bonding: Adhesives create strong and durable bonds between different materials, providing structural integrity and stability.
Uniform stress distribution: Adhesives can distribute stresses more evenly across bonded surfaces, reducing the risk of failure.
Aesthetics: Adhesives and sealants can be used to create clean, seamless joints, improving the appearance of products.
Lightweight: Adhesives can often be used to replace mechanical fasteners, resulting in lighter and more efficient products.Effectiveness: Adhesives can often be applied more efficiently than mechanical fasteners, reducing labor costs and streamlining production processes, leading to increased productivity.
Corrosion protection: Adhesives can provide a protective barrier against corrosion, especially in applications exposed to harsh environments.
Impact resistance: Adhesives can create strong and durable bonds between materials, enhancing their ability to withstand external shocks and forces
Vibration damping: Some adhesives can absorb vibrations and reduce noise, improving product performance and comfort.
Failures model
The adhesive failure model refers to how an adhesive bond breaks under stress. Analyzing these failures helps understand factors affecting bond strength, leading to better bonding processes, adhesive selection, and durable joints




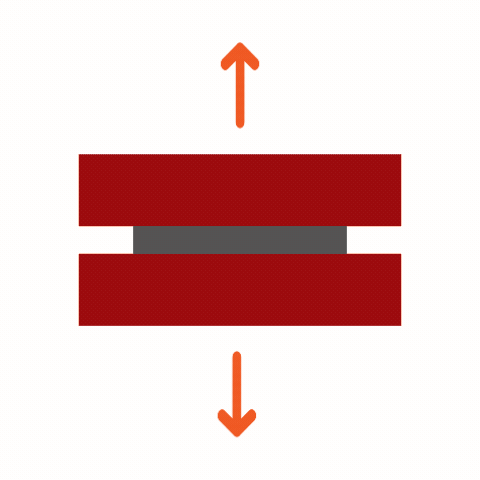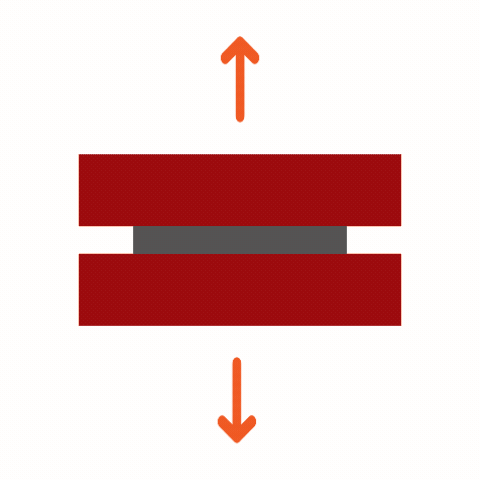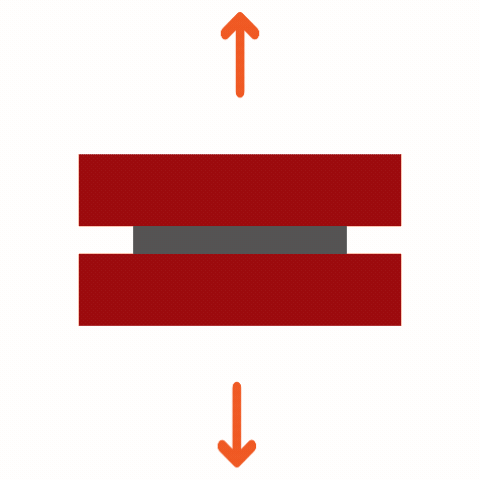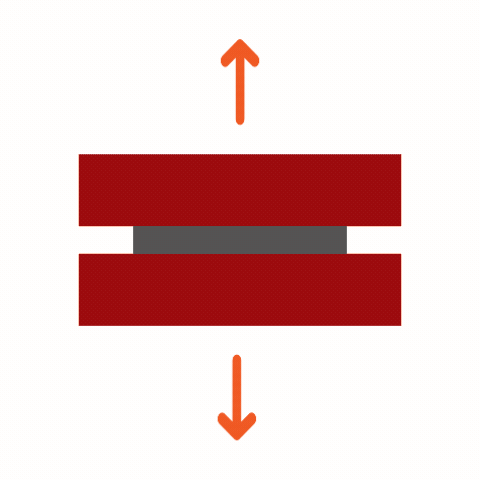
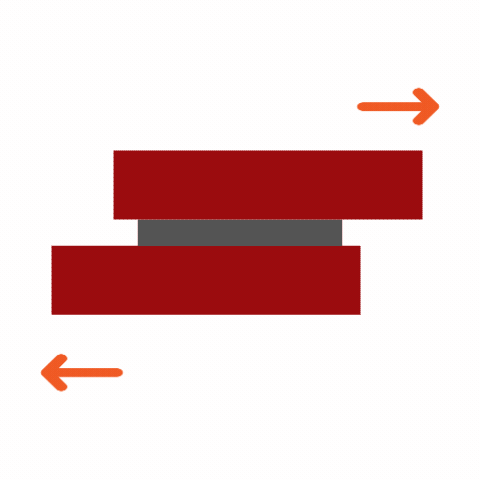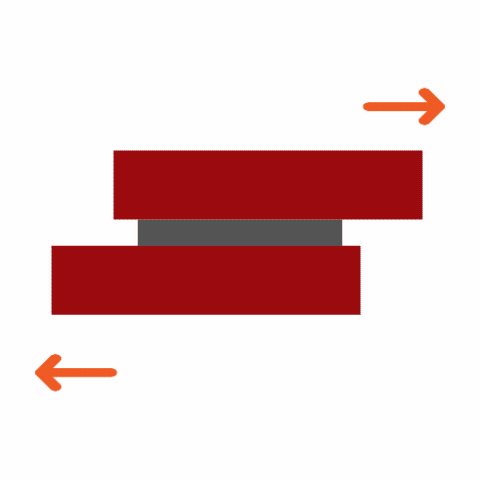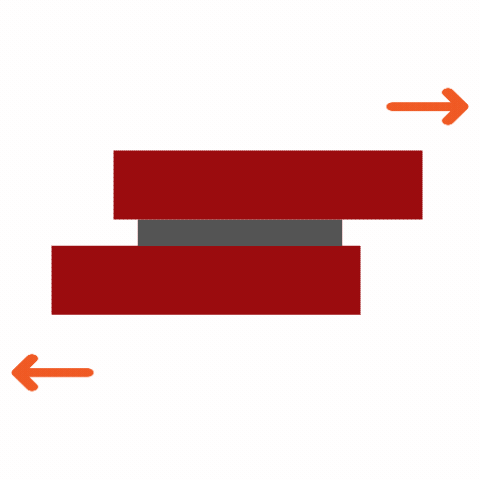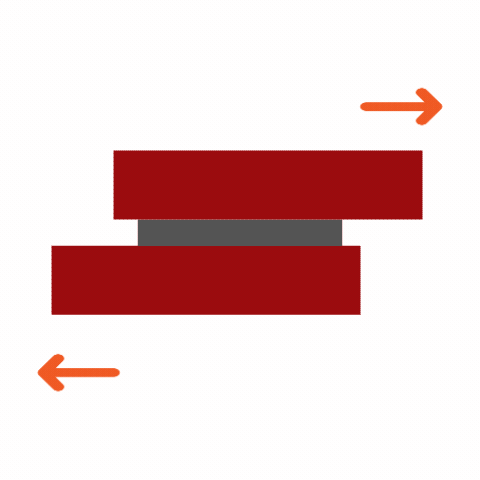
Common Adhesive Stresses
Understanding these stress types is essential for selecting the right adhesive and designing durable joints. Knowing how different adhesives respond to various stresses ensures optimal performance and reliability in multiple applications.

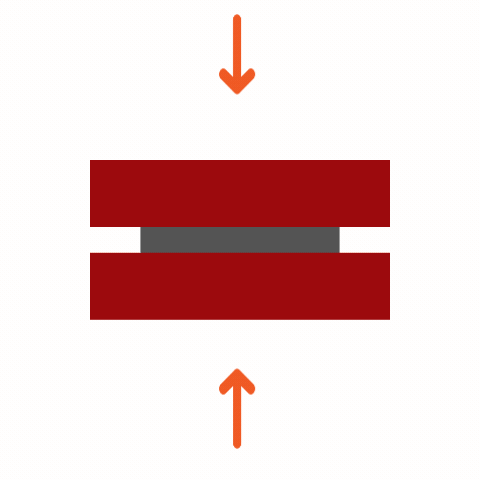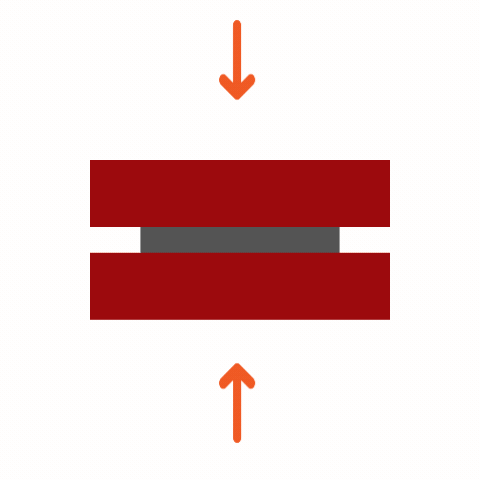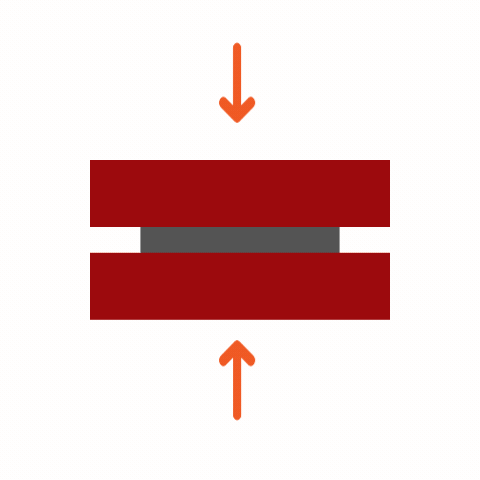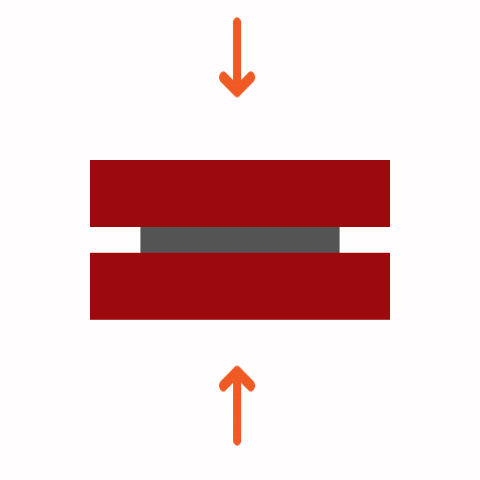
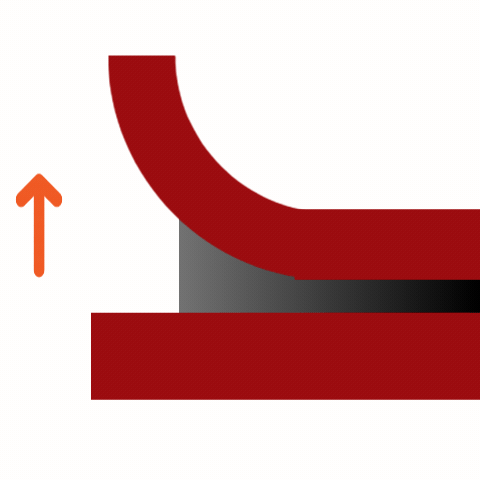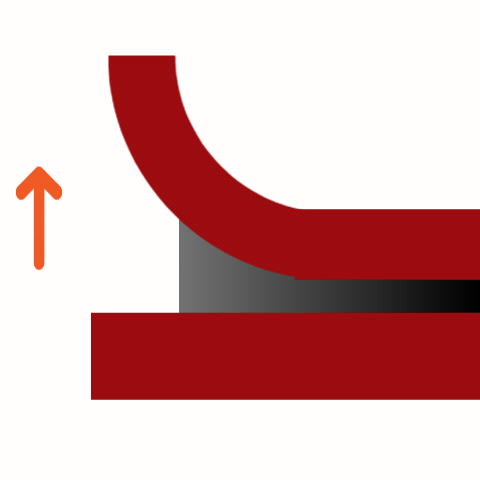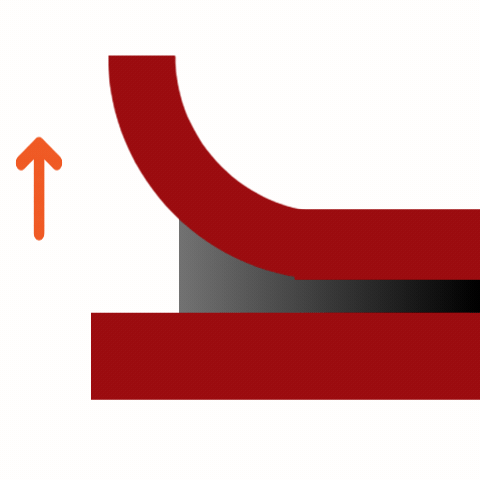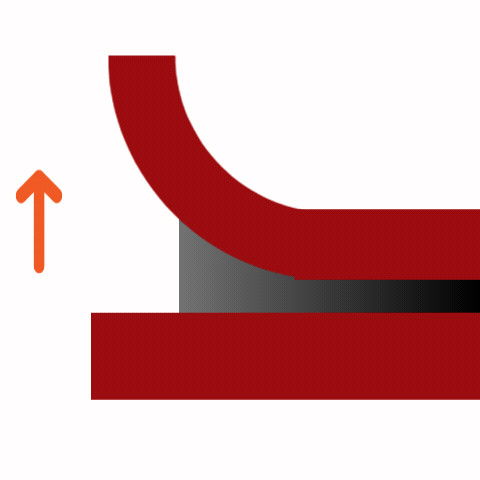
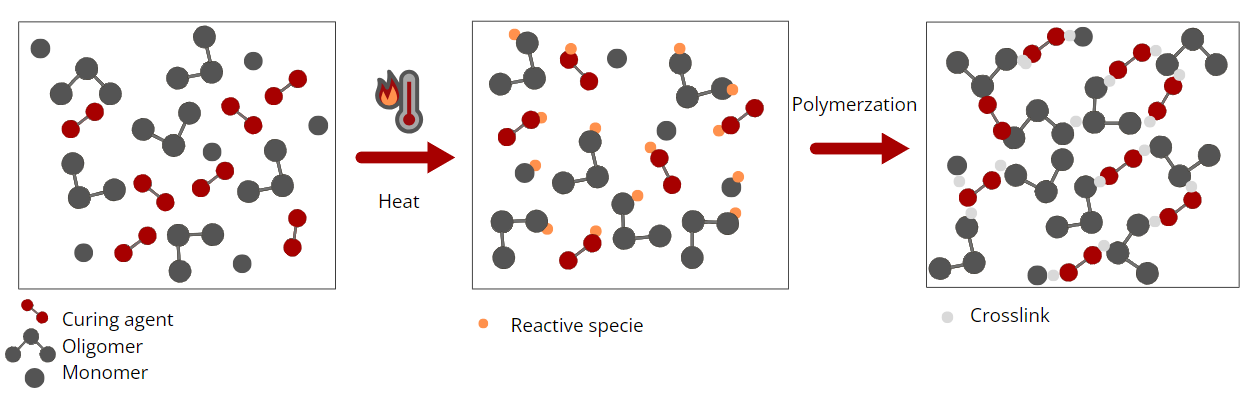
Curing Machemnism
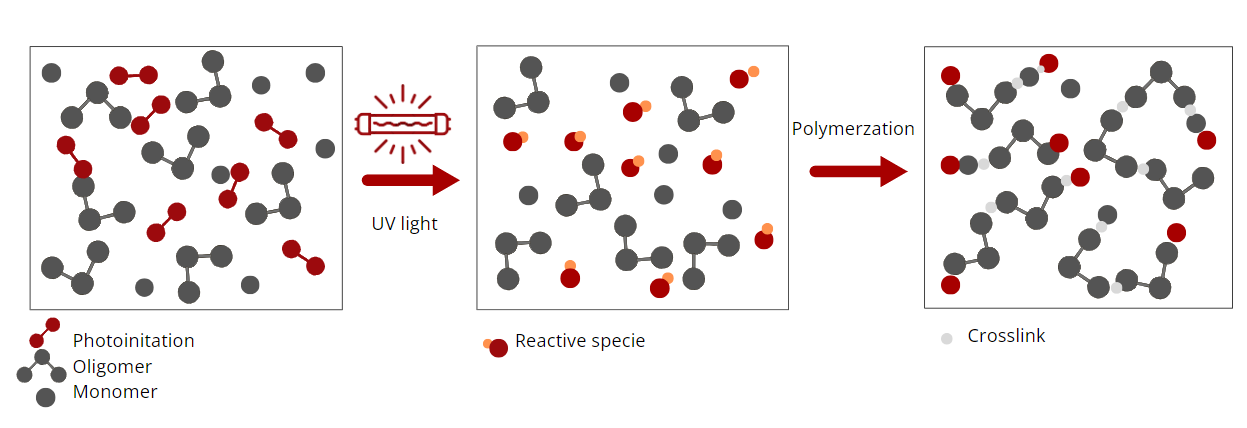
UV-curing
UV-curable materials contain photoinitiators that are activated by UV light. When exposed to UV radiation, these photoinitiators undergo a chemical reaction that initiates the polymerization process, causing the adhesive to solidify. UV-curing adhesives such as epoxy acrylate adhesives, polyurethane acrylate adhesives, and polyester acrylate adhesives are widely used.
It brings fast curing times, less energy consumption, environmental friendliness, and accurate and consistent results
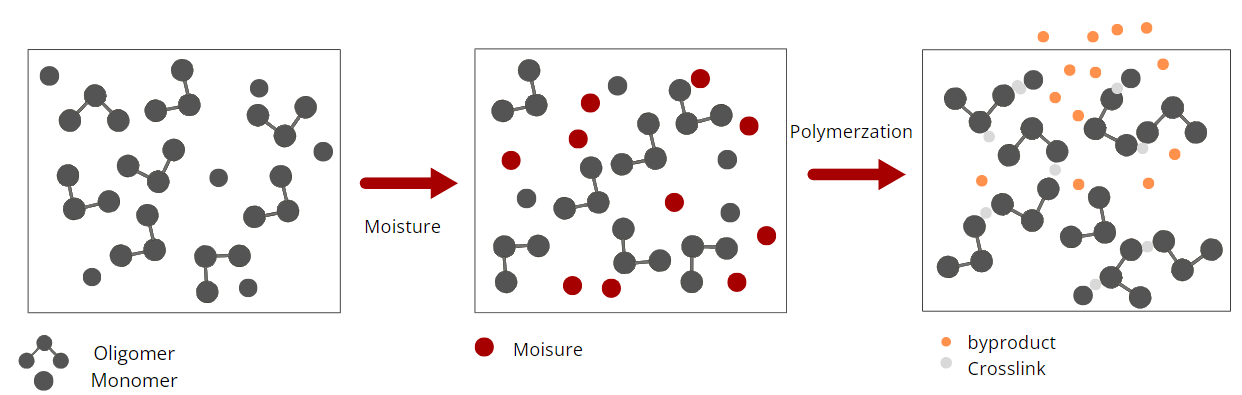
Moisture-curing
Heat-curing