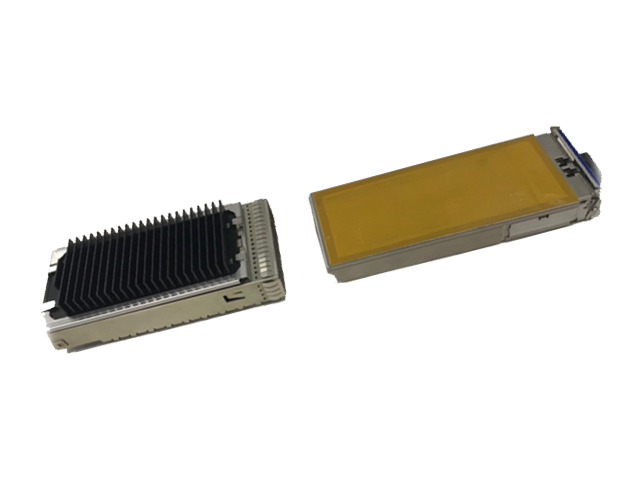
RTM-X22 | Pluggable Phase Change Pad
- 0.7 Thermal Impedance
- >50 Pluggable performance
- 0.15 - 0.22mm Thickness
Product Description
Honeywell RTM-X22, a pluggable thermally conductive Phase Change Material (PCM), offers multiple pluggable performance. It is designed to minimize thermal resistance at interfaces, maintain excellent performance through reliability testing, and provide scalable application at a competitive cost.
Based on a novel polymer PCM system, Polyimide (PI) film was used as substrate, allowing direct contact of PCM to provide multiple pluggable performance. The edge is coated with pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) to provide adhesion with other devices. This material exhibits excellent wetting at interfaces during typical operating temperature ranges, resulting in very low surface contact resistance.
Honeywell RTM-X22 Pluggable TIM for pluggable optical modules reduces operational temperature and can withstand repeated mechanical insertions. We can share a plethora of Technical Information with a signed NDA. Contact us for more information.
Technical Specifications
| General Properties | |
| Thickness range | 0.15 - 0.22 mm |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Breakdown Voltage Breakdown Voltage Breakdown voltage is the minimum voltage necessary to force an insulator to conduct some amount of electricity. It is the point at which a material ceases to be an insulator and becomes a resistor that conducts electricity at some proportion of the total current. After dielectric breakdown, the material may or may not behave as an insulator any more because of the molecular structure alteration. The current flow tend to create a localised puncture that totally alters the dielectric properties of the material. This electrical property is thickness dependent and is the maximum amount of voltage that a dielectric material can withstand before breaking down. The breakdown voltage is calculated by multiplying the dielectric strength of the material times the thickness of the film. | 5000 V |
| Thermal Properties | |
| Thermal Impedance | 0.7 °C·cm²/W |