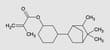
MM304 | Methacrylate adhesion promoter Additive
Harmonization Code : 2925.19.95.90 | Carboxyimide-function compounds (including saccharin and its salts) and imine-function compounds : Imides and their derivatives; salts thereof : Other : Other : Other
Main features
- Mild pleasant odor
- Hydrolytic resistance
- Lower weight loss on cure than IBOMA
Product Description
MM-304 is a liquid mono-functional methacrylate monomer. It has similar properties as Isobornyl Methacrylate (IBOMA) when polymerized but with lower weight loss on cure. It has a mild, pleasant odor. MM-304 has good resistance to hydrolysis.
MM-304 is recommended as a reactive diluent monomer for use in UV or peroxide cure formulations. It is particularly recommended for applications that require hydrolytic resistance.
Technical Specifications
| General Properties | |
| Appearance Appearance Appearance at room temperature. | Colorless |
| Density (g) | 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Molecular weight | 304 g/mol |
| Refractive index Refractive index The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. It is calculated by taking into account the velocity of light in vacuum compared to the velocity of light in the material. The refractive index calculation can be affected by the wavelength of light and the temperature of the material. Even though it is usually reported on standard wavelengths it is advised to check the TDS for the precise test parameters. | 1.5 |
| Thermal Properties | |
| Flash Point Flash Point The flashpoint of a solvent is the lowest possible temperature at which it can vaporize to form an ignitable vapor. Flashpoint is often confused with “autoignition temperature”, which is the temperature at which a solvent ignites without an ignition source. | >175 °C |
| Other Properties | |
| Storage Temperature | 5 °C |
| Physical Properties | |
| Viscosity Viscosity Viscosity is a measurement of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Viscosity is commonly measured in centiPoise (cP). One cP is defined as the viscosity of water and all other viscosities are derived from this base. MPa is another common unit with a 1:1 conversion to cP. A product like honey would have a much higher viscosity -around 10,000 cPs- compared to water. As a result, honey would flow much slower out of a tipped glass than water would. The viscosity of a material can be decreased with an increase in temperature in order to better suit an application | 80 mPa.s |