Epoxy Coating Powders
Epoxy coating powders (ECP) are often called "functional" coating powders because they serve a much larger purpose than simply a decorative coating with corrosion protection. Also called fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE) powder, they differ from other powder coatings because of the high level of functional fillers that give ECPs their electrical and mechanical properties. The most important property for these functional epoxy coating powders is electrical insulation. The temperature and environmental conditions under which electrical insulation is provided define the unique applications for which epoxy coating powders are so well suited.
Fusion-bonded epoxy coating powders are used in a wide range of applications including motor armature slot insulation, busbar & power distribution insulation, passive component coating and many more. Wherever metal or ceramic parts require electrical insulation and mechanical protection, epoxy coating powders have found a use. CAPLINQ offers a range of functional epoxy coating powders for specific market and industrial end-use applications.
BCP-1522 | Medium voltage Busbar Coating Powder
- Low and medium voltage applications
- Suitable for applications up to 38 kV
- Optimized for fluidized bed coating process
- 12 weeks
BCP-1134 | Medium voltage Busbar Coating Powder
- Designed for EV and panel busbars
- 82 kv/mm insulation
- Thermoplastic
- 8 weeks
BCP-1034 | Medium voltage Busbar Coating Powder
- Designed for electric busbars, fuel pipes, tubes, fittings
- 80 kv/mm insulation
- Thermoplastic
- 8 weeks
BCP-1631 | Medium voltage Busbar Coating Powder
- 49 kv/mm breakdown voltage
- Specifically formulated for steel
- Thermoplastic Polymer Alloy
- 8 weeks
BCP-3502 | 130℃ RTI Busbar Coating Powder
- Black, red halogen-free epoxy coating powder
- Flexible use for low and medium voltage systems
- High heat resistance (RTI 130 °C) with UL94 V-0 rating
- 12 weeks
RC-6253 | One-Part Epoxy Coating Resin
- Thermally stable polymer (140 °C Tg)
- 14-day pot life
- Low moisture absorption
- 6 weeks
BCP-1507 | Medium voltage Busbar Coating Powder
- Multiple colors
- All around usage
- RTI Class A
- 8 weeks
BCP-1509 | Medium voltage Busbar Coating Powder
- Reddish Brown Color
- Up to 3mm thickness
- RTI Class B
- 8 weeks
GCP 1805 | Halogen-free Insulating Epoxy Coating Powder
- Blue and Gold Colors
- Halogen-free Epoxy Coating Powder
- For class 2 & 3 capacitors and varistors
- In stock
DK15-0463 Black Insulating Epoxy Coating Powder
- DK15-0463 Coating Powder
- Black, insulating, epoxy based
- Humidity-resistant for outdoor low voltage busbars
- No longer available
DK15-0907 | Red Insulating Epoxy Coating Powder
- DK15-0907 Coating Powder
- Red, insulating, epoxy based
- For low and medium voltage bus bars
- No longer available
DK15EG-05 Black Insulating Coating Powder
- DK15EG-05 Coating Powder
- Black, insulating, epoxy based
- Gasohol resistant, for automotive fuel pump motor armatures
- No longer available
DK17-01 Light Orange Insulating Epoxy Coating Powder
- DK17-01 Coating Powder
- Light Orange, insulating, epoxy based
- For passive electronic components
- No longer available
DK18-05 Blue Insulating Epoxy Coating Powder
- DK18-05 Coating Powder
- Blue,insulating, epoxy based
- For class 2 & 3 capacitors and varistors
- No longer available
DK19 Red Insulating Coating Powder
- DK19 Coating Powder
- Insulating, Epoxy based
- For low and medium voltage bus bars
- No longer available
DK52 Gray Insulating Coating Powder
- DK52 Coating Powder
- Gray, insulating, epoxy based
- For high voltage fuses and low voltage bus bars
- No longer available
DK7-0953 Blue Insulating Epoxy Coating Powder
- DK7-0953 Coating Powder
- Blue,insulating, epoxy based
- Electrostatic Fluidized Bed
- No longer available
DK7-3100 Black Insulating Epoxy Coating Powder
- DK7-3100 Coating Powder
- Black, insulating, epoxy based
- High productivity class H rated
- No longer available
Product Selector Guide
| Linqsol Series | BCP-Series | MCP-Series | GCP-Series | GCP-Series |
| Examples |  |  |  |  |
| Applications | Busbars, switchgear, power distribution | Coil windings, armatures and stators | Resistors, capacitors, inductors and other passive electronics | Toroids, magnetic cores, and powder cores |
| Products |
| |||
| Applying Method | Fluidized bed dipping Electrostatic spray | Electrostactic fluidizied bed Blow coating | Fluidized bed dipping | Fluidized bed dipping |
| Useful Information | Motor Insulation Application | - |
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions about Epoxy Coating Powders
What\'s the difference between fusion bonded epoxy powder and epoxy coating powder?
In a word: Nothing. The term fusion bonded epoxy coating powder or fusion-bond epoxy coating powder, abbreviated as FBE is often reserved for applications such as concrete reinforcement bars (rebars), pipe-coating or valve coating.
The name epoxy coating powders, on the other hand, are more common in the electronics, automotive and power distribution industries for passive component coating, motor iron armature insulation, and busbar coating. Both are thermoset plastic epoxy coatings.
How much insulation can be achieved using epoxy coating powder?
Epoxy coating powder can insulate parts as low as 1.5 volts and as high as 50,000 volts. Low voltages (traditionally defined as less than 600V) can be coated with very thin layers of epoxy. Medium voltages (defined as up to 38,000 volts) require high dielectric strength epoxy and thicker coating layers.
How thick can we coat using epoxy coating powder?
Coating thickness depends on the application method used. Using electrostatic coat only, the maximum thickness you could spray is approximately 250 microns. Depending on the epoxy type, this could insulate up to approximately 1000 volts. If the parts are preheated before electrostatically spraying, you could achieve up to 1200 micron thickness which could insulate up to approximately 12,000 volts.
Using a fluidized bed and preheated parts with multiple dips, you can easily coat to 4mm (4000 microns) and could insulate medium voltage busbars up to 40,000 volts. With special epoxy coating powders, it is possible to build as thick as 5mm and achieve insulation up to 50,000 volts.What is the difference between the various formulations of epoxy molding compounds?
Epoxy coating powders\' basic function is to provide electrical insulation and mechanical protection. The difference between the formulations has mostly to do with the applications for with they are designed and their application methods.
Application types require more or less of each electrical insulation and mechanical properties and the rest of the properties are designed to be optimized for electrostatic spray, fluidized bed or electrostatic fluidized bed applications methods.
Are there known brand names that use epoxy coating powder?
We have a relationship with Nordson, who make a range of electrostatic powder coating equipment. We have been successful implementing solutions with Nordson and are proud to recommend their equipment.
We also have experience with GAT finishing systems who make very complete epoxy powder coating rooms.
How do I prevent bubbles from forming after coating?
Parts must be very clean beforehand (no oil, fingerprints, etc.) and the powder should be sprayed at room temperature. Running a Design of Experiment to find the the best temperature and time to preheat and post cure materials is always recommended.
Can I make my own fluidized-bed for epoxy coating powder?
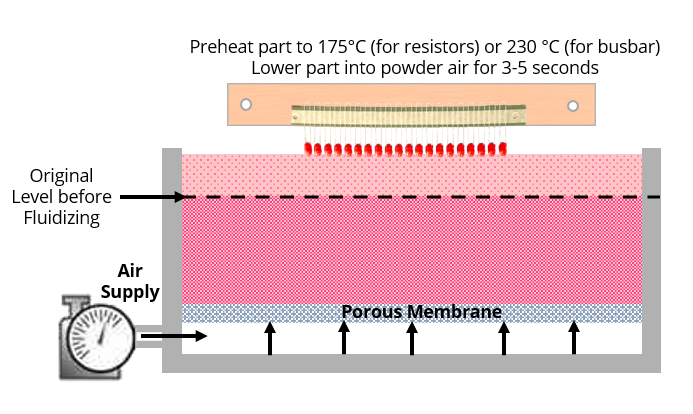
Yes you can, it is not very complicated at all. You simply need a design that allows you to pass clean compressed air through a porous membrane or fluidizing sheets. Two references are Genpore Fluidizing Sheets and Porex\'s porous membranes. We have designs that we can offer you.
How are epoxy coating powders cured?
Epoxy coating powders are cured at two different temperatures using a process known as a 'step cure.' This step involves initial curing at a lower temperature followed by second curing at a higher temperature.
Starting with a lower temperature in the first step minimizes stress buildup, as epoxy tends to shrink during the evaporation of volatile materials. During this first step, moisture and volatile materials that could evaporate at this temperature are removed at a slow rate. This controlled evaporation rate prevents the formation of porosities within the epoxy caused by the vapor as it exits the resin.
The second step, conducted at a higher temperature, enhances epoxy crosslinking, optimizing the cured material properties, including CTE (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion), Tg (Glass Transition Temperature), and modulus.
Learn More
Epoxy Coating Powder Applying Method
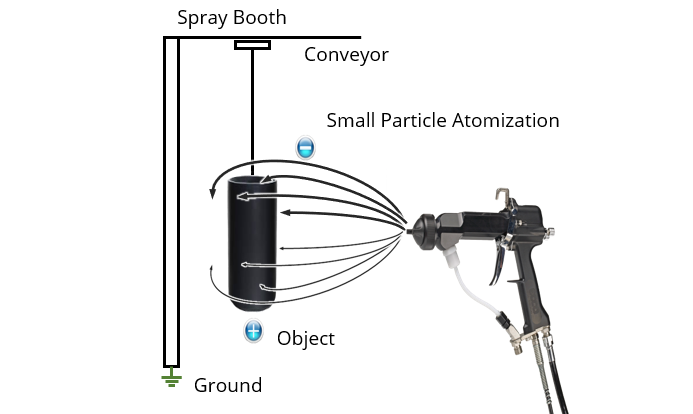
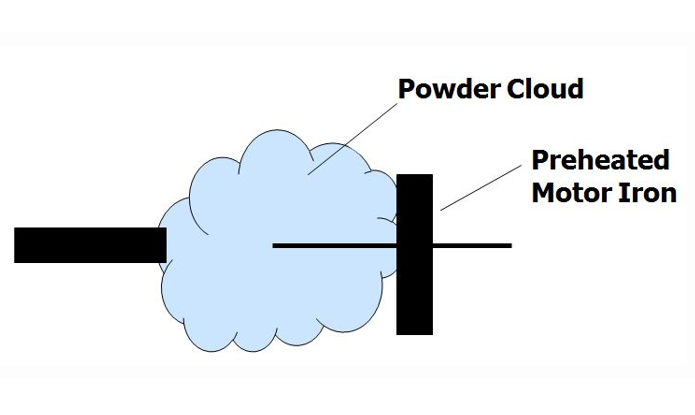
There are several methods for applying epoxy coating powder. Parts can be coated using a fluidized bed, sprayed with an electrostatic gun or applied using an electrostatic fluidized bed. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages and is suitable for different components coating.
Fluidized dipping is industry standard method for busbar coating for high productivity. It is also used in passive electronics coating.
Eletrostatic spray coating can adhere powder to a wide area from a single spray direction. It is applied for busbar and passive components.
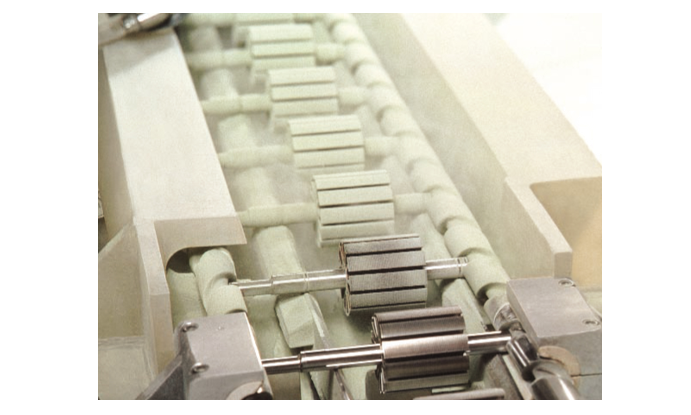
Electrostatic fluidized bed coating is a industry standard method in motor armatures coating for providing a thin, uniform coating thickness.
Blow coating is an old technology for motor coating that is less expensive, but orders of magnitude less consistent.
Epoxy Coating Powder Key Features
There are many features or considerations people talk about while selecting coating powders for their specific applications. To understand how those properties could influence the coating performance and insulation results, here we list a table.
| Key Features | How It Affect The Coating Performance | Especially Important For |
| Specific Gravity | A low specific gravity combined with high dielectric strength reduces the amount of epoxy coating power needed. | ♦ ♦ ♦ |
| Stick Point | Optimal stick point temperature reduces material build-up across multiple shifts, minimizing cleaning time. | ♦ ♦ |
| Edge Coverage | High edge coverage means no chance of failure in corners. It enables high build thickness, crack resistance and corner toughness. | ♦ ♦ |
| Cut Through Resistance | A high cut through resistance passes automotive requirements and protected from coil windings even at high temperatures. | ♦ |
| Flexibility | High flexibility prevents cracks in coating when thin conductor bends. Low stress powder has better thermal shock resistance. | ♦ ♦ |
| Good Ahesion To Substrate | High adhesion to copper/aluminum/.. and cross layers could bring better heat resistance for good insulation and also thicker coating performance. | ♦ ♦ ♦ |
| High Insulation Class RTI | The industry wants a one-powder solution to meet high productivity demands. | ♦ |
| Short Cure Time | A shorter cure time at lower temperatures ensures increased coating productivity. | ♦ ♦ ♦ |
| Hot Plate Flow | Longer flow means: easy to apply in production; able to cover hard to reach parts; consistent and even coverage. | ♦ |
| Shelf Life | A longer shelf life at higher temperatures saves storage and transport costs. | ♦ ♦ ♦ |
| Dielectric Strength | Good dielectric strength Saves material, allows to reach same breakdown voltage with less material. | ♦ |
| Cost-Efficient | An economical product offering for the price-sensitive supply chain. | ♦ ♦ ♦ |
| Halogen-Free | Halogen-free powder contains no bromine, chlorine or antimony, which is considered as green product. | ♦ ♦ ♦ |
| Scratch Resistance | Epoxy coating powders are tough enough to prevent damage from typical handling. | ♦ |
| Environment Resistance | Epoxy coating powders seal against mositure, chemicals and heat. | ♦ ♦ ♦ |
| ♦: Busbar Coating ♦: Motor Coating ♦: Passive Component Coating | ||
Epoxy Coating Powders: Their origins all stem from Hysol DK18-05
Motor iron slot insulation, switchgear, capacitors, toroid cores, busbars, thermistors, varistors, and resistors: What do they all have in common? They are all applications that use epoxy coating powder for insulation and protection.
Epoxy coating powder has been around since the 1950’s. Hysol (which derived its name from "High Solids" epoxies) introduced epoxy coating powder to the world with DK18-05. It was a plastic composite with world class adhesion, toughness, strength and insulation, and the market for it grew and grew.
Every epoxy coating powder company has their own version of DK18-05 in their product portfolio.
Since then DK18-05 has been copied, adapted, and further developed by a multitude of competitors. Since the 1950’s the variety of epoxy coating powders that are available is mind-blowing. Each developed and perfected for a particular application in mind.

All epoxy powder coatings are applied electrostatically to metal parts usually in a fluidized bed or with a blow gun. A fluidized bed is better for high quantities and larger components. Electrostatic spray guns are better for lower quantities of perhaps more complicated components.
In both cases the powder is given an electrostatic charge which makes it cling to earthed components which have an opposite charge. A little like how a balloon will stick to wool. This process ensures a uniform evenly applied layer: eliminating over or under coating and unnecessary texture. The part is then heated in a kiln, oven, or induction heater where the powder coating melts and finally cures.
Epoxy Coating Powder: a composite material with variable formulations and properties!The cure time, hot plate gel time, and glass temperature, as well as its final cured characteristics depend on the type of epoxy resin, hardener, fillers, and additives used to create that particular epoxy coating powder.
Important characteristics to bear in mind when selecting a coating is powder are thermal conductivity, how thin or thick it can be applied, as well as how compatible it is with your equipment, and finally the regulations of the countries where it will be made and used in the end product.
It isn\'t the 1950\'s anymore. The world has changed and so have Epoxy Coating Powders!
If we take DK18-05 as an example we can see why it’s been one of the most successful epoxy coating powders. What made it so popular? DK18-05 is perfect for tantalum capacitors that need a low cure temperature. It’s also extremely thermal shock resistant: surviving thermal cycles of -125C to +125C. This makes it highly relevant for ceramic capacitors. It also comes in a great set of colors: blue, gold, green, and black.
But the world is a changing place and the golden days of DK18-05 are over. It’s no longer acceptable to use Halogens, which Dk18-05 is full of. Recently the EU added TMA to its list of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC): making DK18-05 and its many copies no longer suitable for the European Market.
There is also a new trend in Tantalum capacitors to use polymer capacitors. Polymer capacitors need even lower cure temperatures that DK18-05 can provide, making it now irrelevant. Ceramic capacitors are getting bigger and DK18-05 is too brittle to meet the specifications for these larger Class 1 ceramic capacitors.
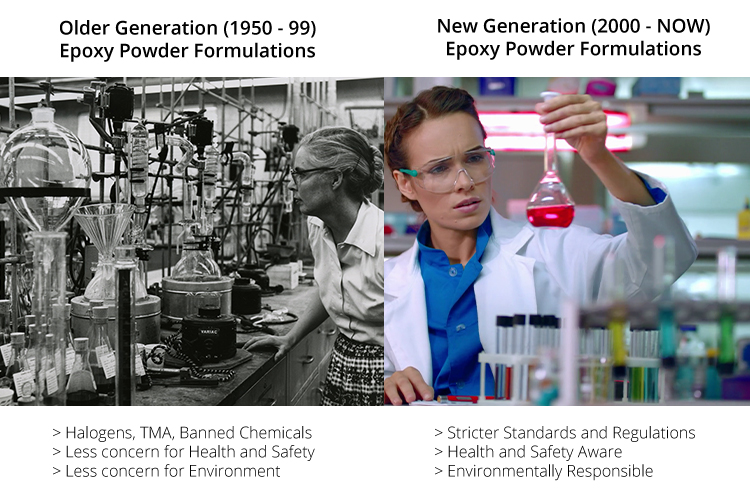
Selecting the right Epoxy Coating Powder for the world of today
So if your searching for a new generation epoxy coating powder that is ready for the requirements of today CAPLINQ is here help. Whether you’re concerned about Pick-up temperature or Glass transition temperature CAPLINQ can help inform and guide you. At CAPLINQ we have to expertise to guide you in your epoxy coating powder product choice, adjust formulations to suit you, or create altogether completely new custom epoxy coating powder formulation together with you.