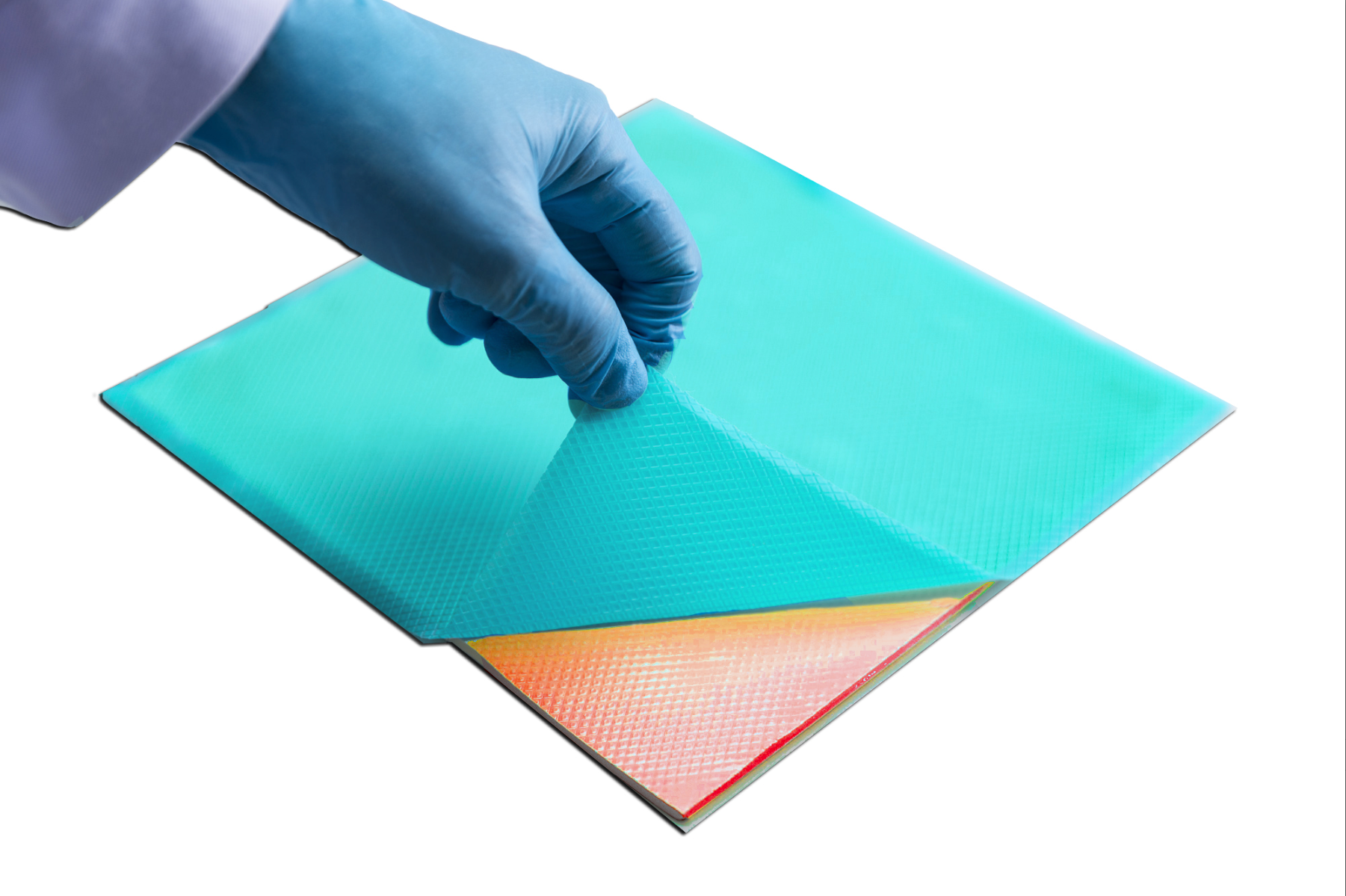
TGP 2000E | Thermal Gap Pad
Harmonization Code : 3824.99.96.99 | Prepared binders for foundry moulds or cores; chemical products and preparations of the chemical or allied industries (including those consisting of mixtures of natural products), not elsewhere specified or included : Other : Other: Other
Main features
- 0.95 Thermal Impedance
- 2.0 Thermal Conductivity
- Excellent surface wetting
Product Description
Honeywell TGP2000E Thermal Gap Filler Pads provide high thermal performance with ease of use across multitude of applications. Its ultra-high compressibility enables low stress and excellent conformity to mating surfaces. It is designed to minimize thermal resistance at interfaces, and maintain excellent performance through reliability testing.
TGP2000E is naturally tacky, and requires no additional adhesive which could inhibit thermal performance. Even though these pads come in large dimensions, it is suggested to cut and apply them in smaller pieces to ensure part uniformity and to avoid any issues related to their application. Products are available in a thickness range from 0.5mm to 5.0mm.
Technical Specifications
| General Properties | |||||
| Color Color The color | red | ||||
| Density (g) | 2.3 g/cm3 | ||||
| Electrical Properties | |||||
| Breakdown Voltage Breakdown Voltage Breakdown voltage is the minimum voltage necessary to force an insulator to conduct some amount of electricity. It is the point at which a material ceases to be an insulator and becomes a resistor that conducts electricity at some proportion of the total current. After dielectric breakdown, the material may or may not behave as an insulator any more because of the molecular structure alteration. The current flow tend to create a localised puncture that totally alters the dielectric properties of the material. This electrical property is thickness dependent and is the maximum amount of voltage that a dielectric material can withstand before breaking down. The breakdown voltage is calculated by multiplying the dielectric strength of the material times the thickness of the film. | 4000 V | ||||
| Volume Resistivity Volume Resistivity Volume resistivity, also called volume resistance, bulk resistance or bulk resistivity is a thickness dependent measurement of the resistivity of a material perpendicular to the plane of the surface. | 1.0x1014 Ohms⋅cm | ||||
| |||||
| Mechanical Properties | |||||
| |||||
| Thermal Properties | |||||
| Operating Temperature | -40 - 150 °C | ||||
| Thermal Conductivity Thermal Conductivity Thermal conductivity describes the ability of a material to conduct heat. It is required by power packages in order to dissipate heat and maintain stable electrical performance. Thermal conductivity units are [W/(m K)] in the SI system and [Btu/(hr ft °F)] in the Imperial system. | 2.0 W/m.K | ||||
| Thermal Impedance | 0.95 °C·cm²/W | ||||
| UL 94 Rating UL 94 Rating Flammability rating classification. It determines how fast a material burns or extinguishes once it is ignited. HB: slow burning on a horizontal specimen; burning rate less than 76 mm/min for thickness less than 3 mm or burning stops before 100 mm V-2: burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of flaming particles are allowed. V-1: burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of particles allowed as long as they are not inflamed. V-0: burning stops within 10 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of particles allowed as long as they are not inflamed. 5VB: burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical specimen; no drips allowed; plaque specimens may develop a hole. 5VA: burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical specimen; no drips allowed; plaque specimens may not develop a hole | V-0 | ||||