Graphitized Carbon Papers
LINQCELL™ Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers and Panels are made from polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fibers formed into thin veils through a wet-laying process. These veils are bonded with a carbonizable resin and then carbonized and graphitized. Graphitization at temperatures up to 2000 °C converts the structure into one similar to graphite, resulting in superior electrical conductivity, chemical stability, and mechanical properties. The thin products (thickness < 1 mm) are graphitized carbon fiber papers, while the thicker products (thickness > 1 mm) are graphitized carbon fiber panels or plates.
Carbon Porous Transport and Gas Diffusion Layers for Fuel Cells and Electrolyzers
LINQCELL™ Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers are ideal for gas diffusion layers in fuel cells, offering excellent chemical and thermal stability with low resistance. The thicker Graphitized Carbon Fiber Panels, designed for water electrolyzers, provide improved compressibility under high-pressure conditions (up to 30 bar), ensuring optimal performance as anode porous transport layers in proton exchange membrane (PEM) and anion exchange membrane (AEM) electrolyzers. Both products are also suitable for other electrochemical devices, such as carbon dioxide electrolyzers and redox flow batteries.
LINQCELL™ Graphitized Carbon Fiber products come in sizes of 20 x 20 cm or 40 x 40 cm, with thicknesses ranging from 0.18 mm (7 mil) to 2.9 mm (114 mil) and densities from 0.5 g/cm3 to 0.8 g/cm3. These panels can be coated, inked, or loaded with anode or cathode catalysts for membrane electrode assemblies. Some thin papers are also available in roll form. We can also coat the products with microporous layers and hydrophobic PTFE layers.
Custom sizes, machined discs, and other customer-defined shapes, along with additional services such as waterproofing and surface grinding, are available. Contact us with your inquiry.
LINQCELL GDP180 | 180um Carbon Paper
- 0.18 mm - 180 um - 7 mil
- Alternative to Spectracarb 0850
- Gas diffusion layer and electrode
- 8 weeks
LINQCELL GDL1000 | 1.0mm Carbon Plate
- 1.00 mm – 1000 µm – 39 mil
- High electrical conductivity and tunable compressibility
- Porous transport and gas diffusion layers for water electrolyzers and fuel cells
- 12 weeks
LINQCELL GDP090 | 90um Carbon Paper
- Ultra-thin thickness (0.09 mm - 90 µm - 3.54 mil)
- High graphitization temperature (2000 °C)
- Optimized as gas diffusion layers in fuel cells
- 12 weeks
LINQCELL GDP250 | 250um Carbon Paper
- 0.25 mm – 120 µm – 9.84 mil
- Customizable with PTFE Coating and Available in Roll Form
- Optimized as gas diffusion layers in fuel cells
- 12 weeks
LINQCELL GDP120 | 120um Carbon Paper
- 0.12 mm - 120 µm - 4.72 mil
- High graphitization temperature with enhanced hydrophobicity from MPL coating
- Optimized as gas diffusion layers in fuel cells
- 12 weeks
LINQCELL GDP280 | 280um Carbon Paper
- 0.28 mm - 280 µm - 11.0 mil
- Enhanced hydrophobicity from MPL/PTFE and Available in Roll Form
- Optimized as gas diffusion layers in fuel cells
- 2 weeks
LINQCELL GDP340-MP | 340 um Carbon Paper
- 0.34 mm - 340 um - 13.4 mil
- Enhanced hydrophobicity from MPL/PTFE and Available in Roll Form
- Optimized as gas diffusion layers in fuel cells
- 12 weeks
LINQCELL GDP210 | 210um Non woven Carbon Paper
- 0.21mm - 210um - 8.2mil
- Non woven
- Roll form is possible.
- 8 weeks
LINQCELL GDP210-MP | 210um Carbon Paper
- 0.21mm - 210um - 8.2mil
- Treated at 1600°C
- With MPL and Hydrophobic coating
- In stock
LINQCELL GDP210-MPS | 210um Carbon Paper
- 0.21mm - 210um - 8.2mil
- Treated at 2000 °C
- With MPL and Hydrophobic coating
- 8 weeks
LINQCELL GDP240 | 240um Carbon Paper
- 0.24 mm - 240 um - 9.5 mil
- Alternative to Spectracarb 1050
- Gas difussion layer and electrode
- 8 weeks
LINQCELL GDP250-MP | 250um Carbon Paper
- 0.25mm - 250um - 9.85mil
- Enhanced hydrophobicity from MPL and PTFE coating
- Optimized as gas diffusion layers in fuel cells
- 12 weeks
LINQCELL GDP340 | 340um Non woven Carbon Paper
- 0.34mm - 340um - 13.4mil
- Non woven
- Highly flexible - Roll form
- In stock
LINQCELL GDL1500 | 1.5mm Carbon Plate
- 1.5mm - 1500um - 59mil
- Alternative to Spectracarb 6060
- Graphitized Carbon Plate
- In stock
LINQCELL GDL1500B | 1.5mm Carbon Plate
- 1.5mm - 1500um - 59mil
- Alternative to Spectracarb 6060
- Improved compressibility
- In stock
LINQCELL GDL1850 | 1.85mm Carbon Plate
- 1.85mm - 1850um - 73mil
- Alternative to 7590
- Graphitized Carbon Plate
- In stock
LINQCELL GDL1900 | 1.9mm Carbon Plate
- 1.9mm - 1900um - 74.8mil
- Alternative to 7590
- Graphitized Carbon Plate
- In stock
LINQCELL GDL2000 | 2.0mm Carbon Plate
- 2.0mm - 2000um - 78.7mil
- Ideal for electrolyzers
- Graphitized Carbon Plate
- 8 weeks
LINQCELL GDL2200 | 2.2mm Carbon Plate
- 2.2mm - 2200um - 86.6mil
- Ideal for electrolyzers
- Graphitized Carbon Plate
- In stock
LINQCELL GDL2900 | 2.9mm Carbon Plate
- 2.9mm - 2900um - 114mil
- Thickest GDL available
- Graphitized Carbon Plate
- In stock
Spectracarb 2050A | Graphitized Carbon Fiber GDL Sheets
- Spectracarb 2050A - Multiple grades
- Gas Diffusion Layer Sheets
- Discontinued Q4 2020
- No longer available
Product Selector Guide
| Product | Thickness (in) | Thickness (mm) | Basis weight (g/m2) | Through-Plane Resistance (mΩcm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LINQCELL GDP 90 | 0.0035 | 0.09 | 55 | 6 |
| LINQCELL GDP 120 | 0.005 | 0.12 | 80 | <15 |
| LINQCELL GDP 180 | 0.007 | 0.18 | 50 | 7 |
| LINQCELL GDP 210 | 0.008 | 0.21 | 51 | 10 |
| LINQCELL GDP 240 | 0.009 | 0.24 | 90 | 15 |
| LINQCELL GDP 250 | 0.0098 | 0.25 | 65 | 6 |
| LINQCELL GDP 250-MP | 0.0098 | 0.25 | 99 | 12 |
| LINQCELL GDP 280 | 0.011 | 0.28 | 100 | 10 |
| LINQCELL GDP 310 | 0.012 | 0.31 | 80 | <5 |
| LINQCELL GDP 340 | 0.013 | 0.34 | 90 | 10 |
| LINQCELL GDP 340-MP | 0.013 | 0.34 | 125 | <10 |
| Product | Thickness | Thickness (mm) | Density (g/cm3) | Basis weight (g/m2) | Through-Plane Resistance (mΩcm2) | Through-Plane Resistivity (mΩcm) | Voltage Loss (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LINQCELL GDL 1000 | 0.039" | 1.0 | - | 580 | 11.11 | 109.9 | 25.2 |
| LINQCELL GDL 1500 | 0.059" | 1.5 | 0.60 | 858 | 13.32 | 90.6 | 24.3 |
| LINQCELL GDL 1500B | 0.059" | 1.5 | 0.60 | 670 | 21 | 140 | 39 |
| LINQCELL GDL 1850 | 0.072" | 1.85 | 0.85 | 1562 | 13.18 | 70.5 | 25.5 |
| LINQCELL GDL 2000 | 0.079" | 2.0 | 0.65 | 1302 | 10.7 | 51.7 | 29.8 |
| LINQCELL GDL 2200 | 0.086" | 2.2 | 0.6 | 1550 | 17 | 110 | 35 |
| LINQCELL GDL 2900 | 0.011" | 2.9 | 0.60 | 1734 | 24.57 | 87.7 | 27.6 |
All values are indicative and subject to tolerance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently asked questions about Graphitized Carbon Fiber Panels
What is Carbon GDL Wet proofing?
A very common technique that is applied on Carbon GDLs is Wet proofing. Wet proofing the panels improves the water transport, increasing the total power generation. Additionally, wet proofing can stop GDLs from shedding carbon particles which helps with GDL handling.
Wet proofing Gas diffusion layers can be achieved by teflon dispersion or by applying hydrophobic treatments.
What is the GDL role in the assembly?
Gas diffusion layers structurally help the stack withstand the extension caused by the water absorbency. In addition to that, they aid with heat transfer, electrical surface conductivity, and the removal of excess water from the electrodes that is produced by redox reactions.
Finally, and most importantly, they clear the path for the Fuel and the Oxidizing agent towards the catalyst layers.
Can I just get an MPL treatment?
The carbon paper are not able to have a Microporous layer without PTFE. If you apply it on carbon paper without PTFE coating, the MPL will penetrate the back side of the carbon paper..
Do you have carbon papers in roll form?
Yes. Not every grade is flexible enough to be rolled without breaking or cracking but we do have sub-340um carbon papers that come in roll form. Higher than that it is usually difficult to roll without breaking so we can only provide standard 20 x 20cm, 40 x 40cm sheets, or custom dimensions if the quantities allow. Die cutting is also possible.
Do Carbon papers contain PFAS?
Since there are some talks about a PFAS ban in the European Union, starting from 2025, it is important to clarify where PFAS are present. Generally pure carbon paper doesn't contain any PFAS. Microporous layers and PTFE treatments are by nature susceptible to them. To outline:
- Carbon papers without any special treatments do not contain any PFAS
- Carbon papers with a Microporous layer contain PFAS
- Carbon papers with a PTFE treatment contain PFAS
Read our blog article that explains more about where PFASs are used in Graphitized Carbon Paper.
What's the most common thickness for Carbon Paper?
Generally, thin (<1mm) sheets are used for fuel cell GDLs, while thicker panels (1.5 - 3.0 mm) are used for electrolyzers. While CAPLINQ can custom-make specific thicknesses, these are what our customer most often ask us for.
Read our blog article that explains the most common thicknesses in GDLs for more info.
What type of binder resin is used for Carbon GDLs?
Carbon GDLs like graphitized carbon fiber papers use phenolic resin as a binder. It’s a non-PFAS, thermosetting resin that holds the fibers together during production.
After heat treatment, most of the resin is converted into carbon, so the final product is mainly carbon with very little binder left. No PFAS-based materials are used in the process.
Does CAPLINQ offer Spectracarb materials?
No. CAPLINQ no longer offers Spectracarb materials, but instead produces its own products under our LINQCELL brand name. Read here the history of CAPLINQ , Spectracarb, and LINQCELL.
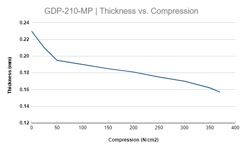
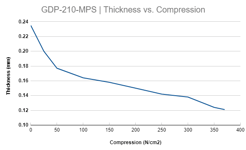
Do you test radius, compression and thickness?
Radius is being tested with a standard PHOENIX tool. Compression is tested at 2 MPa. We conduct a single point stress test and also a 5 point (sides and center) compression test, to ensure that compression is evenly distributed.
Thickness measurements depend on the format. Rolls are being measured every 5 meters at a single point. Sheets are measured on a 5 point basis(center and four sides). The load is always mentioned in the specification sheet.
What is the difference between 1600 and 2000°C graphitization?
Other than being a bit more expensive, due to the much higher energy cost, the 2000°C graphitization can generally achieve better electrical properties. This can come to the expense of other properties like compressibility or brittleness. It is always a balancing act to understand and decide what best suits your application. Also highly graphitized papers are a bit grayer.
We are currently testing a large sheet, high graphitization oven so we will be happy to take any requests for carbon papers that need to be graphitized at those temperatures.
Learn More
Graphitized Carbon Fiber Paper and Panel Manufacturing
Graphitized carbon fiber papers and plates begin as a thin fiber mat or veil, created through a wet-laying process similar to traditional papermaking. The mat is then impregnated with a thermosetting resin, which serves as a binder, bonding the fibers and providing strength and the desired thickness. Depending on the required thickness, multiple layers of the veil are bonded together and undergo thermal pressing. The material is then carbonized, converting the resin into carbon. Finally, the carbonized product undergoes graphitization at temperatures ≥ 1600 °C.
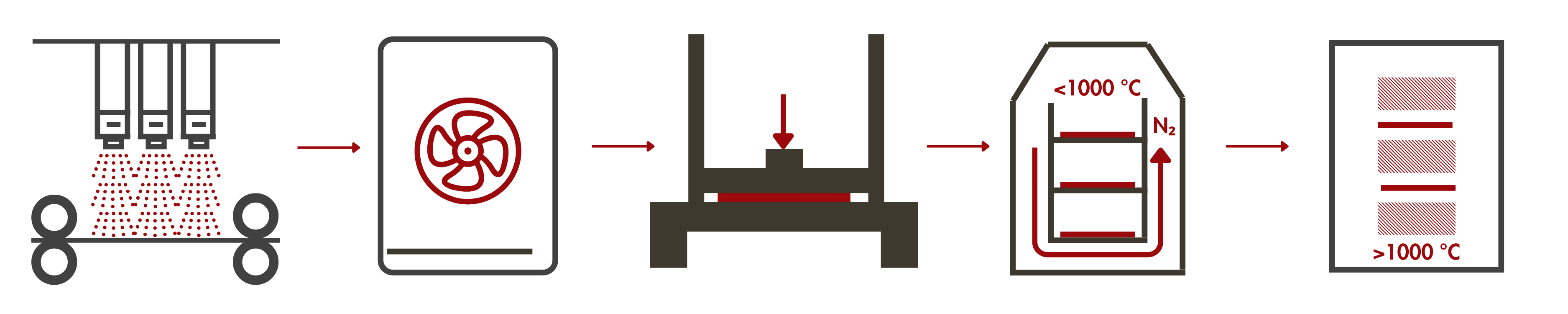
For products requiring additional microporous layers (MPL) and PTFE coating, the graphitized part is fed into a coating machine, where it is coated with the MPL or PTFE dispersion. After coating, the material is dried in an oven to evaporate the solvent.
Read more about the LINQCELL Graphitized Carbon Fiber Paper and Plate Manufacturing Process.
Hydrophobization (PTFE Treatment) in Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers and Panels
Graphitized carbon paper and plate after manufacturing is somewhat hydrophobic. Water contact angle of graphitized carbon papers that are untreated are usually around 100 °. For some applications, like in fuel cells, more hydrophobic character is needed as water management is critical for fuel cell stacks. For this reason, a hydrophobic, polymer coating is applied to the graphitized carbon fiber product.


Comparison of the water contact angle on graphitized carbon paper before and after hydrophobic PTFE treatment.
The untreated carbon paper (left) has a contact angle of 114°, indicating moderate hydrophobicity. After PTFE treatment (right), the contact angle increases to 139°, enhancing water repellency. This improvement helps prevent water accumulation in fuel cells and electrochemical applications, optimizing gas diffusion and overall performance.
Microporous Layers in Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers and Panels
The polymer coating on carbon paper and panels makes them more hydrophobic, which helps with water management. However, this comes at a cost. It reduces both porosity and electrical conductivity:
❌ The polymer coating fills some of the pores in the carbon paper or panel, which reduces the overall porosity.
❌ At the same time, most polymer coatings are electrically insulating. When the coating covers the carbon fibers, it disrupts the conductive pathways, increasing electrical resistance and lowering the overall conductivity of the material.
To balance this, a thin microporous layer (MPL) is added on top of the hydrophobic coating. The MPL is made of carbon powder mixed with a polymer and has very small pores, typically around 100 nm in size (ranging from 50 nm to a few micrometers). Because of its small pores and hydrophobic nature, the MPL prevents liquid water from clogging the material, which is especially useful in fuel cell stacks. Additionally, the carbon in the MPL improves electrical conductivity and lowers contact resistance between the gas diffusion layer (GDL) and the catalyst layer. This helps manage water buildup without negatively affecting the GDL’s conductivity.
It has a textured, fibrous surface with a metallic gray appearance, showing a visible fiber pattern. The surface looks slightly rough and uneven, indicating its raw carbon fiber structure.
This paper has a smooth, matte black surface. The microporous layer gives it a dense, coated look, reducing the visibility of underlying fibers.


LINQCELL Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers with MPL and PTFE Treatment
| Product | Thickness [mm] | Basis weight [g/m²] | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP120 | 0.12 | 80 | Available in sheet form only |
| GDP210 | 0.21 | 50 | Available in sheet and roll form, can come with optional 10 wt% PTFE coating |
| GDP210-MP | 0.21 | 85 | Available in sheet form only |
| GDP210-MPS | 0.21 | 85 | Available in sheet form only, produced at 2000°C |
| GDP240 | 0.24 | 90 | Available in sheet and roll form |
| GDP250 | 0.25 | 65 | Available in sheet and roll form, can come with optional 10 wt% PTFE coating |
| GDP310 | 0.310 | 80 | Available in sheet and roll form, can come with optional 10 wt% PTFE coating |
| GDP340 | 0.34 | 125 | Available in sheet and roll form |
Note: The standard width of a roll of graphitized carbon fiber paper with MPL and PTFE coating is 40 cm.
Is it possible to coat thick (thickness > 340 um) with MPL and PTFE coating?
Yes, it is possible, though more challenging and cost-intensive compared to thinner materials. While roll-to-roll processing is typically more efficient for thinner sheets (<340 µm), we have successfully coated thicker materials as well. Although less commonly requested, CAPLINQ has experience with this and continues to optimize the process for improved efficiency.
What does Graphitization do?
Graphitization is a heat treatment of carbon-based materials typically above 1000 °C under controlled conditions. It is similar to carbonization, but carbonization occurs at lower temperatures, between 600 °C and 1000 °C. During carbonization, volatile materials like water, gases, and light organic compounds are removed from carbon fiber papers and panels, resulting in a carbon-rich material. After carbonization, the carbon fiber paper generally retains its original structure and properties.
The story is different during graphitization. In addition to being carbon-rich, the material undergoes structural changes as the high temperature provides the energy needed for the carbon atoms to rearrange into a more ordered, crystalline structure similar to that of graphite. This transformation enhances the material properties, such as electrical conductivity, mechanical properties, and thermal stability.
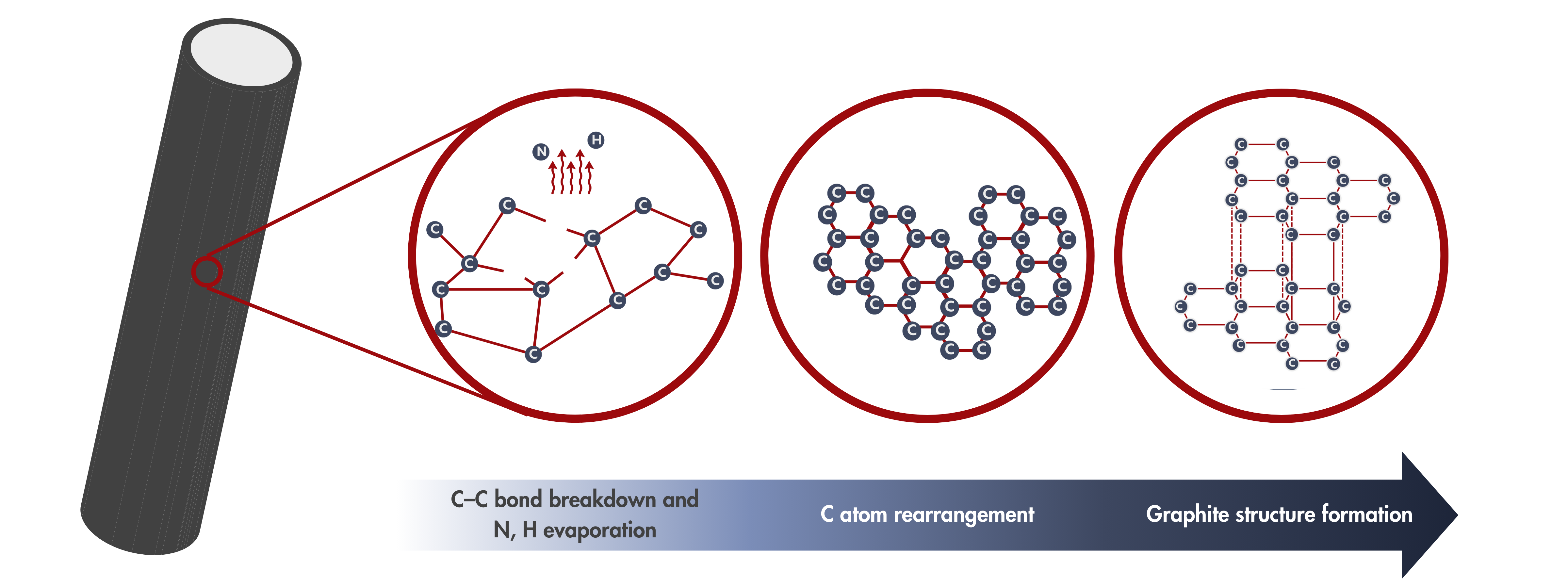
Structural Changes after Graphitization
✅ Increased Crystallinity
Carbon atoms form a hexagonal structure.
✅ Graphite-like Structure
Parallel stacking of hexagonal carbon rings, resembling graphite.
✅ Higher Carbon Purity
Loss of N, H, and other volatiles
✅ Defect Reduction
Fewer disordered or amorphous regions as sp² bonding increases.
What happens at increasing graphitization temperatures?
Our LINQCELLTM graphitized carbon fiber papers and panels have been graphitized at 1600 and 2000 °C. As a general rule of thumb, higher graphitization temperatures yield higher degree of graphitization. In other words, carbon-based material becomes more graphite-like with increasing graphitization temperature. From this, materials graphitized at higher temperatures are expected to exhibit more (improved) graphite-like properties. That is, at increasing graphitization temperatures, higher Young’s modulus (lower compressibility), higher electrical and thermal conductivities, and better chemical stabilities are to be expected.
| Higher degree of graphitization | As the graphitization temperature increases, carbon atoms move more freely, creating a more ordered, graphitic structure. This improves the material's graphitization level, resulting in enhanced performance and better efficiency in various applications. | Lower compressibility | Higher graphitization temperatures also increase the Young’s modulus of carbon materials, making them stiffer and more resistant to deformation. A sheet graphitized at a higher temperature will be less compressible than one treated at a lower temperature, assuming the same porosity. |
| Higher electrical and thermal conductivity | As the graphitization temperature increases, both electrical and thermal conductivity of carbon materials improve. Higher graphitization temperatures align carbon layers, allowing electrons to move more freely, improving electrical conductivity. The more ordered structure also allows heat to travel more efficiently, significantly improving thermal conductivity. | Improved chemical stability | As the graphitization temperature increases, the chemical stability of carbon materials also improves. Higher temperatures promote a more ordered structure, enhancing resistance to oxidation by making the carbon layers more tightly bonded. This reduces reactivity, as the material becomes less likely to interact with external chemicals. Additionally, thermal behavior stabilizes, |
Cost Drivers for LINQCELL Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers and Panels
Graphitization enhances the electrical, thermal, mechanical, and electrochemical properties of carbon fiber products, but it comes with a hefty price tag. Furnaces running at 2000 °C for hours are as expensive and energy-intensive as it sounds. Optimizing carbon paper production schedules can procure both financial and environmental benefits.
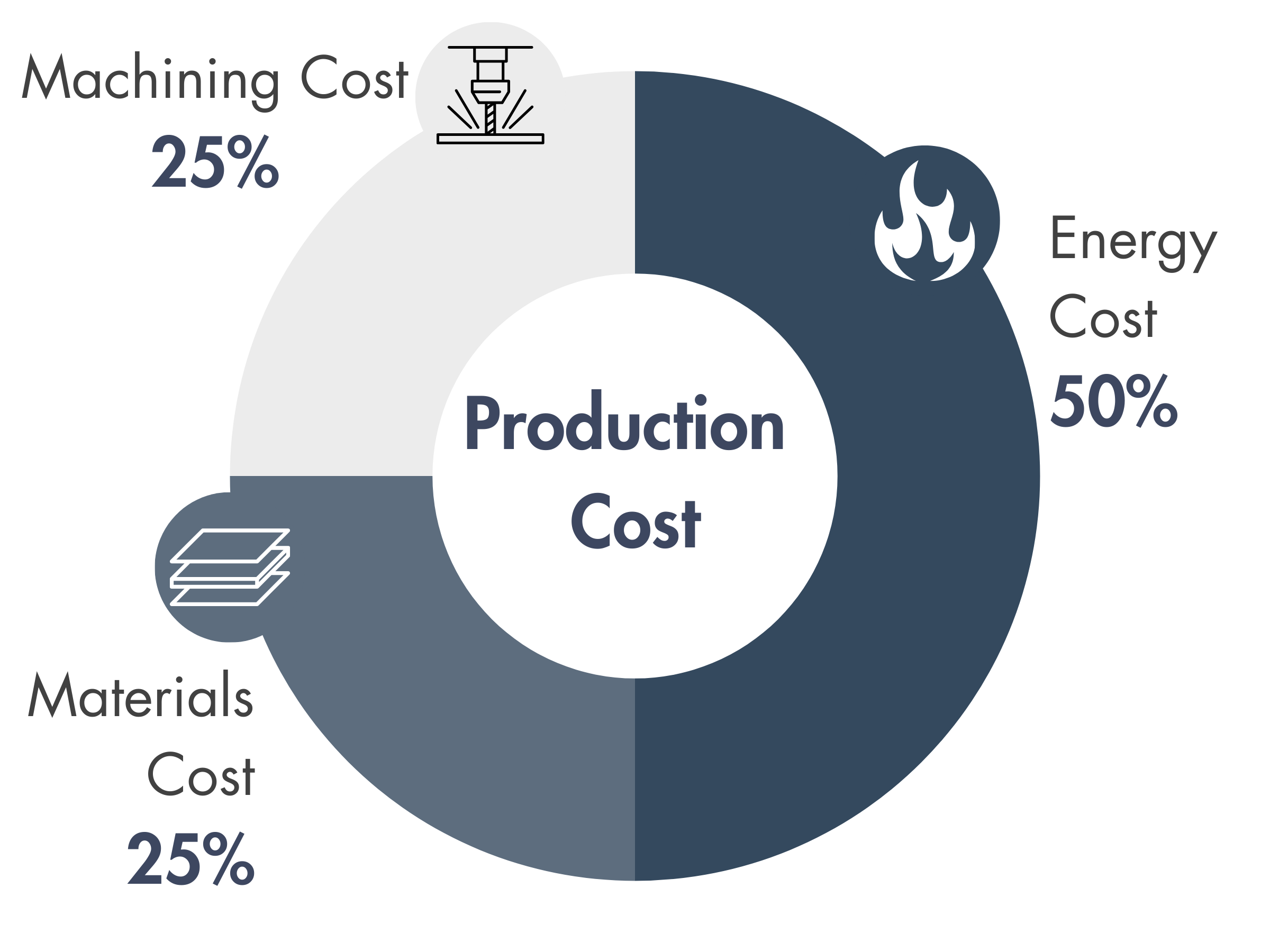
Strategies to Improve Production Costs of Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers
Optimize Furnace Runs
Furnace runs are expensive, contributing to over 50% of operating costs. Running full furnace loads (instead of small batches) minimizes cost per sheet.
Reduce Machining Costs
Using maximum sheet sizes directly from the furnace can cut costs by up to 25%. Relaxing dimensional tolerances reduces material waste and improves yield.
Optimize Material Usage & Sizing
Avoid cutting odd shapes; sheets are rectangular by default. Designing around furnace dimensions (50 cm× 50 cm) maximizes efficiency. Minimizing unnecessary cutting lowers costs and reduces environmental impact.
Read more about the cost drivers and reduction strategies of graphitized carbon fiber papers and panels.
Testing Methods for Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers and Panels
Thickness Measurement
Graphitized Carbon Fiber Paper: It typically ranges from 100 µm to 500 µm, depending on the specific use case. These thin papers are often used as gas diffusion layers (GDLs) in fuel cells. The thickness of the paper affects the transport properties, such as gas diffusion and conductivity.
Graphitized Carbon Fiber Panels/Plates: These can vary more widely, often between 1 mm to several millimeters in thickness, depending on their intended use, structural requirements, and the desired mechanical properties. In water electrolyzers, thicker panels may be used to handle higher mechanical stresses or improve thermal conductivity.
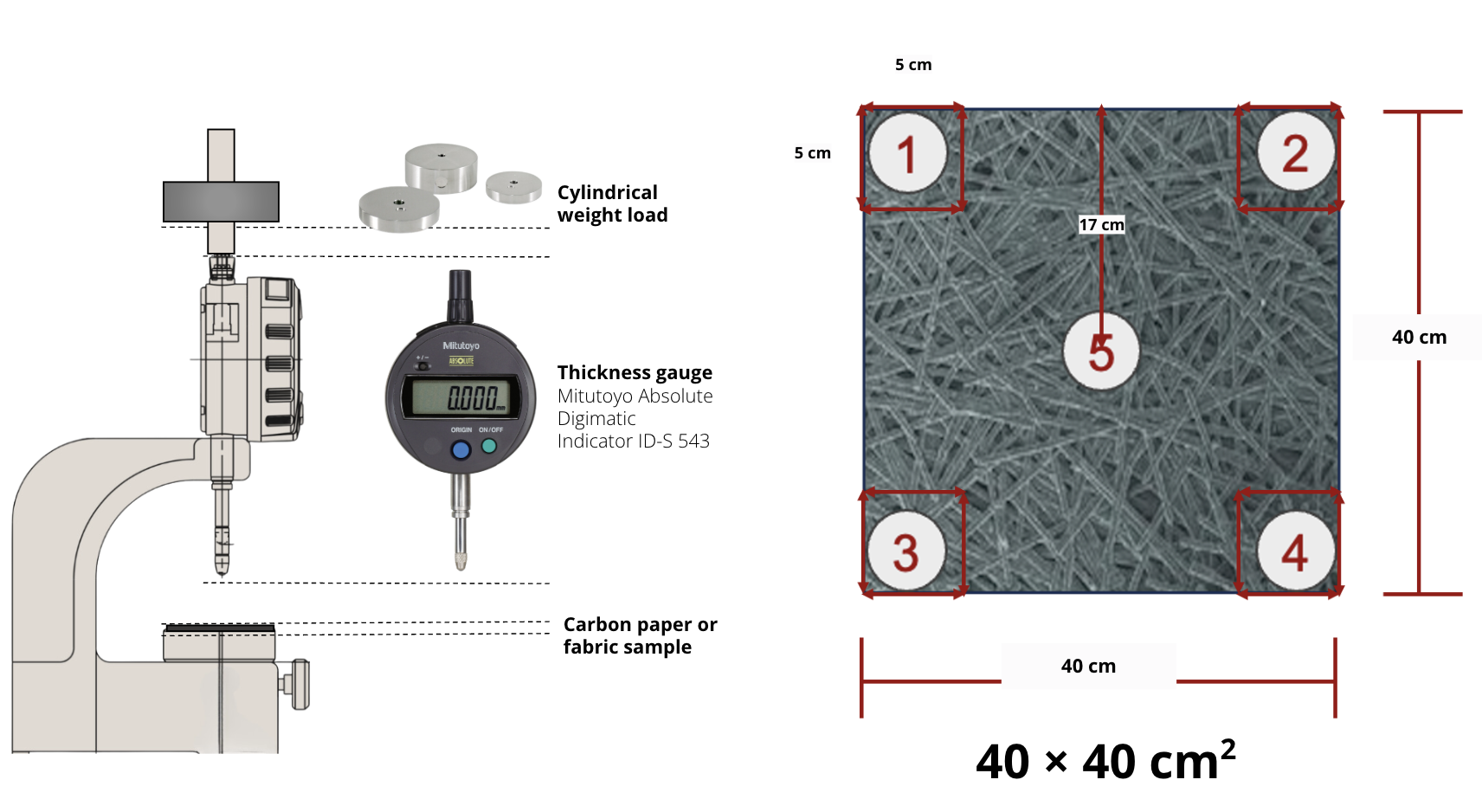
Thickness Gauge: Mitutoyo Absolute Digimatic Indicator ID-S 543
Test Standard: ASTM D645 (Standard Test Method for Thickness of Paper and Paperboard)
Weight Load: 50 kPa according to ASTM D645 but can be chosen according to specifications.
Note: The thickness of our products is reported at 50 kPa, per the standard, unless otherwise specified.
Parallelism
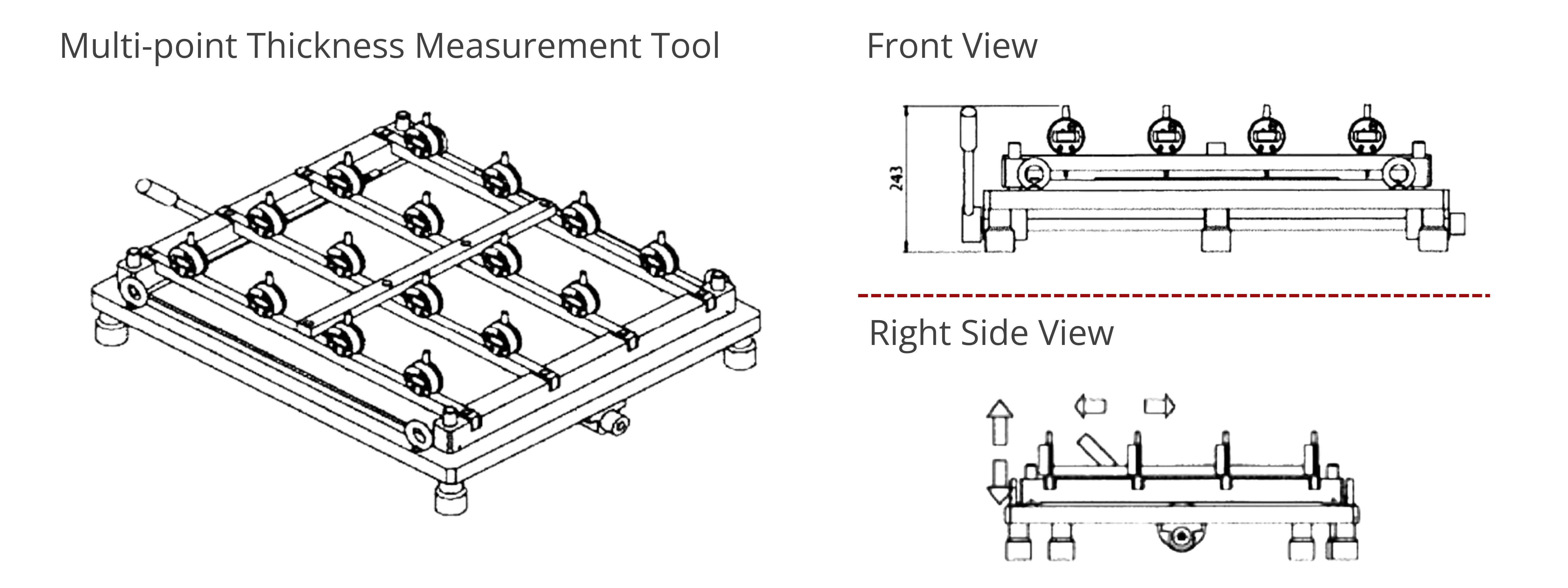
Parallelism Measurement Equipment
- Precision steel base (600 × 600 mm2) and testing parts
- Electronic meter
- Statistical software, 4-pin signal output box, and foot switch
- Working table (maximum load = 1000 kg)
Parallelism Measurement Procedure
- Fix the sample on the flat plate.
- Measure straight by moving either the sample or the height gauges. The number of measurement points will vary depending on the sample dimensions. For example, a 54 × 54 cm2 carbon sheet has 16 measurement points.
- Parallelism is the difference between the highest and lowest measurements. For example, if the thickest point on a plate measures 2.307 µm and the thinnest point measures 2.302 µm, the parallelism is within 0.005 µm. The plate is reported to be parallel within 0.005 µm.
Electrical Resistance Measurement and Resistivity Calculation
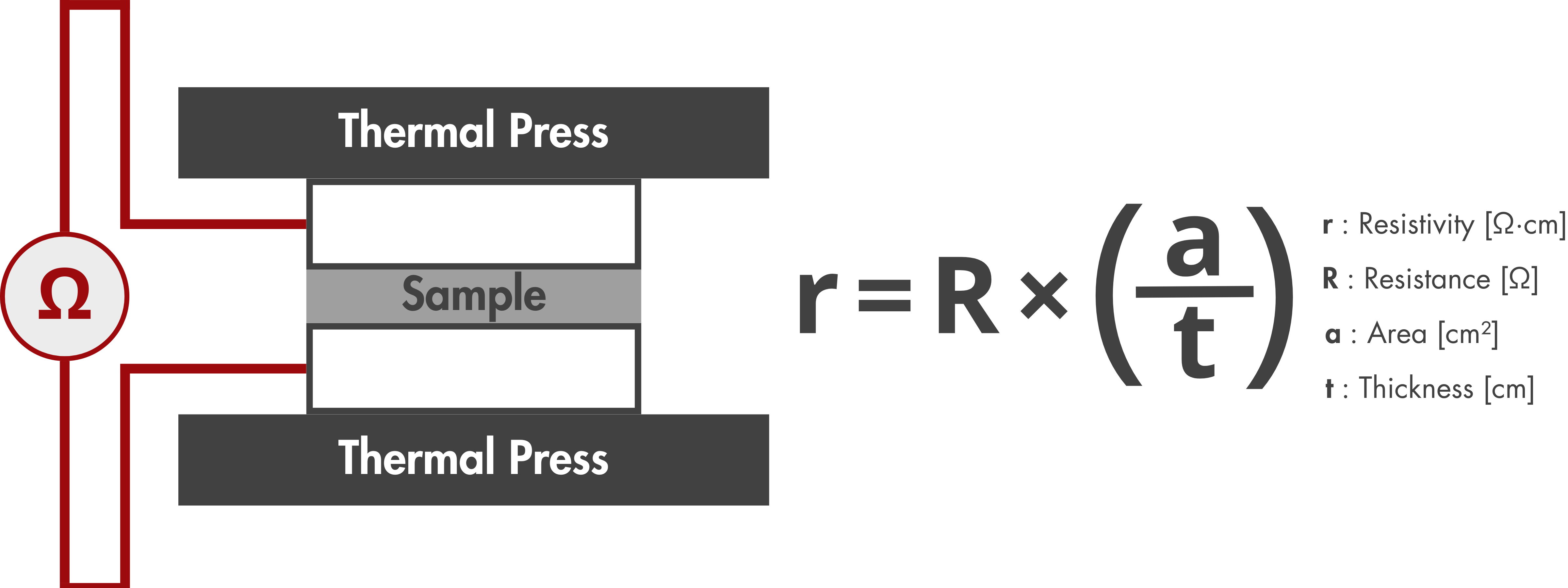
Test Standard: ASTM C611-98
Pressure: 200 psi (14.1 kgf/cm2)
Electrical Resistivity Measurement Procedure
- Prepare a circular sample with a diameter of 5cm.
- Set up the TSURUGA 3566 battery internal resistance AC tester according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Calibrate the tester to ensure accurate resistance measurements.
- Place the prepared circular testing sample in the heat press.
- Apply pressure to the sample using the hydraulic cylinder (area = 9.7 cm2).
- Using the calibrated TSURUGA 3566 AC tester, measure the resistance (R) of the sample under the specified test conditions.
- Calculate the resistivity of the sample.
Voltage Loss in Graphitized Carbon Fiber Paper, Plates, or Panels
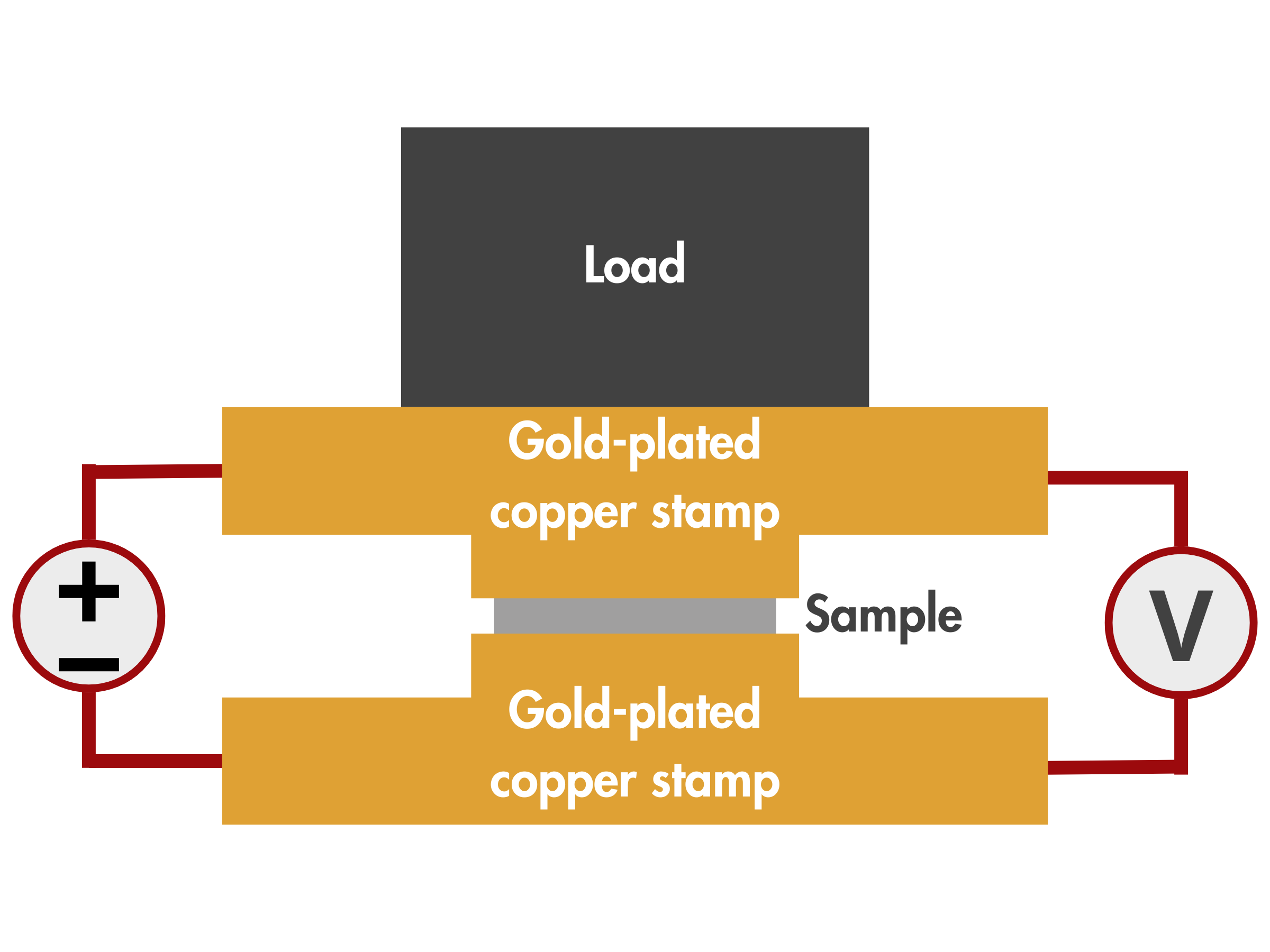
Pressure: 20 N/cm2
Constant current: 500 mA/cm2
Voltage Loss Measurement Procedure
- Ensure that the gold-plated copper stamp and the gold-plated base plate are clean and free from contaminants that could affect electrical contact.
- Set up the voltage measurement instrument (digital multimeter) and connect it to the electrical contact points.
- Position the sample between the gold-plated copper stamp and the gold-plated base plate.
- Apply the pressure and constant current.
- Measure the voltage drop across the contact points using the voltage measurement instrument.
Read more about CAPLINQ's test methods and quality control measures for graphitized carbon fiber paper and panels/plates.
Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers as Gas Diffusion Layers in Fuel Cells
Thin (thickness < 1 mm) graphitized carbon fiber papers effectively function as both the anode and cathode gas diffusion layers (GDLs) in fuel cells. Gas diffusion layers (GDLs) are key components in fuel cells and electrolyzers, performing several key functions. They ensure efficient diffusion of feed gasses to the catalyst layer, which is essential for continuous electrochemical reactions and electricity generation. The porous structure of GDLs optimizes gas permeability, while their conductive properties facilitate electron transport.
Functions of Graphitized Carbon Fiber Papers in Fuel Cells
- Hydrogen and Oxygen Delivery: Facilitates the transport of input hydrogen and oxygen gas to the catalyst layer for the electrochemical reaction.
- Electron Conduction: Serves as an electrically conductive pathway, efficiently transferring electrons from the anode to the external circuit.
- Water Management: Assists in removing produced water while maintaining a balance to prevent membrane dehydration or flooding.
- Heat Dissipation: Aids in thermal management by transferring excess heat to other components, such as the bipolar plate.
How Graphitized Carbon Papers Meet the Requirements for Gas Diffusion Layers in PEM Fuel Cells
| Function | Related Properties | Key Considerations | Graphitized Carbon Paper Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Properties | Thickness, Density/Area Weight, Compressibility | Thin GDL improves mass and heat transfer and reduces resistance. | ✅ Graphitized carbon papers can be manufactured with optimized thickness and density, ensuring lower resistance and enhanced mass and heat transfer properties. |
| MEA Assembly | Stiffness/Flexibility, Tensile Strength, Flexural Modulus | Mechanical strength with appropriate rigidity and flexibility helps the stack withstand expansion due to water absorbency and provides stability under long-term operating conditions. | ✅ Graphitized carbon papers have good mechanical strength, balancing rigidity and flexibility to handle the stresses in fuel cells. The carbonizable resin in them affects porosity, and by optimizing resin content and the carbonization process, we can improve tensile strength and stability over time. |
| Transport Process | Reactant Gas Transport Porosity, Pore Size Distribution, Gas Permeability | Gas permeability is essential for gas transfer. High porosity increases permeability. Proper pore size distribution ensures uniform gas distribution on electrode surfaces. | ✅ Graphitized carbon papers typically offer high porosity (>60%) and controlled pore size distribution, promoting effective gas permeability and ensuring uniform gas flow through the electrode. |
| Water Transport Hydrophobicity (Surface Energy/Contact Angle), Pore Size Distribution | Hydrophobicity prevents excessive moisture from blocking pores and reducing gas permeability. Achieved by adding PTFE layers and using carbon black or graphite in the MPL. | ✅ Graphitized carbon papers often require additional hydrophobic treatments, such as PTFE coating, to achieve the desired water management. The hydrophobicity helps prevent water from blocking pores and compromising gas permeability. | |
| Electron Transport Through-Plane Resistance, Compressibility, Surface Roughness | Compressive stress reduces GDL thickness, increasing electrical conductivity and permeability. | ✅ Graphitized carbon papers offer excellent electron conductivity due to their high degree of graphitization. | |
| Heat Transport Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity is required for heat dissipation. | ✅ Graphitized carbon papers have good thermal conductivity, aiding in the efficient removal of heat during fuel cell operation, ensuring temperature uniformity and preventing overheating. | |
| Stability | Purity, High Corrosion Resistance, Surface Stability, Heat Resistance | Ensures long-term durability and performance. | ✅ Graphitized carbon papers exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and surface stability, particularly in acidic environments. |
Read more about the properties of graphitized carbon fiber papers related to their application as gas diffusion layers in fuel cells.
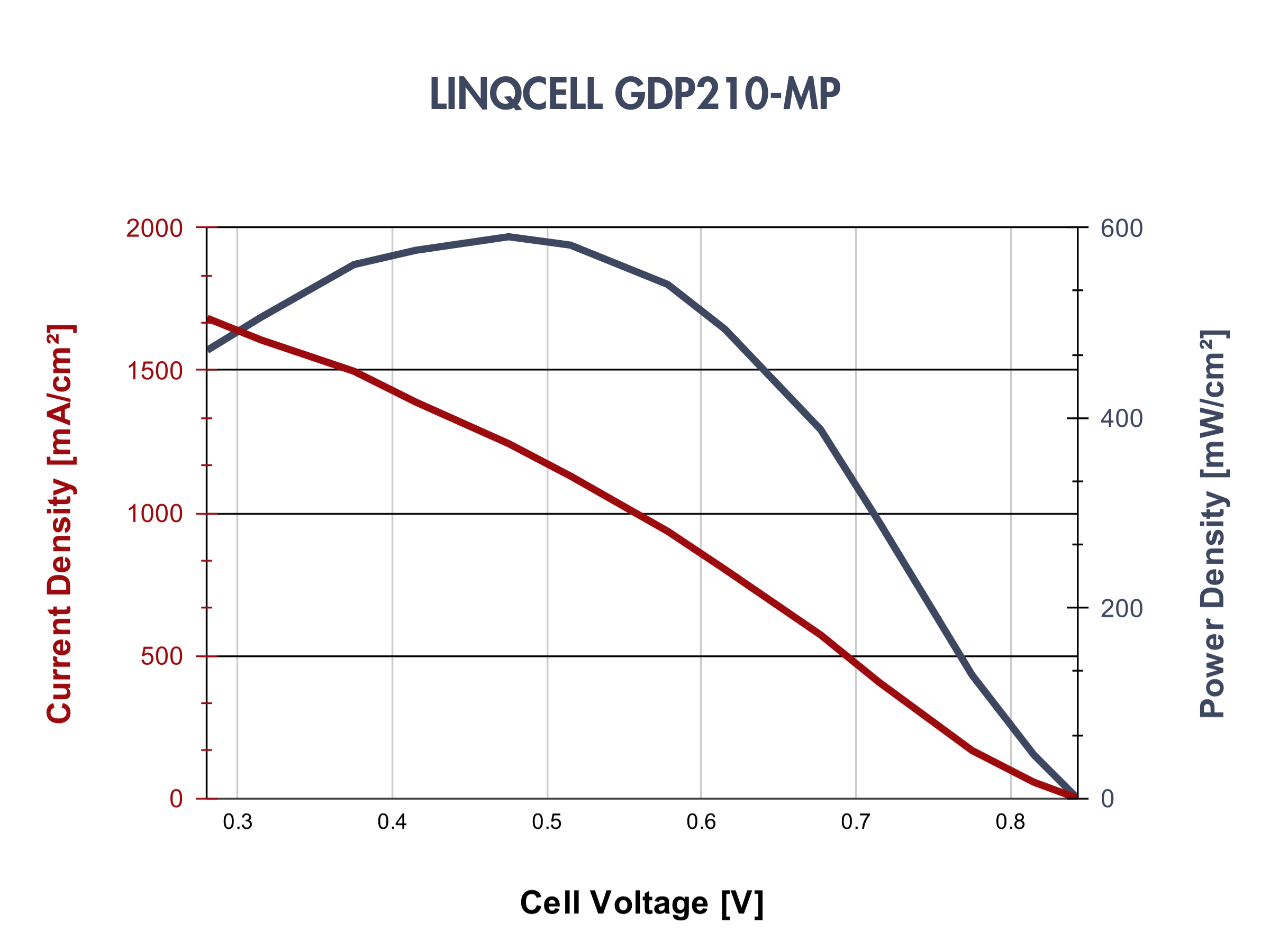
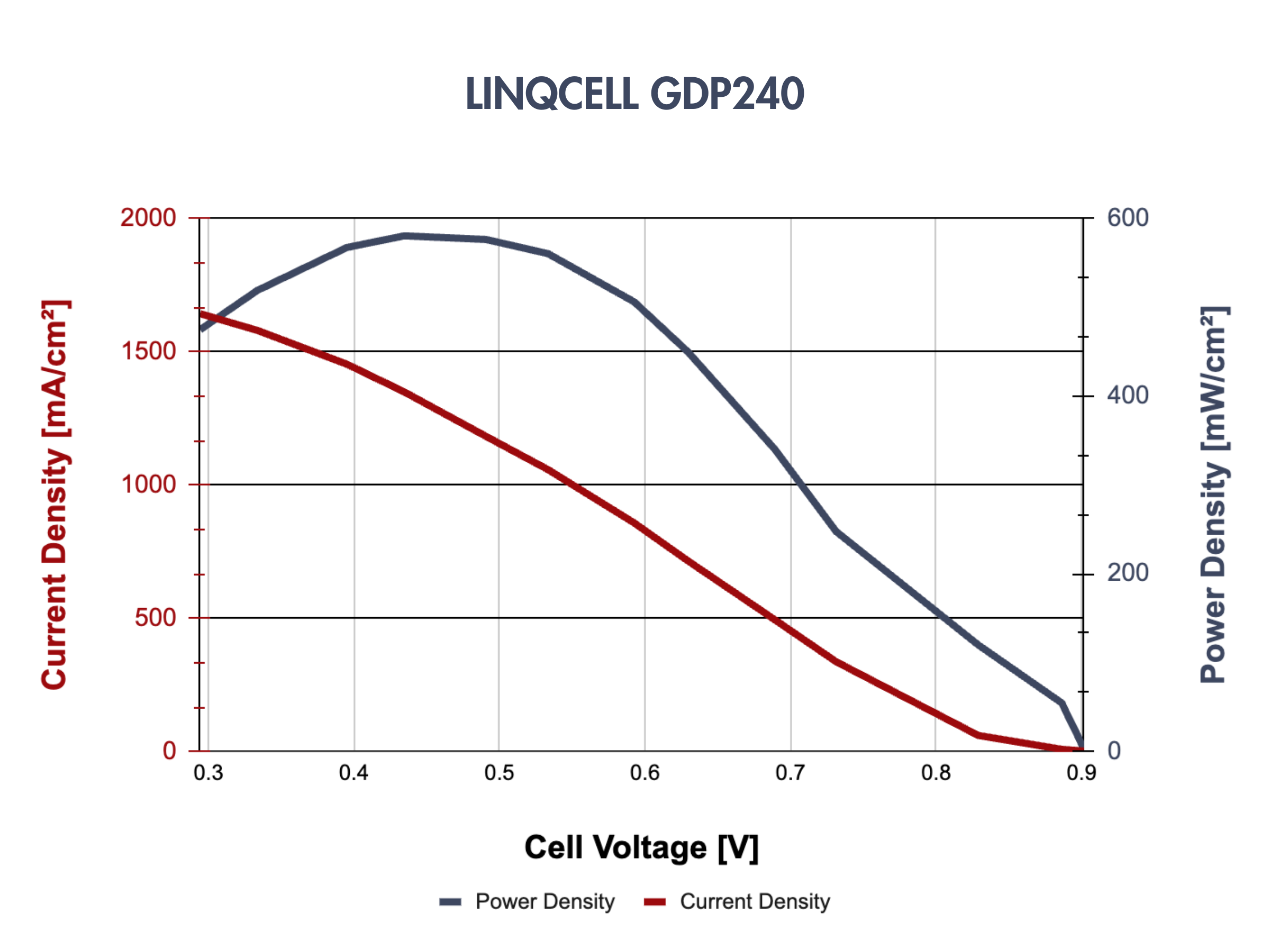
LINQCELLTM Graphitized Carbon Fiber Paper Performance in Fuel Cells
Representative polarization curves for some LINQCELLTM Graphitized Carbon Fiber Paper Products
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Reaction Area | 300 cm² |
| Fuel Supply Method | Constant Flow |
| Relative Humidity | 100% |
| Test Temperature | 60 °C |
| Anode Flow Rate | 1.5 splm (H2) |
| Cathode Flow Rate | 2.5 splm (Air) |
| Operating Pressure | 10 psi |
| Clamping Pressure | 10 psi |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Active Area | 25 cm2 |
| Anode/Cathode Stoichiometric Ratio | 2.5/1.5 |
| Anode Humidification Temperature | 65 °C |
| Cathode Humidification Temperature | 36 °C |
| Cell Temperature | 60 °C |
| Torque | 25 kgf⋅cm |
Graphitized Carbon Fiber Panels as Cathode Porous Transport Layers in Water Electrolyzers
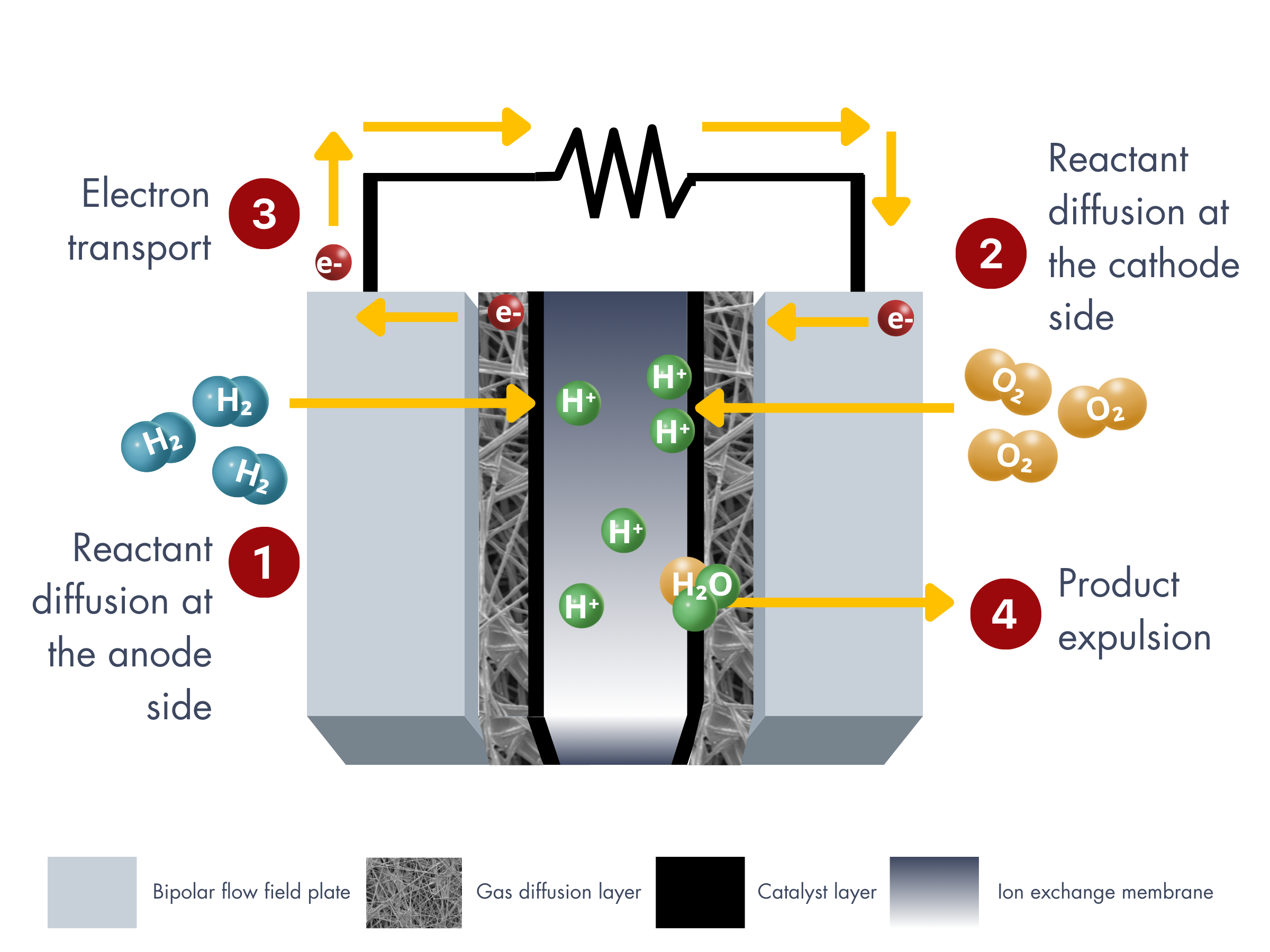
Porous transport layers (PTLs) or liquid/gas diffusion layers are important components in water electrolyzer stacks. s shown in the figure below, PTLs facilitate the delivery of liquid reactants from the flow plate channels to the catalyst layer (①) while also allowing for the efficient removal of gaseous products, oxygen at the anode and hydrogen at the cathode (②). This process creates a countercurrent two-phase flow through the PTL. If the product gasses are not effectively removed from the system, H2 and O2 can clog the pores of the PTL. This blockage not only decreases the availability of liquid reactants for the reaction but also leads to membrane dehydration, which negatively impacts its ionic conductivity.
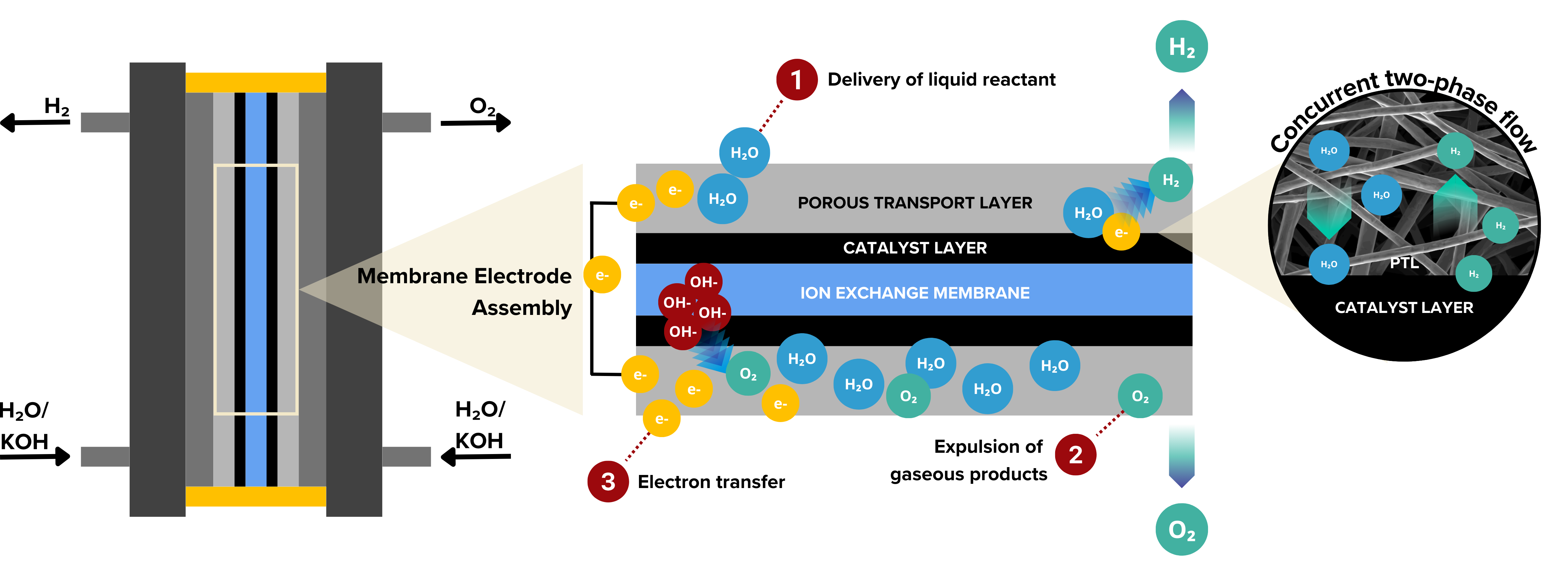
Gas diffusion layers vs. Porous Transport Layers? Gas diffusion layers and porous transport layers are similar terms but with distinct contexts. PTLs is a broader term, commonly used in water electrolyzers, to describe materials that facilitate reactant and product transport. GDLs, on the other hand, are commonly used fuel cells and are designed to manage gas diffusion and electron conduction. While both terms involve mass transport, GDLs are specialized for fuel cells, while PTLs have a more general application.
As mentioned above, graphitized carbon fiber papers are used at the anode and cathode of fuel cells. Is it the same for graphitized carbon fiber panels or plates in water electrolyzers? No. The placement of the PTL is important because the anode and cathode sides of water electrolyzers operate under different conditions and environments. Each side experiences distinct chemical reactions that do not only affect the performance but also the stability of the PTL.
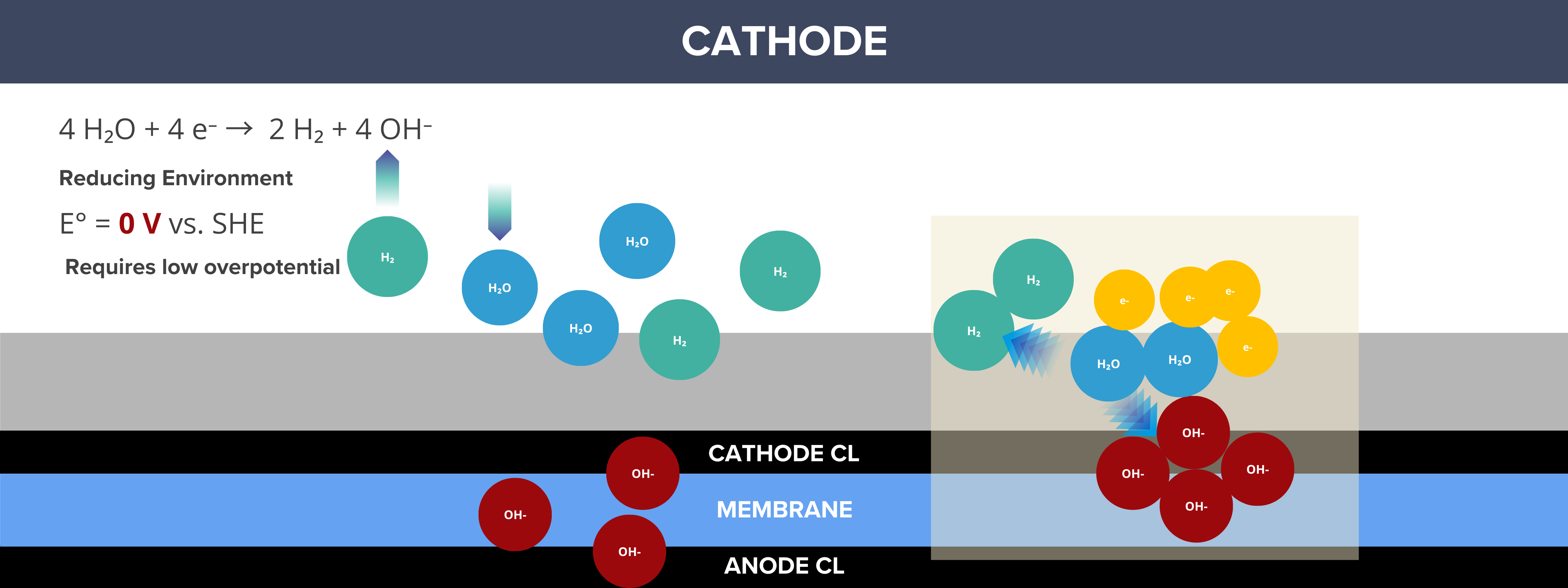
At which side of water electrolyzers are graphitized carbon fiber panels used?
As mentioned above, graphitized carbon fiber papers are used at the anode and cathode of fuel cells. Is it the same for graphitized carbon fiber panels or plates in water electrolyzers?
By convention, the cathode is the site where reduction reactions occur, and in water electrolyzers, this is where the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) takes place, generating H₂ gas. As a result, the cathode side operates under a reducing environment, which minimizes the likelihood of oxidation reactions. Materials on the cathode side are less prone to corrosion because they are not exposed to harsh oxidative conditions. Since oxidation is not a major concern, carbon materials are considered as the benchmark PTL for the cathode side.
Key Features and Benefits of LINQCELLTM Graphitized Carbon Fiber Panels as Cathode PTLs of Water Electrolyzers
Customizable Compressibility of LINQCELLTM Graphitized Carbon Fiber Panels for Water Electrolyzers
CAPLINQ can fine-tune compressibility to achieve the perfect balance of electrical conductivity, gas permeability, and mechanical strength.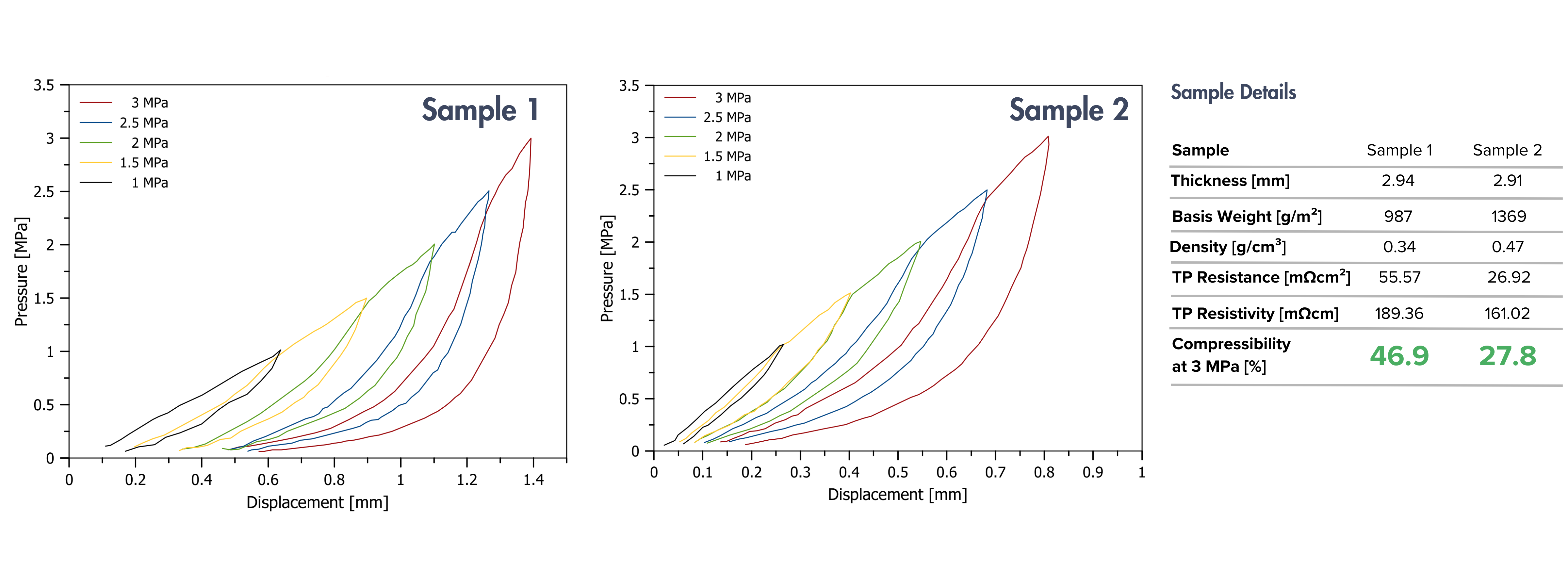
Presentations
LINQCELL Graphitized Carbon Fiber Paper and Panel Production Process Control
This presentation provides an overview of the production process control for LINQCELL Graphitized Carbon Fiber Paper and Plate, highlighting key parameters, quality control measures, and process optimizations.
Cost Drivers for the Manufacturing of LINQCELL GDL
This presentation will cover the key cost drivers in manufacturing LINQCELL GDL, including raw materials, processing techniques, energy costs, and quality control. It will also highlight how these factors impact overall cost efficiency and product performance.
LINQCELL Porous Transport and Gas Diffusion Layers for Water Electrolyzers and Fuel Cells
This presentation showcases CAPLINQ's offerings for porous transport layers in electrolyzers and gas diffusion layers in fuel cells, including graphitized carbon fiber papers and plates, as well as metal PTLs such as titanium, nickel, and stainless steel.
Related Blogs

CAPLINQ Develops Sustainable PFAS-free, Hydrophobic Coatings for Carbon Gas Diffusion Layers
This blog discusses CAPLINQ’s development of sustainable, PFAS-free hydrophobic coatings for carbon gas diffusion layers (GDLs).

What are the Differences between Carbon Cloth, Paper, and Felt?
This blog explores the key differences between carbon cloth, paper, and felt, focusing on the differences between their manufacturing processes and resulting properties.

Benchmark Porous Transport Layers for Water Electrolyzers
This blog explores benchmark porous transport layer (PTL) materials, including carbon, titanium, and nickel, for water electrolyzers. It also discusses the role of thick graphitized carbon fiber plates or panels as cathode PTLs, emphasizing their structural stability and performance in PEM and AEM water electrolyzers.
Product Catalogue
LINQCELLᵀᴹ Carbon Solutions for Redox Flow Batteries, Fuel Cells, and Water Electrolyzers
This catalog showcases LINQCELL Carbon solutions, designed for use as gas diffusion layers, porous transport layers, and electrodes in fuel cells, water electrolyzers, carbon dioxide electrolyzers, and redox flow batteries.
LINQCELLᵀᴹ Graphitized Carbon Fiber Plates for Water Electrolyzers
LINQCELLᵀᴹ Graphitized Carbon Fiber Plates are designed for use in water electrolyzers, offering excellent conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance. Ideal for high-performance electrochemical applications, these plates enhance efficiency and reliability in hydrogen production processes.
For your graphitized carbon fiber paper or panel needs for fuel cells and water electrolyzers, we are here to help!