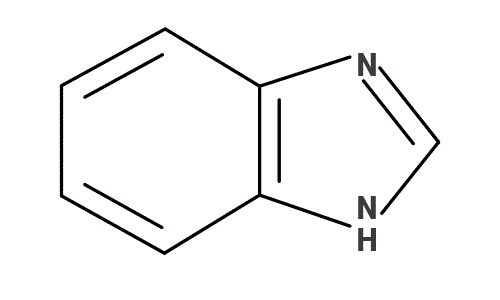
Benzimidazole CAS #51-17-2
- Enhanced Thermal Stability
- Versatile Chemical Base
- Corrosion Protection
Product Description
Benzimidazole (CAS #51-17-2) is a white to slightly beige, heterocyclic aromatic compound, fundamental in both chemical synthesis and industrial applications. With a molecular weight of 118.14 g/mol, it's known for its high purity levels, typically exceeding 98%, and serves as an effective latent curing agent in epoxy mold compounds. This role enhances the thermal and mechanical properties of epoxy resins, making them tougher and more heat-resistant. Additionally, benzimidazole finds use in pharmaceuticals as a base for various drugs, in agriculture for creating pesticides, and as a corrosion inhibitor in protective coatings.
Benzimidazole's versatility in industrial applications, particularly as an additive in epoxy mold compounds, stems from its stability, curing properties, and the ability to enhance product performance. Its role in pharmaceuticals and agriculture further underscores its utility across different sectors, making it a compound of significant interest for both research and industrial applications.
Technical Specifications
Additional Information
Technical Specifications:
- Purity: Typically available in >98% purity, with high-grade versions reaching up to 99.9%.
- Melting Point: Approximately 170-172 °C.
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, and other organic solvents like DMSO and dimethylformamide.
- Appearance: White to light tan powder or crystals.
Applications:
- Epoxy Mold Compounds:
- Curing Agent: Benzimidazole can be used as a latent curing agent for epoxy resins. Its ability to react at elevated temperatures makes it ideal for enhancing the thermal stability and mechanical properties of epoxy mold compounds. It helps in cross-linking, which improves the toughness and heat resistance of the final product.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Benzimidazole derivatives are widely used in pharmaceuticals due to their biological activity. They serve as a base for various drugs, including antivirals, antifungals, and antihelmintics.
- Corrosion Inhibitors:
- It can be employed in coatings to protect metals from corrosion, particularly effective in acidic environments.
- Agriculture:
- As a precursor for pesticides and fungicides. Several benzimidazole derivatives are key in controlling fungal diseases in crops.
- Research and Development:
- Used as a building block in organic synthesis for creating more complex chemical compounds.
Handling and Storage:
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible substances like strong oxidizing agents. Keep container tightly closed.
- Handling: Use in a well-ventilated area or with appropriate respiratory protection. Avoid skin and eye contact; use gloves and protective eyewear.
- Safety: While benzimidazole itself has relatively low toxicity, proper safety measures should always be followed to avoid any potential health risks. Consult the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for detailed safety information.