IPM Motors
What is an IPM Motor?
Interior Permanent Magnet (IPM) motors are a type of permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM). Like PMSM motors, IPM motors have permanent magnets embedded in the rotor. However, the magnets in an IPM motor are arranged in a unique interior configuration, providing several advantages over traditional PMSM motors.
IPM motors are often used in high-performance electric vehicle applications due to their superior efficiency, power density, and torque capability. They are particularly well-suited for applications where a high power-to-weight ratio is required, such as electric sports cars or high-performance electric motorcycles.
While IPM motors are a subcategory of PMSM motors, they differ in their magnet configuration and construction, which can have a significant impact on their performance characteristics. Other types of electric motors commonly used in electric vehicle propulsion systems include AC induction motors and switched reluctance motors. Each type of motor has its own unique benefits and drawbacks, making it important to choose the right motor for the specific application.
How are IPM motors structured?
An IPM (Interior Permanent Magnet) motor is a type of synchronous electric motor that uses permanent magnets located on the rotor surface. The stator winding creates a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor, generating torque and causing the rotor to rotate. The permanent magnets are located inside the rotor core, providing high magnetic flux density and efficiency.
Compared to other types of motors, IPM motors offer several advantages, including high power density, high torque density, high efficiency, and a wide speed range. They also have excellent thermal properties and can operate at high temperatures, making them suitable for use in electric vehicles, industrial machinery, and other high-performance applications.
One of the key advantages of IPM motors is their ability to operate efficiently over a wide range of speeds and loads, making them ideal for electric vehicles where efficiency and range are critical. They also have a high torque density, which allows for smaller and lighter motors, reducing the weight and size of the electric vehicle. Additionally, the use of permanent magnets provides a high power density, making IPM motors highly efficient and capable of delivering high power output.
Interior permanent magnet motor (IPM), has a rotor embedded with permanent magnets that provides a good solution for traction and auxiliary motors in EV markets.
IPM motors use powerful neodymium magnets that make the 30% more efficient than ferrite magnet motors. They have higher power density than induction motors and they use fewer parts, resulting in a reduced motor size.
The industry trends towards combining electric motors with power conversion systems and increasingly miniaturizing components to save space and reduce weight. The result is both higher power density and a higher risk of motor failure. Materials applied in motors generally require resistance to ATF, meet AEC-Q200 standard, and long-term reliability.
Application considerations
These motors are often in or around ATF (Automatic transmission fluids). The ideal ATF temperature is 80°C and the max temperature is 140°C.
In order to pass the AEC-Q200 grade 1-5 requirements materials need to:
- Be automotive solvent resistant
- HTS 1000hrs @ 150°C
- TC 1000 cycles -55°C to 125°C
- TS Air 300 cycles -55°C to 125°C
- Biased 1.5V humidity 1000hrs 85°C/85%RH
- Grade 0 is most extreme: -50°C to 150°C
EV motors generally operate at high voltages. While traditional DC motors operate at 12-24C, 1st gen IPMs operate at 400V AC and next gen motors will operate at 800V AC.
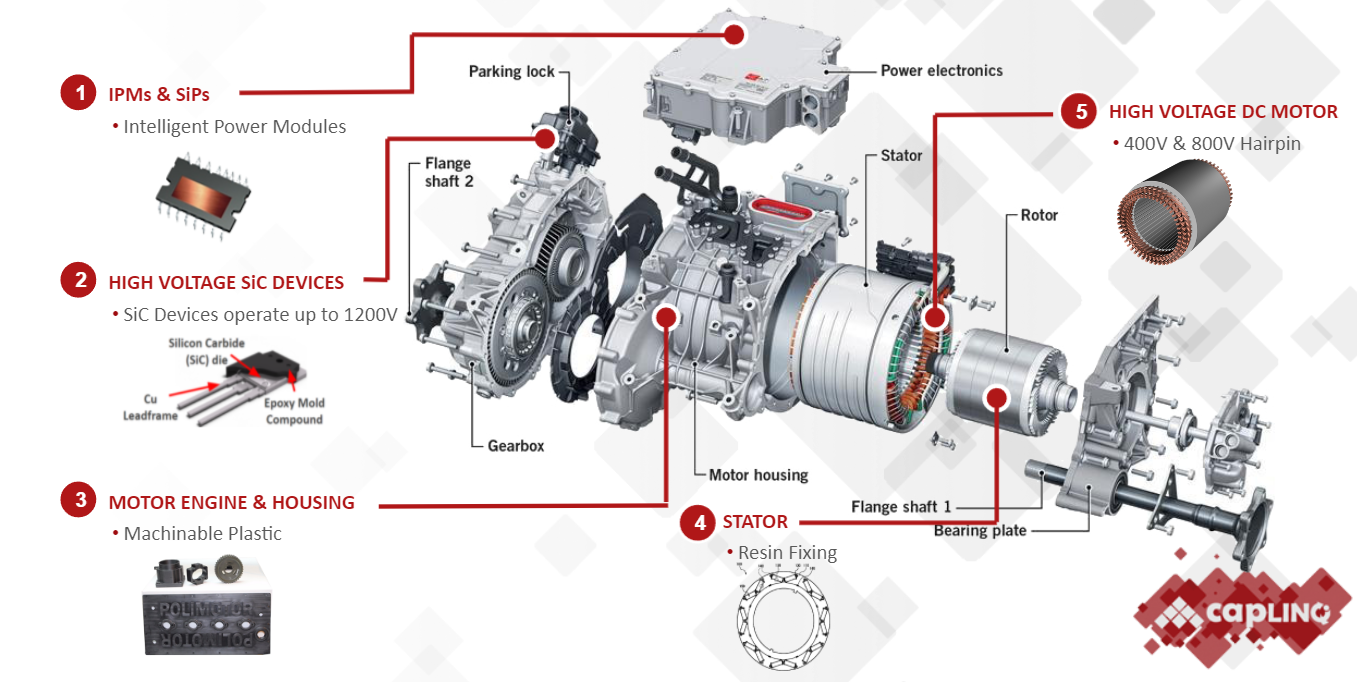
IPM motors have multiple components within them that require their own section:
- Intelligent power modules
- High Voltage SiC devices
- EV motor engine
- Stator
- High voltage DC motor